Streams are a way of reading a file bit-by-bit and passing small chunks of data to the server rather than reading a file as a whole and then passing information to the server as one big data file. This may not look like a big deal but in reality, this saves a lot of time on the server.
Streams in NodeJS
Streams work as a queue with the help of a buffer, a buffer is a small temporary space that is used to store a chunk of data that is to be transferred. Buffer works as a queue, if you want to transfer a large amount of data from one point to another, then the buffer loads a chunk of data, and passes it onto the server, and waits for the server to respond so that it can discard that chunk of data from its queue. While it waits for the server’s response, it loads more chunks of data based on the size of the buffer set by the programmer or the application.
This whole process of getting a chunk from the file, loading it into the buffer, and then parsing that chunk to the application\server is known as a Stream. In NodeJS, there are three different types of streams
- The read-only stream called the readable stream
- The write-only stream called the writable stream
- The read and write stream is called the duplex stream
Reading Data from a file through streams in NodeJS
To start with the tutorial, you need to use the command in the terminal:
This will create a new node project for us along with the package.json file in our directory
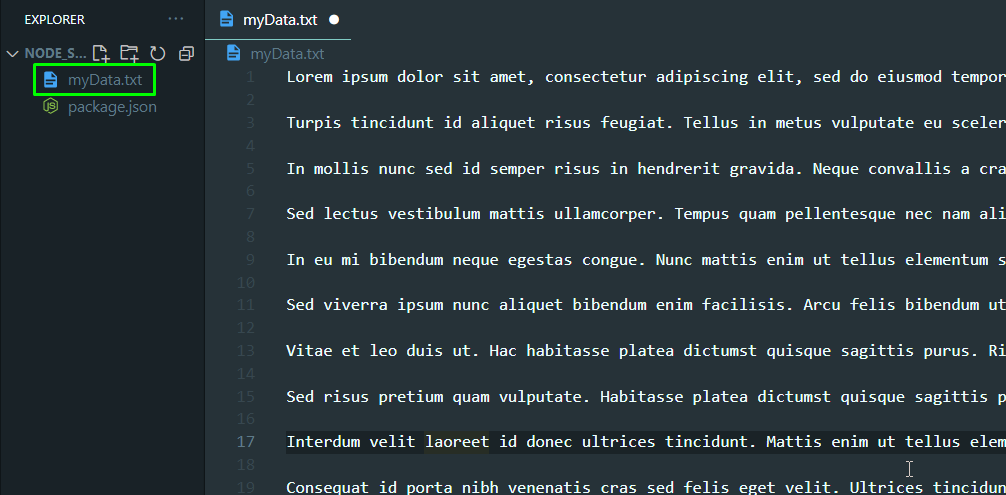
To read some data from a file using NodeJS, you will need a file with some text in it. Therefore, create a new text file and place some “Lorem Ipsum” text using the lorem ipsum generator.
Copy this text, and place it in the text file and save the text file:
As you can see, the name of the text file is “myData.txt”. Create a new javascript file in the same directory and name it “streamDemo.js”
To create a read or write stream we need to use the “fs” module that comes as a built-in module of the node environment. To include the fs module in your program use the following lines of code:
Next, we need to create a read stream from our text file (that is placed in the same directory as the streamDemo.js file) using the following line:
Now, we can use this variable “myReadStream” to perform a task every time it receives a new chunk of data. Use to following lines of code to print the chunk onto the console every time our stream gets a new chunk:
console.log("New chunk has been accepted by the program");
console.log(chunk);
});
To run this program, in the terminal type the following command:
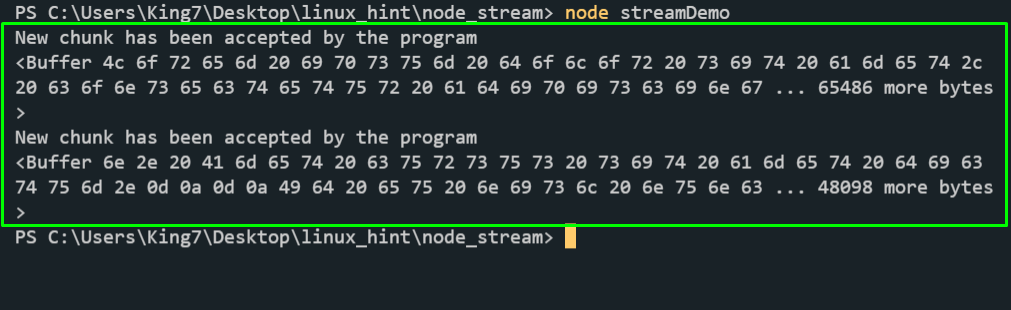
You will see the following output in your console:
As you can see, we were able to receive and print out the data from our file, however, the data that we are getting on the console is not the same as the one we have in our file. This is because we need to set an encoding procedure in the read stream. Alter, the line of the read stream to match the following line of code:
As you can see, we have added the “UTF8” encoding to our stream. Now if we rerun using the “node streamDemo” command we get the following result on our terminal:
And there you go, we are reading the correct data from the file and printing it out onto the console
Writing data to a file through streams in NodeJS
We can write to a file using the write stream in NodeJS which also comes with the module “fs”. We will write the data we received in the previous section and write it a new file which we will writeInMe.txt
To write data to a file we are going to create a new write stream using the following line of code:
As you can notice, we have already included the “UTF8” encoding in the write stream. To write the chunk we receive from the “myData” text file to the new file we are going to use the following code:
console.log("New chunk has been accepted by the program");
myWriteStream.write(chunk);
console.log("Chunk written to the new text file");
});
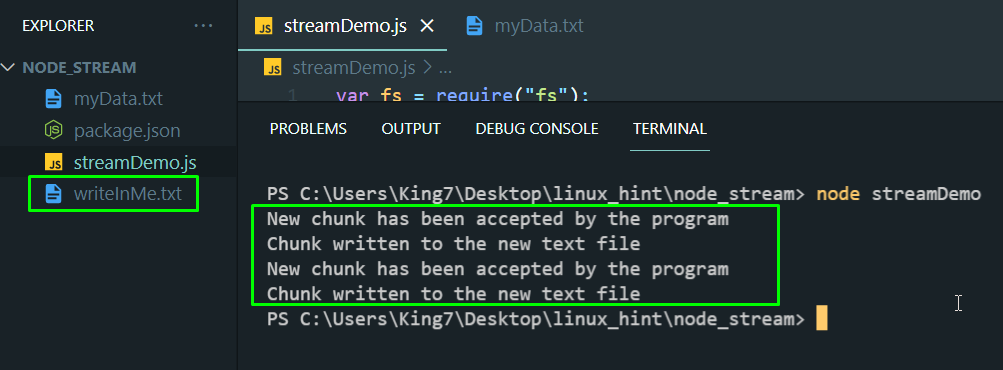
Execute the program by using the command:
You will get the following output:
As you can see in the explorer of your code editor that a new file text was automatically created and if double click on the “writeInMe” text file you will see the following data inside that file:
So, from the image above it is clear that we were able to write data to a file using Streams
Conclusion
Streams are used to load data to\from a file by\onto the application bit-by-bit or in small chunks. We can read and write data by using streams that are included in the fs (file system) module. The file system (fs) module comes as a built-in module with NodeJS. There are three different types of streams namely: readable stream, writable stream, and the duplex stream. In this post, we implemented a simple node program that allowed us to read data from a file and write that to a different file with the help of data streams and buffers.