Installing Required Packages
The first step to deploy your graphQL application is to ready your server by installing the required packages. Log in to the server using SSH.
NOTE: Make sure the security group of the instance is configured to allow connection from port 22 and the private key file has 400 permission.
Update Ubuntu repositories.
Now install node.js and npm on your ubuntu server.
ubuntu@ubuntu:~$ sudo apt-get install npm -y
Verify the installation by checking the version of node.js and npm.
ubuntu@ubuntu:~$ npm -v
Move GraphQL Application to EC2 Server
The EC2 instance is ready to deploy graphQL applications in node.js. Now we will move our code to the EC2 instance. Two common ways to copy the code to the server are listed below and will be discussed here.
- Copy code using scp command
- Clone application code from Github, Gitlab, or Bitbucket
Copy Application Using scp Command
In order to copy your application to the EC2 server using the scp command, First of all, remove the ‘node_modules’ directory from your graphQL application. This directory has all the npm packages required to run the application. We will install these packages later before starting the graphQL application. Now compress the project directory into a zip file. After creating the zip file, we will move the project zip file to the server. Linux and windows have different methods to create a zip file.
Windows
In windows, right-click on the application root directory and go to the ‘send to’ option. It will open a submenu. Click on the ‘Compressed (zipped) folder’ to create a zip file of the graphQL application.
Linux or Mac
In Linux or Mac OS, we will use the ‘zip’ command to create a zip file of the project.
The above command will generate the graphQL.zip file of the graphQL directory.
Upload Application to the Server
Now we have a zip file of our application, and we can upload the zip file to the server by using the scp command.
The above command will move the project zip file to the remote server’s home directory over the ssh connection. Now on the remote server, unzip the project zip file.
Clone Application From Github, Bitbucket or Gitlab
The second method to copy application code to the server is using git. Install git from the command line on the EC2 server.
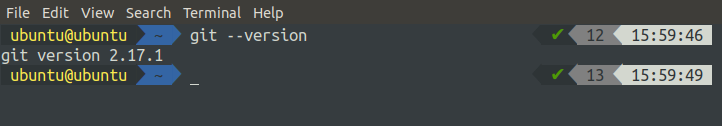
Check the git version to verify the installation.
If it does not give the version of git, then git is not installed. Now clone the application from the github, gitlab, or bitbucket. Here we will clone the application code from the github.
Starting the GraphQL Application
Now we have our graphQL application on the remote server. Go to the root directory of the graphQL application and install the required npm packages to run the graphQL application.
ubuntu@ubuntu:~$ sudo npm install
This command will analyze the package.json file in the project and install all the required npm packages. After installing the required packages, now we will start the graphQL application.
Running Application as Daemon
When we run the application using the standard method as described above, it runs in the foreground, and the application stops when you close the terminal window. We can run the application as a background process by appending the ampersand (&) sign to the command.
The problem with this method is that when we modify our application code, the applied changes will not reflect automatically. We will have to restart the application every time we modify the code to apply the changes. In order to run the application in the background and to apply changes automatically, we will use an npm package named pm2. Install pm2 on the server.
Start the graphQL application using pm2.
The ‘–name’ flag will name the background process, and we can start and stop the application using the name. The ‘–watch’ flag will go on checking the application code to apply changes immediately. You can learn more about pm2 by visiting the following link
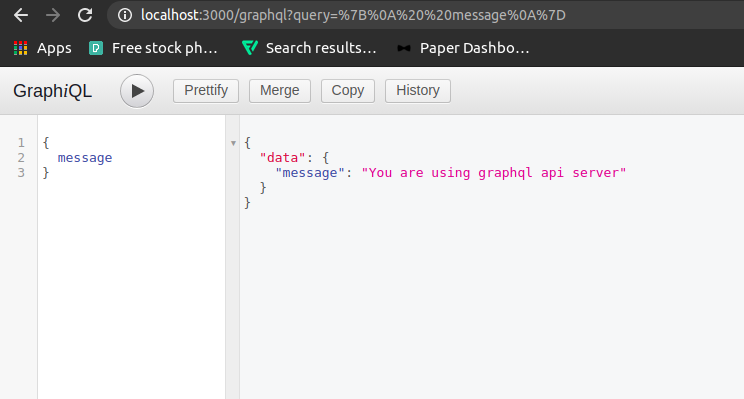
Querying GraphQL API from Browser
We can configure our graphQL application to make graphQL queries from the browser manually. For this, we have to create a separate HTTP endpoint on which we will mount the graphQL API server. And this HTTP endpoint will be used to make manual queries. Following is the code to create the graphQL api server endpoint.
const { graphqlHTTP } = require(‘express-graphql’);
const { buildSchema } = require(‘graphql’);
const graphQLSchema = buildSchema(`
type Query{
message: String
}`
);
const func = {
message: () =>
{
return ‘you are using graphql api server’;
}
};
const server = express();
server.use(‘/graphql’, graphqlHTTP({
schema: graphQLSchema,
rootValue: func,
graphiql: true
}));
server.listen(3000);
Now, after running the server, we can access the graphQL api server on the following route.
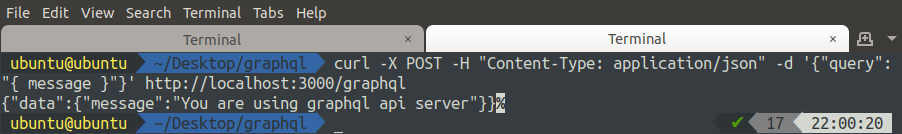
Querying GraphQL API Using CLI
In the previous section, we made graphQL queries from the browser using graphiql. Now we are going to make graphQL queries using the command-line interface in ubuntu. From the command line, to make an HTTP POST request, we will use the curl module.
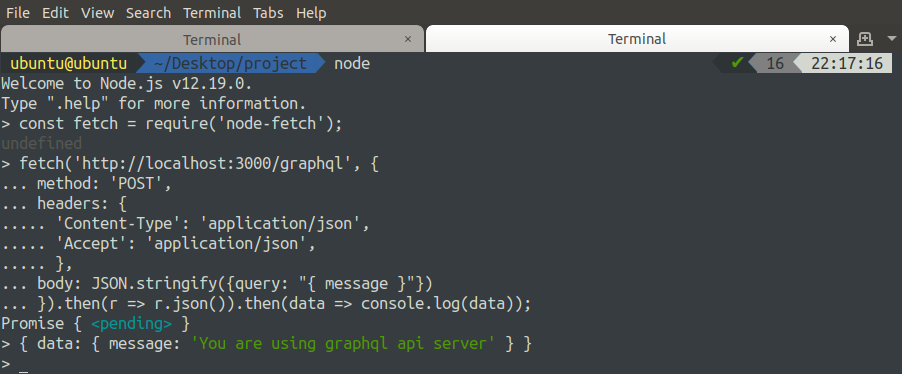
Querying GraphQL API Programmatically
In order to make graphQL query programmatically, we will use the ‘node-fetch’ module in node.js. Open node.js in the terminal.
Now make the HTTP POST request to the server using the ‘node-fetch’ module.
GraphQL is an efficient query language, and it can decrease the response time of a query made to the database. The standard api calls to fetch data from the database involve many unuseful data in the response, and hence response time increases, which decreases the efficiency. The query made to the databases using GraphQL returns only the useful data and hence decreases the response time. In this article, we have deployed our graphQL application on an EC2 instance.