This blog will explain the use of “const” with objects in JavaScript.
Use of “const” With Objects in JavaScript
The “const” with objects in JavaScript allows modification of the object’s properties but does not allow reassignment of the variable to another object.
Example
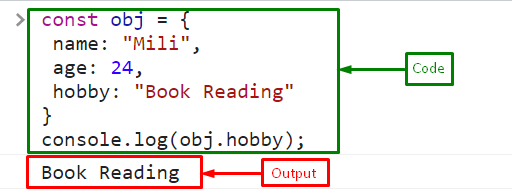
Create or declare an object named “obj” using the “const” keyword with three attributes “name”, “age”, and “hobby”:
name: "Mili",
age: 24,
hobby: "Book Reading"
}
Access the value of the object attribute “hobby” using the dot “.” operator and print on the console with the help of the “console.log()” method:
The output indicates that we have successfully accessed the value of the “const” object property named “hobby”:
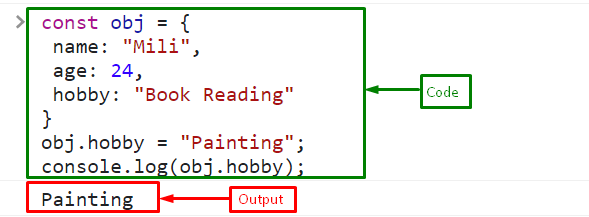
Here, we will modify the value of the “const” object property named “hobby” to “Painting” and print it on the console:
console.log(obj.hobby);
The value has been successfully updated. It indicates that the properties of the const objects can easily be updated:
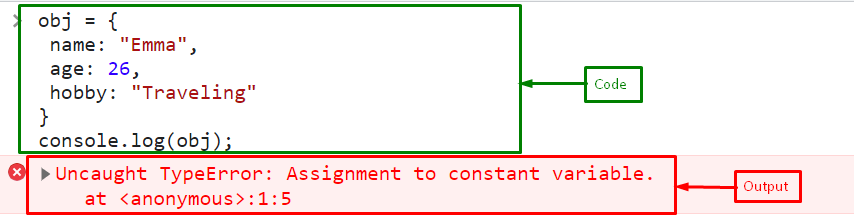
But the “const” will not allow reassigning the variable to another object. Here, we will assign a new object to the “const” object “obj”:
name: "Emma",
age: 26,
hobby: "Traveling"
}
Print the “obj” as an updated object:
Output
That’s all about the usage of the “const” with objects in JavaScript.
Conclusion
The variables with the “const” keyword in JavaScript are immutable but the object with “const” is not immutable, you can still modify its properties. However, const does not allow reassigning the variable to another object. This blog explained the use of “const” with objects in JavaScript.