This write-up will explain the working of Associative arrays in JavaScript. So, let’s start!
JavaScript Associative Array
A JavaScript associative array is considered a collection of keys. These keys are associated with their respective values in such a way that when the key is passed to the array, it returns the corresponding value. That is what the term “association” signifies.
Associative arrays in JavaScript are considered as “Objects,” not normal arrays. That’s why only the methods and properties related to objects are assigned to it.
How to create JavaScript Associative array
To create a JavaScript associative array, you have to follow the below-given syntax:
Here, “array” is an associative array that comprises “key1” and “key2” as string indexes with their respective values as “value1” and “value2”.
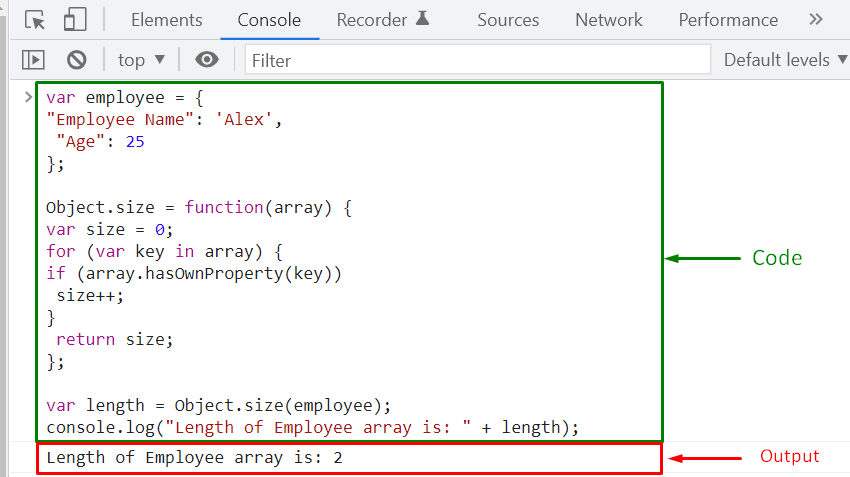
For instance, we will create a JavaScript array named “employee” having two keys, “Employee Name” and “Age”. The “value” of the “Employee Name” key is set to “Alex” and its “Age” as “25”:
"Employee Name": 'Alex',
"Age": 25
};
That’s how you create a JavaScript associative array.
How to calculate the length of JavaScript Associative array
JavaScript Associative array is not a normal array; therefore, we can not utilize an array object’s “length” attribute to view its length.
For calculating the associative array’s length, we have to create an “Object.size()” function. The “Object.size()” function will iterate through the “keys” of the associative array and use the “hasOwnProperty()” method is to verify the existence of keys in it. In case, if the added condition evaluates to be “truthy”, then the size of array will be incremented, that was initially set to “0”:
var size = 0;
for (var key in array) {
if (array.hasOwnProperty(key))
size++;
}
return size;
};
Next, we will invoke the “Object.size()” method to check the length of the created JavaScript associative array:
As you can see from the output, the length of the “employee” associative array is “2”:
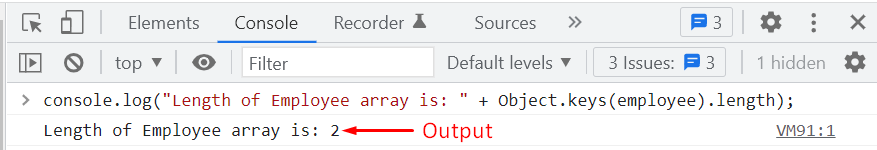
Similarly, you can also use the “Object.keys()” method to calculate the length of an associative array:
Output
How to retrieve values of JavaScript Associative array
In an associative array, you can retrieve the values of the added keys using “for” loop:
{ var value = employee[key];
console.log(key + " = " + value + '');
}
The above-given “for” loop will iterate through the “employee” array and fetch values of added keys:
How to convert JavaScript Associative array into Normal array
Want to convert the JavaScript Associative array into a normal array? To do so, invoke the JavaScript “map()” function. The map() function will return a normal array from calling the function for every key “k” of the “employee” associative array:
return employee[k];
})
console.log(elements);
The newly created array placed the values of the “employee” key at sequential indexes 0 and 1:
That was all about JavaScript Associative array. Before wind up, let’s check out the difference between an associative array and normal array in JavaScript.
Difference between Normal Array and Associative Array in JavaScript
Have a look at the following table to understand the difference between normal array and associative array in JavaScript:
We have compiled the essential information related to the JavaScript Associative Array. Explore it according to your preferences.
Conclusion
A JavaScript associative array is considered a collection of keys. These keys are associated with their respective values in such a way that when the key is passed to the associative array, it returns the corresponding value. Associative arrays in JavaScript are considered Objects, not normal arrays; that’s why only the methods and properties related to objects are assigned to an associative array. This write-up explained JavaScript associative arrays.