This article provides an insight into the innerText property to achieve the following targets.
- How the innerText property works in JavaScript
- How to use the innerText property in JavaScript
- Difference between innerText and innerHTML
How the innerText property works in JavaScript
The working of innerText depends on the following syntaxes.
To get the text of an HTML element:
To set/update the text of an HTML element:
In the above syntaxes:
- The node refers to the HTML element and all its descendants.
- The text represents the new text that would be updated or set in place of the existing text.
How to use the innerText property in JavaScript
The following examples demonstrate the usage of the innerText property in HTML.
Example 1: Get the text of an HTML element
We have illustrated this example to show how text of an element can be obtained using innerText. property.
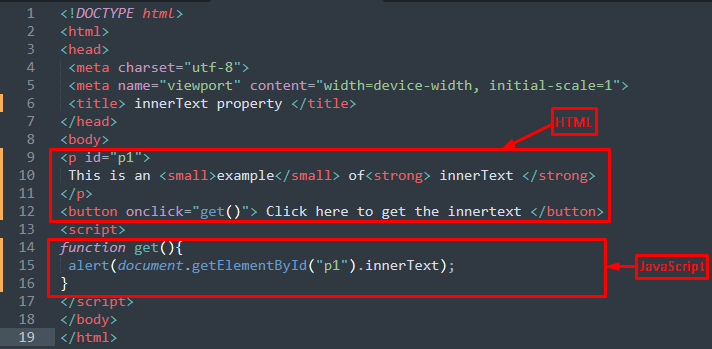
HTML
In the above code, a paragraph(id=”p1“) is created that contains a small tag and a strong tag. Moreover, a get() function is called on the click of the button.
JavaScript
alert(document.getElementById("p1").innerText);
}
A function named get() is created that contains an alert statement to display the text of an element(id=”p1“).
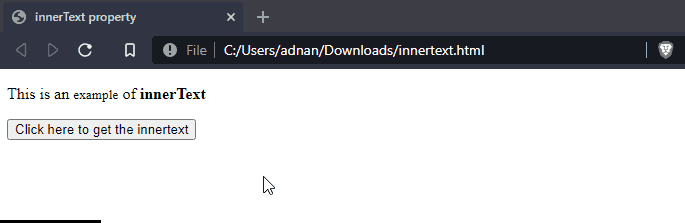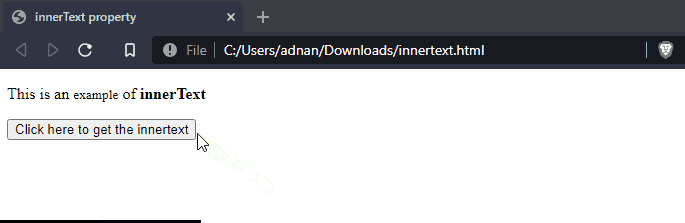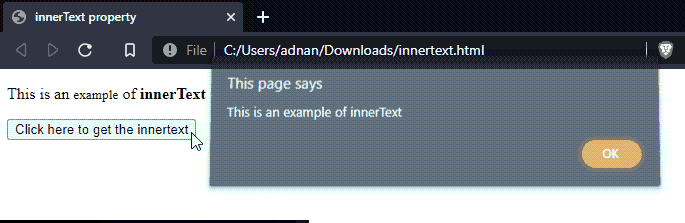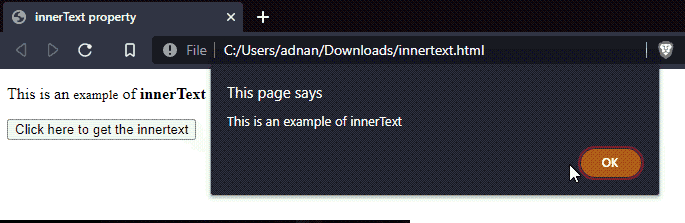
Output
It is observed that the text of the paragraph(id=”p1“) and all its descendants(span and strong) is displayed.
Example 2: Update the text of an HTML element
The HTML and JS code provided below assist in updating the text of the element.
HTML
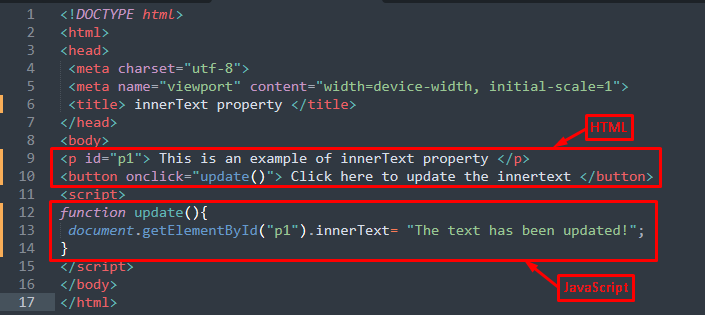
The HTML code creates a paragraph with id=”p1” and button that executes the update() function on its onclick property.
JavaScript
document.getElementById("p1").innerText= "The text has been updated!";
}
The JavaScript code provided above creates an update() function that applies the innerText property to the paragraph with id=”p1“.
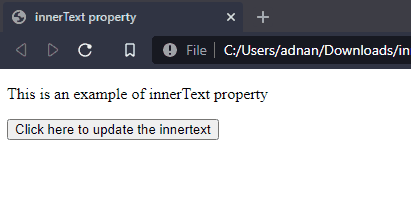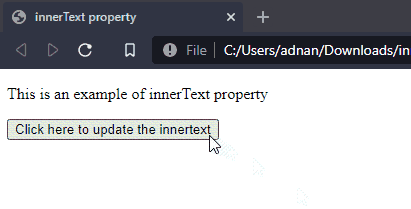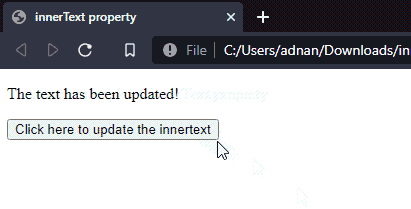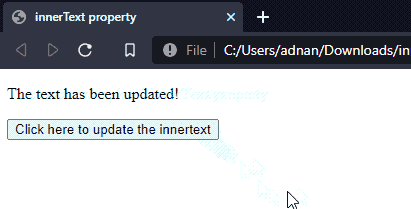
Output
It is observed from the output that the text of the paragraph has been updated to new text.
Example 3: Set the text for an HTML element
In this example, the text of one element will be placed inside the other element and the following code assists in doing so.
HTML
The HTML code contains a paragraph with id=”old“, a button to trigger the set() function, and a heading with id=”new“.
JavaScript
document.getElementById("new").innerText=document.getElementById("old").innerText;
}
The above code gets the text of a paragraph element (id=”old“) and assigns this text to the heading-element (id=”new“).
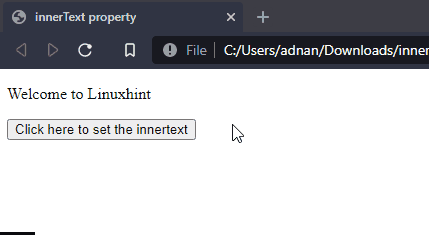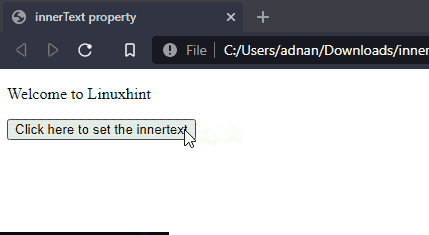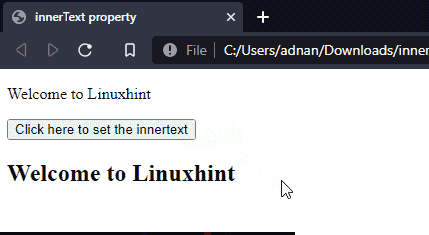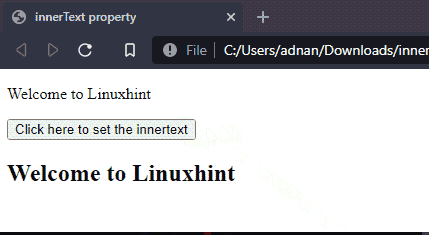
Output
The above output shows that the text of paragraph (id= “old”) is set to a heading (id= “new”).
Difference between innerText and innerHTML
The innerText and innerHTML may put confusion in your head. The innerText only considers the textual content whereas the innerHTML functions on the HTML content of an element which may include the tags as well. This section provides the difference between innerText and innerHTML by using the following code.
HTML
The above code creates a paragraph tag and two buttons. The first button triggers the text() function whereas the second function executes the html() function.
JavaScript
alert(document.getElementById("text").innerText);
}
functionhtml(){
alert(document.getElementById("text").innerHTML);
}
Two functions are created that practice the innerText and innerHTML properties on a paragraph id=”text“.
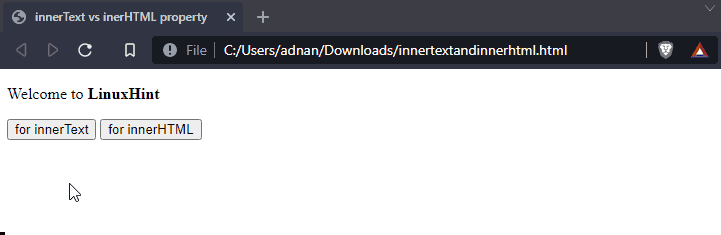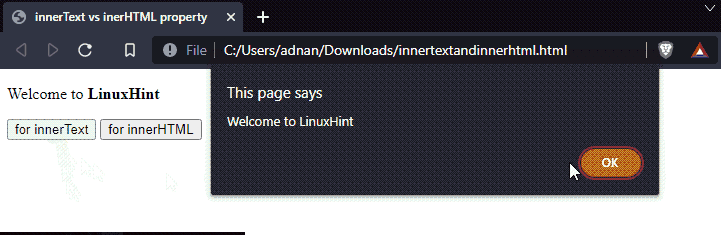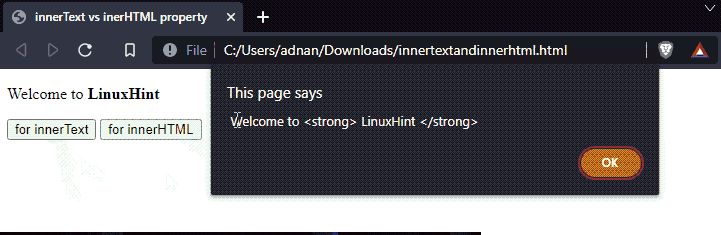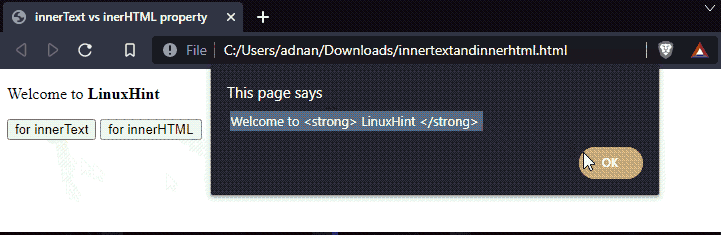
Output
It is observed that the innerHTML shows the inner elements whereas the innerText has only retrieved the textual content.
Conclusion
The innerText property of JavaScript allows you to get or update/set the content of an HTML element. This article demonstrates various syntaxes of the innerText property of JavaScript with examples that better convey the concept. By going through the article, you would have learned to get the text, update the text, or set a text to an HTML element using the innerText property of JavaScript. Lastly, we have presented the difference between innerText and innerHTML to pave the concept in your head.