It requires the users to keep the mirror list updated and enables downloading package updates quickly. The article demonstrates how to work around Manjaro mirrors, maintain the mirror list, and change the mirror’s location to increase package download speed.
Manjaro Mirrors
Like any other distribution, mirrors for Manjaro also contain a variety of package releases well-suited for 32-bit and 64-bit installations. The distribution support package maintainer: Pacman, for system maintenance, new installs, and updates. Pacman is responsible for managing the content of Manjaro repositories, including its unique packages (Manjaro hardware detection utility method) and patching packages.
Pacman-mirrors
For Pacman to function with a list of mirrors distributed worldwide and maintain the repo: Manjaro has introduced a specific utility, pacman-mirrors, that generates and maintains the system mirror list.
Use the following command with superuser privileges to display the pacman-mirror utility version followed by mirror status listed in the mirror list from the available mirror pool.
[sudo] password for manjaro:
Pacman-mirrors version 4.21.2
Local mirror status for the stable branch
Mirror #1 OK 00:32 United_States https://repo.ialab.dsu.edu/manjaro/
Mirror #2 OK 00:58 Iceland https://mirrors.opensource.is/manjaro/
Mirror #3 OK 00:18 Germany https://manjaro.moson.org/
Mirror #4 OK 03:21 Sweden https://ftpmirror1.infania.net/mirror/manjaro/
Mirror #5 OK 01:56 Australia https://manjaro.lucassymons.net/
Mirror #6 OK 04:29 Bulgaria https://mirror.telepoint.bg/manjaro/
Mirror #7 OK 02:33 South_Africa http://mirror.is.co.za/mirrors/manjaro.org/
________________________________________
Or use the cat command to output the content of the mirrorlist file in the /etc/pacman.d directory. It will be similar to the above command.
Similarly, use the following commands for help on usage, and version or mirror status details:
manjaro@manjaro:~$ pacman-mirrors --help
manjaro@manjaro:~$ pacman-mirrors --version
manjaro@manjaro:~$ pacman-mirrors --status
________________________________________
Mirror Pool Customization
The pacman-mirrorlist allows users to customize mirror pools as per preference. However, it’s also an ideal practice not to limit the mirrorlist as pacman-mirrorlist only writes the updated mirrors to the /etc/pacman-mirrors.conf file.
Note: It’s mandatory to synchronize the database after updating Manjaro mirror servers in the configuration file or after any changes via the pacman-mirrors utility. The synchronization ensures no potential risks while updating and downloading software packages via the package manager.
Continent Based Customization
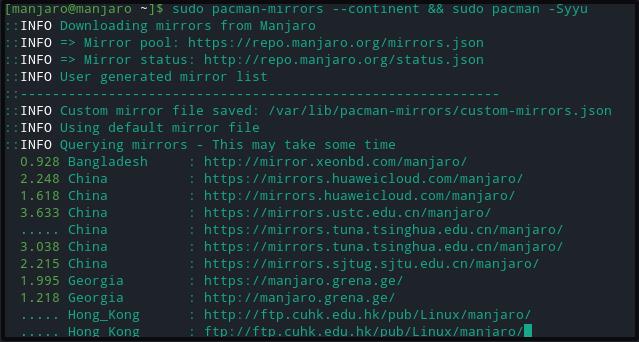
Use the pacman-mirrors command with the –continent option to create a customized mirror pool.
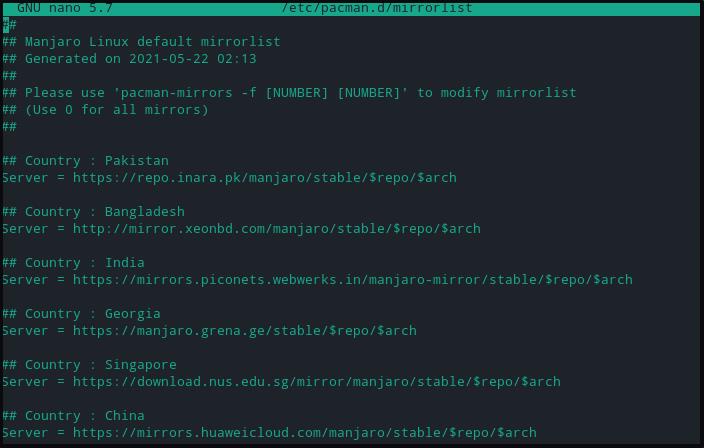
Now check the Pacman mirrorlist configuration file to notice the customized mirror pool, as shown below:
Country Based Customization
Similarly, the user can customize the mirror list by confining the search to the country or countries of their choice. Use the pacman-mirrors command with the –country option, as follows:
manjaro@manjaro:~$ sudo pacman-mirrors --country France && sudo pacman -Syyu
manjaro@manjaro:~$ sudo pacman-mirrors --country Germany,France,Austria && sudo pacman -Syyu
________________________________________
Reset to Default
The utility also offers to reset the mirrorlist to the default mirror pool as follows:
manjaro@manjaro:~$ sudo pacman-mirrors --country all --api --protocols all --set-branch stable && sudo pacman -Syyu
________________________________________
It’s important to note that the default configuration of the pacman-mirrors file is to overwrite the mirrorlist in the /etc/pacman.d/mirrorlist file. Check the mirrorlist file to check the mirrors reset to default.
Setting Fastest Server
The purpose of Manjaro mirrors is to enable the user with an efficient system upgrade, as some locations provide fast internet speed. Hence, server location in the user’s country or city can make a huge difference. Some of the circumstances for a slow software package download include:
- slow connection
- slow server speed
- server proximity to the system
Even though the first two scenarios are out of reach, Manjaro pacman-mirrors utility allows selecting the fastest and closest server in the area. Run the pacman-mirrors tool with the –fasttrack option to fetch all mirrors to the list that consumes minimum time.
It also allows fetching a limited number of mirrors that are sorted based on the response time.
Lastly, pacman-mirrors also selects and adds mirrors to the mirrorlist file via –geoip. However, not all countries have Manjaro mirrors and use all mirrors in this scenario.
Interactive Method to Update Mirrors
Manjaro also provides an interactive way to update mirrors and choose preferred locations. Use the –interactive command to list all mirrors in a GUI window; it will sort the columns and select mirrors.
The above screenshot shows a fetched list of servers. Now select the desired server checkbox and click OK.
Lastly, enable the Manjaro Package Manager to utilize the server by synchronizing the database.
Conclusion
The article details the use of Mirrors in Manjaro Linux and explains how to identify existing mirrors via command-line Manjaro utility pacman-mirrors and Pacman configuration files. We demonstrated how to customize the existing mirror pool via various commands. Furthermore, we also learn how to update the mirrorlist with the fastest mirrors from CLI and interactively.