What is File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
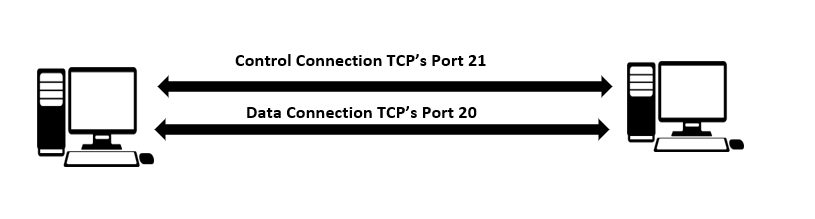
The main function of FTP is to send and receive files over the Internet. Its full form is file transfer protocol which is used to establish two different connections with a client and server; one for control information and the other for data transfer; after establishing connection, you can transfer files to any system. FTP can handle files in both binary and text formats.
The initial FTP client software relied on the DOS command prompt, which had standardized commands and syntax. The availability of graphical user interface (GUI) to the users has eased the process of uploading and downloading documents since then, it is based on RFC 959 standards, with additional RFCs providing safety precautions.
How FTP works
A TCP connection to the FTP (reserved port 21) is created when an FTP client wishes to connect to the FTP server. After authentication, a new TCP connection is created on port number 20 for the actual data transmission. So, FTP establishes two connections when copying a file from one host to another: one for data transmission and one for control.
FTP is an application layer protocol. When transferring files over FTP, it can solve difficulties like different file conventions, ways of representing text and data, and a different directory layout. The communication in the control connection (port 21) is based on basic rules. The data connection, on the other hand, is more complicated since it employs several instructions to transfer the various types of data. Even though the user is authenticated at the time of connection formation, FTP is not secure since the user’s password is in plain text, and the data is also sent in plain text, which may be intercepted by the attacker using SSL (Secure Socket Layer).
What is Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) protocol
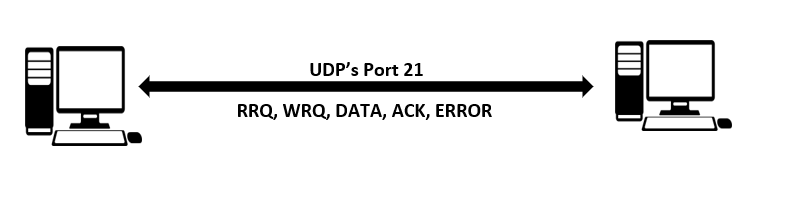
TFTP is an acronym for Trivial File Transfer Protocol which is also used for sending files from a client to a host. TFTP uses port number 69 for its service and the data is delivered via UDP. It is less complicated than FTP because it transfers files between client and server without using authentication and other valuable features that FTP offers.
The communication is accomplished by inserting a short header between the data and the UDP header. This header contains read, write, and acknowledgment codes, as well as a 512-byte data numbering scheme. Sending or receiving files over TFTP requires no security or encryption. TFTP can easily be implemented using a small amount of memory and that makes it a valuable tool for booting computers and devices without hard disk drives.
Comparison between FTP vs TFTP
In this section we will compare the features of FTP and TFTP and what are the similarities and differences between them.
| FTP | TFTP |
|---|---|
| It works by using TCP port 20 and 21 | It works by using UDP port 69 |
| It manages file transfers using TCP and offers a secure connection-oriented service | It transfers files using UDP |
| It uses TCP connection control commands to send the data | It does not require a connection as it uses UDP |
| It required authentication between the source and destination for communication | It doesn’t require any authentication for the communication |
| It is complex | It is less complex |
Conclusion
Protocols are necessary for communication and tell you about the standards that need to be followed between multiple network devices. Two of the most commonly used protocols are file transfer protocol (FTP) and trivial file transfer protocol (TFTP). This post compared these two network protocols; discussed their significance and their drawbacks. As their name suggests, both of these are used to transfer files but there are also some differences between them which have also been discussed at the end.