This article is a specific guide to finding the desktop screen resolution from the command line on Raspberry Pi.
How to Find Desktop Screen Resolution from Command Line on Raspberry Pi
There are two ways to find the desktop screen resolution from the command line on Raspberry Pi:
Method 1: xdpyinfo Utility
The first method to find the screen resolution is the xdpyinfo utility, which is present on most Linux-based systems including Raspberry Pi. xdpyinfo utility displays general information related to how a Linux-based machine can be used as a server, it displays vendor release number, number of extensions and visual information. To display the screen resolution using xdpyinfo utility just simply run the below-written xdpyinfo command and along with other Linux details the display details will also be displayed:
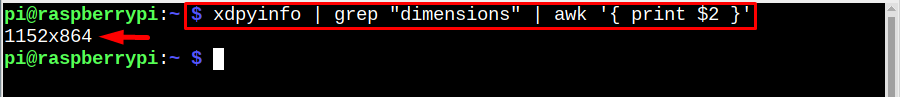
If you want only directly to display the resolution, just run the below-mentioned command and it will display the resolution as an output:
Method 2: By Using xrandr Utility
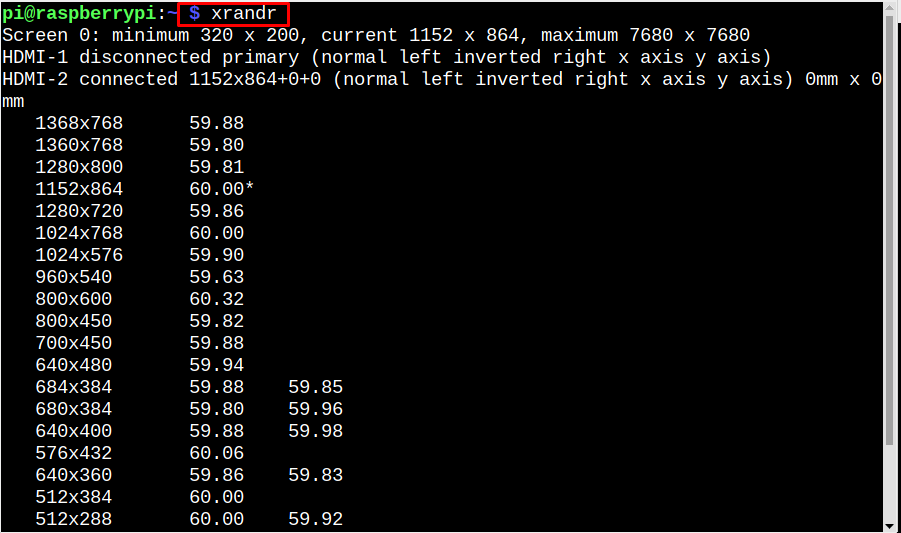
xrandr utility also comes pre-installed in Linux distributions; it belongs to the RandR (Rotate and Reflect) extension. The X in xrandr is for Resize along with Rotate and Reflect extension. Using the xrandr command, the output will display the current screen resolution along with other detailed visual-related information:
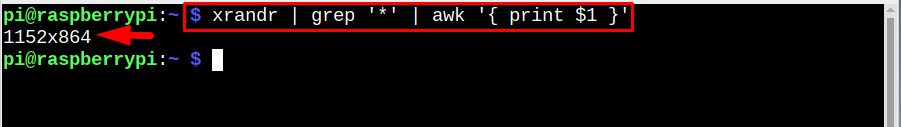
To exactly display the resolution and no other details, you can run the xrandr utility by using the below-mentioned command:
If you want to know more xrandr utility then you can open its manual for description using the below-written command:
Conclusion
To find the screen resolution from the command line on Raspberry Pi, there are two ways which are discussed in the article. One is by using the xdpyinfo utility and the other is by using xrandr utility. Both these utilities are installed by default in Raspberry Pi and you can use these utilities to find the desktop resolution from the command line.