Advance Package Tool, commonly referred to as apt, is the default package manager for most Linux-based operating systems. Through this manager, the users can manage packages with all the required dependencies on the system. The packages installed from the apt will move to the cached directory ‘/var/cache/apt/archives’.
The reason for storing these files in the cache directory is that the next time you install other dependencies of these packages, the apt will not install the existing package again on your system. However, with the passage of time, these packages have become old and are no longer useful for the system. Thus, it’s a good practice to disable the apt cache on your system to free up disk space.
This article is a detailed guide to disable apt cache in the Ubuntu system.
How to Disable APT Cache Ubuntu
You can disable the apt cache on the Ubuntu system from the following steps:
Step 1: First, create a 00clean-cache-dir file on the Ubuntu system from the following command:
Step 2: Inside this file, you must add the following line:
Step 3: Save the cache file using “CTRL+X”, add “Y” and enter to exit.
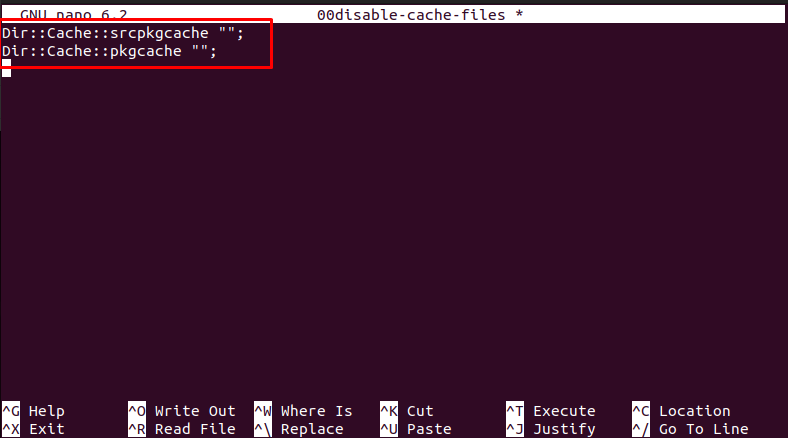
Step 4: Create another file in the system using the following command:
Step 5: Inside the file, add the following lines:
Dir::Cache::pkgcache "";
Step 6: Then save the file using the “CTRL+X”, add “Y” and press enter to exit.
This will disable the apt cache on the Ubuntu system.
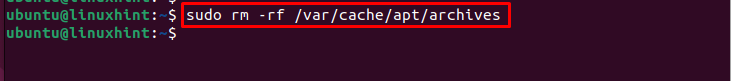
Step 7: Now, you can empty the ‘/var/cache/apt/archives’ directory using the following command:
Step 8 (Optional): Alternatively, you can also remove all the files from the cache directory by running the following command:
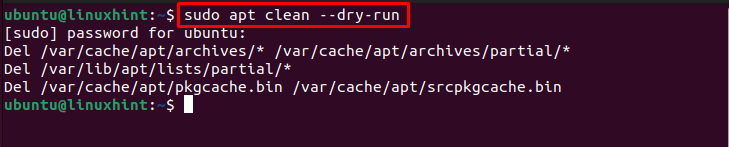
Step 9 (Optional): You can also remove all files and directories from the cache folder by running the following command:
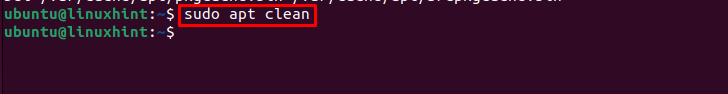
Step 10 (Optional): There is another similar command called autoclean that helps you remove the cache directories and files from the Ubuntu system.
Conclusion
Disabling the apt cache on the Ubuntu system is a good practice for users worried about the disk space issue on the system. They can disable the apt cache on the Ubuntu system at any time by creating some files on the system and adding a few lines inside the files as mentioned above. Afterward, they can remove the cache files and directories using the rm -rf command or alternative apt commands.