While working on Raspberry Pi OS, sometime you may find a service not working on your Raspberry Pi system and you might feel the need to check the status of it to resolve it. If you don’t know how to check for service status on Raspberry Pi, follow this article guidelines.
Let’s begin!
Check the Status of a Service
To check the status of the services on Raspberry Pi, first you must find the number of services running on your Raspberry Pi system. You can use the command mentioned below to see the status of all the services running on your Raspberry Pi system.
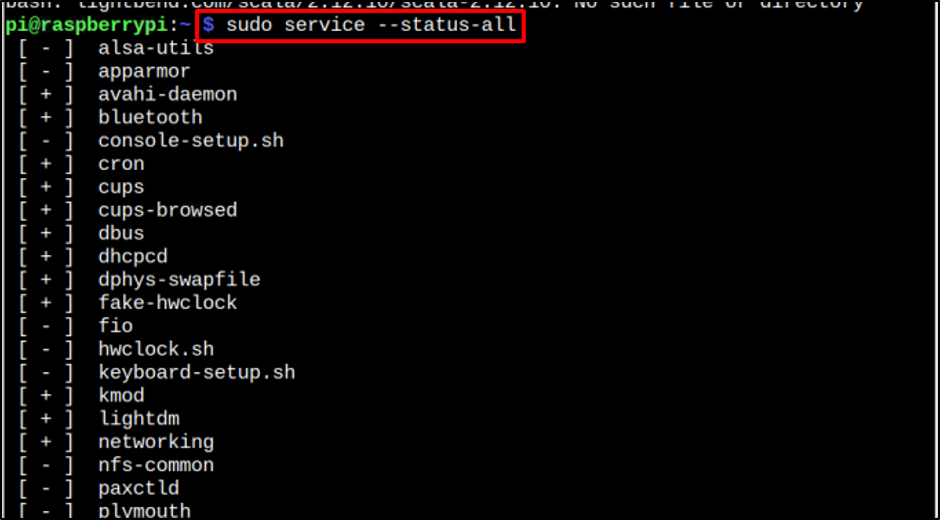
After running the above command, all services will show up on the screen along with service indicators. There are three service indicators which are:
- Plus [+]
- Minus [-]
- Question Mark [?]
The description of each indicator is mentioned below:
1: Plus [+] Indicator
The plus indicator represents that these services are working fine; like in above image avahi-daemon, bluetooth and crons have plus [+] indicator with them that means they are working fine in the system.
2: Minus [-] Indicator
The Minus indicator represents that the service is not running or is inactive on your Raspberry Pi system. In my case alsa-utils, apparmor, fio, and some other services are not running, which is represented by the [-] Indicator.
3: Question Mark [?] Indicator
This indicator shows up when a user has restricted some services. In my case, I haven’t restricted any of the services so there is no question mark [?] indicator.
Now, after finding the services running on the Raspberry Pi system, it’s now time to check the status of a service whether it’s active or not and you can do so by running the following command:
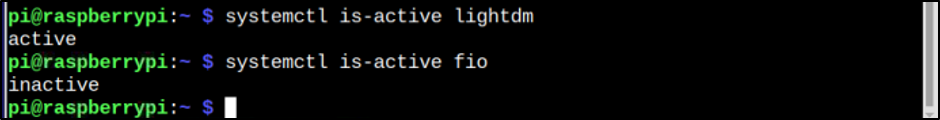
Note: Remember to replace <service name> with the name of service you want to check the status. Like in the below example, I have checked the status of two services, which are lightdm and fio.
As a result of the above command, the active and in-active status of the service is displayed as output.
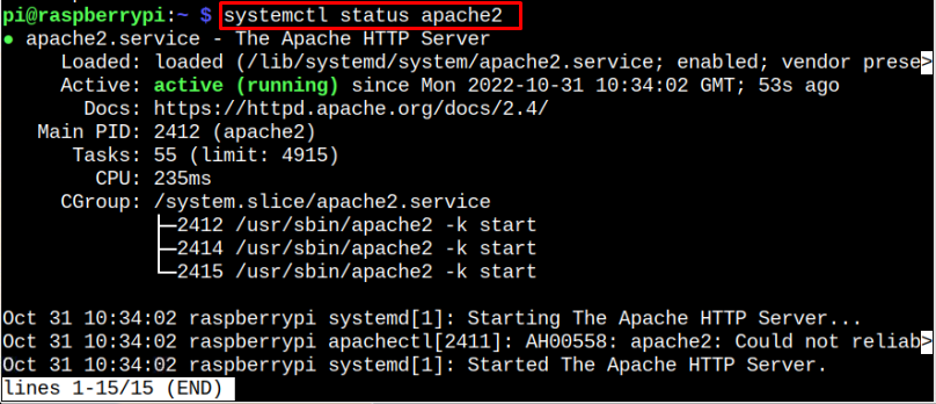
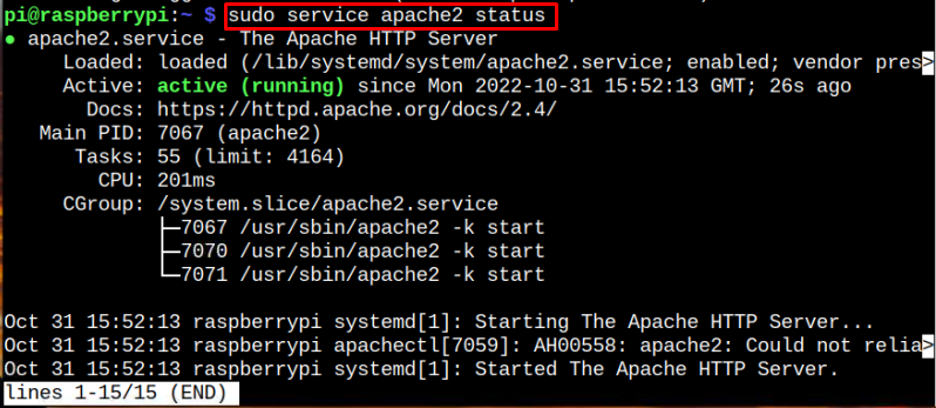
You can also check the service status using the following command:
In case the service is stopped, you can start it using the following command:
The active (running) status of the service shows that it’s running fine on Raspberry Pi.
To reload or restart the service, just replace the “start” with “reload” or “restart” in the above command. This will restart the service on your Raspberry Pi system.
The same type of output you will get when execute the following command:
Conclusion
To check the status of all services running on the Raspberry Pi system, you can use the “service all” command as it displays the status of all the services with service indicator signs [+], [-], and [?]. These indicators show whether the service is active, inactive, or restricted on your Raspberry Pi system. You can also check the status of a particular service using the “systemctl” or “service” commands along with the name of the service. If somehow the service is stopped, you can start it anytime by using the “systemctl start” command.