All these math built-in functions are included in the math.h library. In this write-up, the math library has been discussed in detail with the help of examples.
What are the macros of the math library
In Arduino, the default functions are pre-included in it. Like in c programming, if we have to use the string library, we have to include the header file of strings.h at the start of the code. These header files which are included in the code are known as “macros”. In Arduino, the built-in libraries are by default included so there is no need to add them in the header files, we can simply use these macros libraries without including them in every code. The difference between the macros and functions is that functions are processed only when they are called whereas the macros are processed when the library is included.
The macro library of some of the most frequently used functions of math.h is:
| Macros | Value | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| M_E | 2.71828 | It is used for the exponent |
| M_LOG2E | 1.4426 | It is the value of the log of e to base 2 |
| M_1_PI | 0.318 | It is the value of Pie |
| M_SQRT_2 | 1.414 | It is the value of the square root of 2 |
| fmodf | – | It is used for the mode() function |
| fcosf | – | It is used to for the acos() function |
| fsinf | – | It is used to for the asin() function |
| ceilf | – | It is used for the ceil() function |
What are the functions of the math library in Arduino
The functions take the two input values and after performing some specific action on it, returns a single output. In the math library of Arduino, there are different functions, which take one or two input values and return a single output by performing a particular math operation on them. These math operations include finding the power, finding the mode, finding the cosine, and finding the other trigonometric operations.
The most commonly used math functions included in the math library of Arduino are explained in the table below:
| Functions | Explanation |
|---|---|
| cbrt(x) | It will return the cube root of the x |
| copysign (value1, value2) | It will return the value1 but with the sign of value2 |
| exp(x) | It will return the exponential value of the x |
| fabs(x) | It will return the absolute value of x |
| floor(x) | It will return the largest integral value less than or equal to x |
| ceil(y) | It will return the smallest integral value which is equal to or larger than the given value of y |
| fmax(value1,value2) | It will return the maximum value among value1 and value2 |
| fmin(value1,value2) | It will return the minimum value among value1 and value2 |
| pow(value1,value2) | It will find the power of value1 according to value2 |
| acos(x) | It returns the value by calculating the arc cosine of x in the range of zero to pi and if the answer is out of range, it will generate domain error |
How to use math.h library functions in Arduino
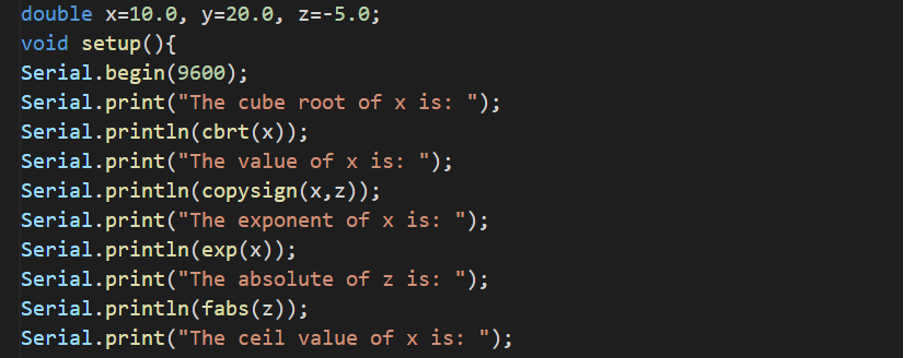
For a better understanding of the math functions in the math library of Arduino, consider the following Arduino code:
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.print(“The cube root of x is: ”);
Serial.println(cbrt(x));
Serial.print(“The value of x is: ”);
Serial.println(copysign(x,z));
Serial.print(“The exponent of x is: ”);
Serial.println(exp(x));
Serial.print(“The absolute of z is: ”);
Serial.println(fabs(z));
Serial.print(“The ceil value of x is: ”);
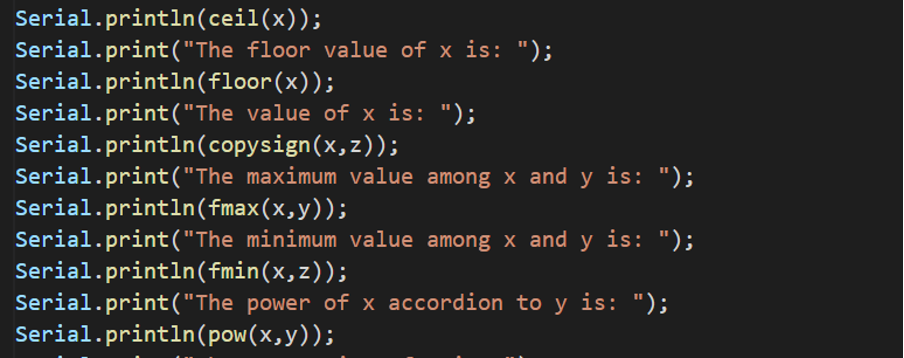
Serial.println(ceil(x));
Serial.print(“The floor value of x is: ”);
Serial.println(floor(x));
Serial.print(“The value of x is: ”);
Serial.println(copysign(x,z));
Serial.print(“The maximum value among x and y is: ”);
Serial.println(fmax(x,y));
Serial.print(“The minimum value among x and y is: ”);
Serial.println(fmin(x,z));
Serial.print(“The power of x accordion to y is: ”);
Serial.println(pow(x,y));
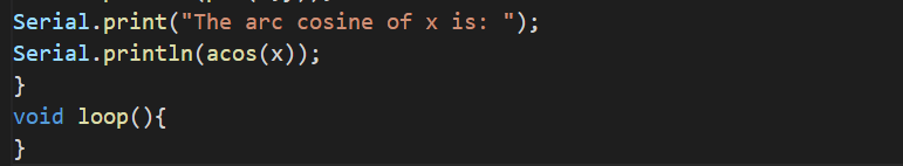
Serial.print(“The arc cosine of x is: ”);
Serial.println(acos(x));
}
void loop(){
}
The output of the above code is:
In the above code, we have declared three variables x,y, and z with some values. We perform different functions with the help of math.h library and display the results on serial monitor output through the serial communication at baud rate of 9600. In the output, the result of the power function is “ovf” (overflow) which means the result is beyond the range. Similarly, in the result of acos() function, it returns nan(not a number) which means the value is a negative integer.
Conclusion
The math library in Arduino contains the functions related to maths. These functions provide the ease of doing mathematical operations; both arithmetic and trigonometric. This library is very important when you are designing a project in which mathematical calculations are included. In this write-up, we have discussed the math library which is by default included in Arduino. And also explain the functions of math.h library with the help of examples in Arduino.