This article will explain the steps to pack a Python application into a container.
What are the Steps to Package Python Applications into Docker Containers?
To package a Python application into a container, check out the given-provided steps:
- Create a Docker file with some instructions.
- Create a program file.
- Build an image from the Docker file through the “docker build -t <image>” command.
- Build and run the container to package the Python application using the “docker run –name <container-name> <image-name>” command.
- View running container.
Step 1: Create Docker file
On Visual Studio Code, create a new file named “Docker file” and specify the below-provided instructions into it:
WORKDIR /app
COPY . /app
CMD [ "python", "./python-app.py" ]
In the above code:
- The “FROM” instruction is used to define the container image. For instance, we have defined the “python:latest” image.
- The “WORKDIR” specifies the working directory for container to “/app”.
- The “COPY” instruction is utilized to copy the current directory’s file to the container’s working directory.
- The “CMD” command specifies the default command to be executed when the container launches. In our case, the Python script “python-app.py” will run utilizing the “python” command.
Step 2: Create a Program File
Then, create a new Python program file named “python-app.py” and paste the following snippet into it:
print("Hello, This is Python application")
Step 3: Create Docker Image
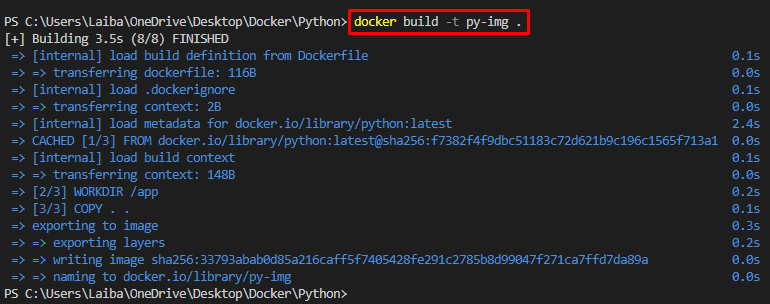
Next, build the Docker image from the desired Docker file by writing out the “docker build” command along with “-t” option to specify the image name:
This builds a Docker image with the tag “py-img” based on the Docker file in the current directory.
Step 4: Package the Application into the Container
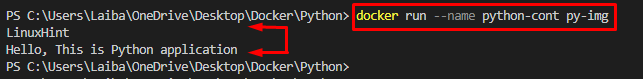
Now, build and run the container to package the Python application using the “docker run –name <container-name> <image-name>” command:
Here:
- The “–name” option is used to define the container name which is “python-cont” in our case.
- The “py-img” is the Docker image that is used for building the container:
Our Python application has been packaged and deployed successfully.
Step 5: View Python Container
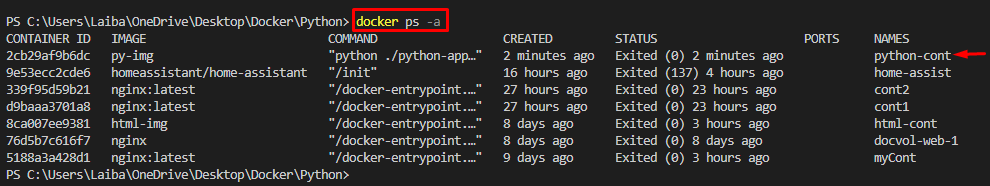
Lastly, view the Python container by executing the below-stated command:
In the above output, the Python container can be seen.
Conclusion
To package a Python application into a container, first, create a program file and Docker file with some instructions. Then, build an image from the Docker file through the “docker build -t <image>” command. Next, run the “docker run –name <container-name> <image-name>” command for building and running the container to package the Python application. This article has explained the steps to packaging a Python application into a container.