PostgreSQL is a free-to-use relational DBMS that offers a variety of functions, data types, operators, and features. It is designed to manage complicated queries and to ensure data integrity and reliability. It supports numerous operating systems, such as Windows, Docker, and Linux. PostgreSQL is also extensible that allows users to define their own functions, operators, data types, and extensions.
This write-up will illustrate the steps to create a PostgreSQL Database using Docker.
What are the Steps to Create a PostgreSQL Database Using Docker?
To create a PostgreSQL database using Docker, follow the below-provided steps:
- Pull Postgres Image from Docker Hub
- Build and Start Postgres Container
- View Running Postgres Container
- Access Postgres Container
- Connect to a PostgreSQL Database Server
- Create a PostgreSQL Database
- View all Databases
- Connect to a Particular Database
- Create New Table in Database
- Insert Values in Table
- Select Data From Table
- Delete the Database
Step 1: Pull Postgres Image From Docker Hub
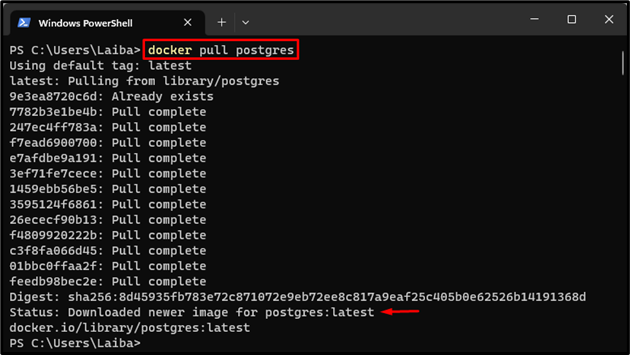
First, pull the Postgres image from Docker Hub to the local system by running the provided command in Windows PowerShell:
The above output indicates that the latest version of the Postgres image has been downloaded successfully.
Step 2: Build and Start Postgres Container
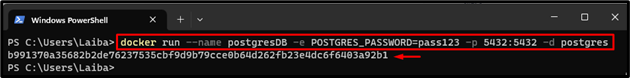
Next, build and execute the Postgres container using the Postgres image through the “docker run –name <cont-name> -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=<password> -p 5432:5432 -d postgres” command:
Here:
- “–name” option defines the name for the container i.e., “postgresDB”.
- “-e POSTGRES_PASSWORD” specifies the password to “pass123”.
- “-p” allocates the port for the container i.e., “5432:5432”.
- “-d” flag is utilized to start/execute the container in the background.
- “postgres” is the latest Postgres Docker image to use for the container:
The Postgres container has been built and started.
Step 3: View Running Postgres Container
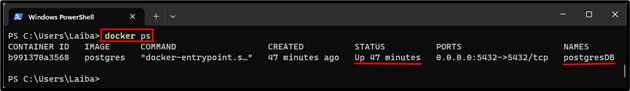
Then, type out the given-provided command to verify whether the Postgres container is running or not:
According to the above output, the Postgres container is running successfully.
Step 4: Access Postgres Container
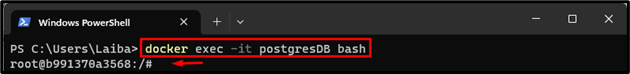
Now, utilize the “docker exec -it” command along with the container name to open the Bash shell inside the running Postgres container:
The Postgres container has been accessed and now users can execute commands inside the running container.
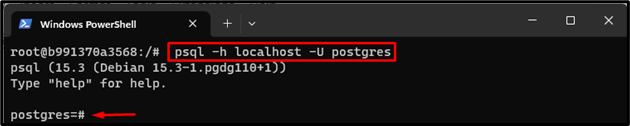
Step 5: Connect to a PostgreSQL Database Server
After that, connect to the PostgreSQL database server via the provided command:
The Postgres shell has been started. Now, users can execute SQL queries and other commands in it.
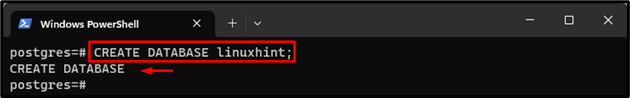
Step 6: Create a Database in Postgres
To create a database in Postgres, run the “CREATE DATABASE <database-name>;” command:
The new PostgreSQL database has been created i.e., “linuxhint”.
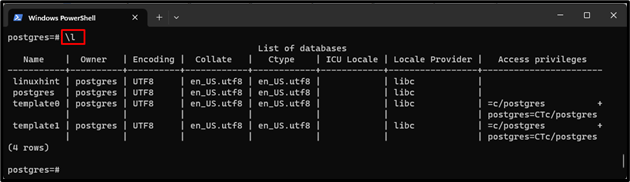
Step 7: View all Databases
Execute the below-listed command to display all the existing databases:
The above output has displayed the list of databases.
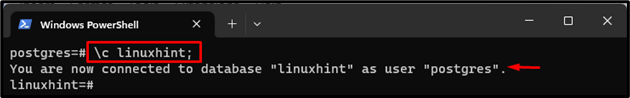
Step 8: Connect to a Particular Database
In order to connect to a desired database, utilize the “\c <database-name>;” command:
The new database has been selected and we have connected to it.
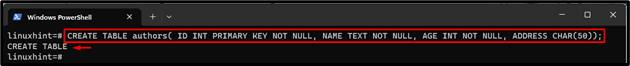
Step 9: Create New Table in Database
Now, use the “CREATE TABLE <table-name>(column1 <datatype>, column2 <datatype>, column3 <datatype>,….., columnN <datatype>);” command and specify the table name, columns name, and datatype to make a new table in the selected database:
The new table has been created with some columns.
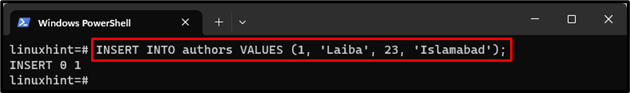
Step 10: Insert Values in Table
Then, insert some values in the table via the “INSERT INTO <table-name> VALUES (value1, value2, value3, …);” command:
The above output indicates that the values have been added to the table successfully.
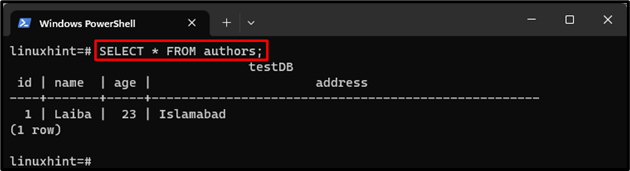
Step 11: Select Data From Table
Now, type out the following command to get the desired table’s data:
The data of the “authors” table can be seen in the above output.
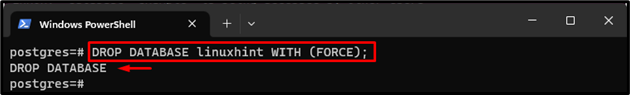
Bonus Tip: Delete the Database
If the database is in use, the simple “DROP DATABASE <database-name>” command does not delete the database. So, in order to delete a particular database, utilize the “WITH FORCE” option with the same command:
This command closed the database session forcefully and removed the “linuxhint” database.
Conclusion
To create a PostgreSQL database using Docker, first, download the Postgres image from Docker Hub. Then, create and run the Postgres container using the “docker run –name <cont-name> -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=<password> -p 5432:5432 -d postgres” command. Next, access the Postgres container and connect to the Database Server. After that, create a Database using the “CREATE DATABASE <database-name>;” command. Moreover, users can create a new table in the database, insert values in the table and select data from the database.