The environment variables are the variables that specify important configurational settings. The Docker environment variables help us to define additional configurations to the Docker container for deploying Docker applications such as the “USER” variable is used to specify the username, the “PASSWORD” variable is used to set the password on the application or container, or “DOCKER_HOST” to define the remote host.
This blog will demonstrate how to set environment variables in Docker using:
Method 1: Set Environment Variable Through Dockerfile
The Dockerfile is a file that defines instructions to create the Docker container’s snapshot which is also known as the Docker image. In Dockerfile, users can set the environment variables using the “ENV” command in the file. For illustration, go through the listed steps.
Step 1: Create Dockerfile
First, make the file named “Dockerfile”. Add the given code to the file:
WORKDIR /app
COPY . /app
ENV USER="Docker-User"
CMD ["python", "app.py"]
The above snippet contains the following instructions:
- “FROM” command is defining the Docker base image.
- “WORKDIR” is utilized to specify the container working directory.
- “COPY” command is copying the build content in the container’s defined path.
- “ENV” is specifically used to set environment variables for containers. For demonstration, we have set the “USERNAME” environment variable.
- “CMD” command defines the container’s executables.
Step 2: Make Python File
Next, make the Python file that will print the environment variable set in Dockerfile:
user = os.environ.get("USER")
print(user)
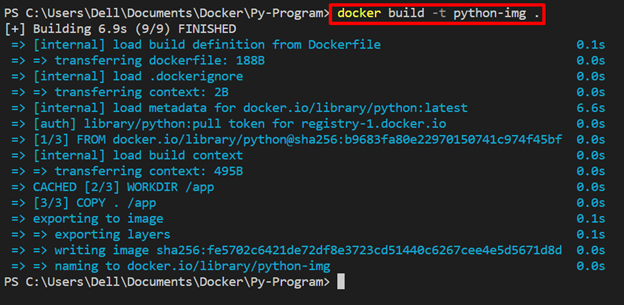
Step 3: Make Docker Image
Generate the new Docker image/snapshot from the Dockerfile instruction through the given command:
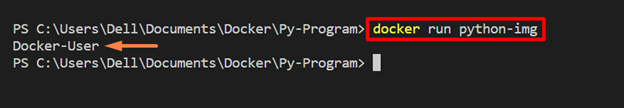
Step 4: Run Docker Container
Next, execute the Docker container by executing the Docker image using the mentioned command:
The output shows the “USER” environment variable value:
Method 2: Set Environment Variable Through Command
Users can also set the environment variables while creating and executing the container through the “-e” option in Docker “run” command.
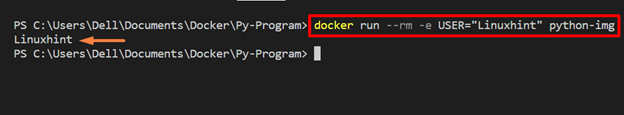
For this purpose, use “docker run -e <Variable= “Value”> <image-name>” command as mentioned below:
In the above command, we have set the “USER” environment variable:
The above output indicates that we have successfully set the “USER” environment variable as “Linuxhint”.
Method 3: Set Environment Variable Through Compose File
The users can configure the Docker environment variables through Docker Compose. To do so, simply provide the environment variable by utilizing the Docker compose “environment” key in the “docker-compose.yml” file.
For implementation, follow the provided procedure.
Step 1: Create Compose File
First, create the “docker-compose.yml” file and add the below given configurations to the file:
services:
py-app:
build: .
environment:
- USER="Linuxhint"
In the above code block:
- “services” is utilized to define the compose service.
- “build” is providing the build context. For instance, we are using a Dockerfile placed in the currently opened directory.
- “environment” key is used to set the environment variable for compose service or container.
Step 2: Fire Up the Container
Next, fire up the compose service in a container using the “docker-compose up” command:
That’s all about setting up an environment variable in Docker.
Conclusion
To set the environment variable in Docker, users can use the ENV statement in Dockerfile, or the “environment” key in Docker compose. Docker users can also set the environment variable while creating and executing the container through the “docker run -e <Variable= “Value”> <image-name>” command. This post has provided the methods to set the environment variables in Docker.