The shell script is used to process or execute multiple commands simultaneously. It is also utilized to perform repetitive tasks. In Docker, you can use the shell script to set up the container, specify the program, or run the commands within the container. More specifically, to run the shell script in the container, developers can use Dockerfile or the “docker exec” command. The Dockerfile is used to containerize the program or file. However, the “docker exec” command executes the commands within a container using the container’s shell.
This post will demonstrate how to run the shell script within a container using the “docker exec” command.
How to Run Shell Script in Container Using “docker exec”?
To run the shell script in a container, first, run the container and copy the script to the container’s path. After that, run the shell script using the “docker exec <container-name> bash -c “script”” command.
For the demonstration, follow the given steps.
Step 1: Create Shell Script
First, create the file named “test.sh” file and add the commands you want to execute. For instance, we have specified the two “echo” commands.
echo "Hello"
echo "Welcome to Linuxhint"
Note: The file must start with “#!/bin/bash” to execute the script in the container.
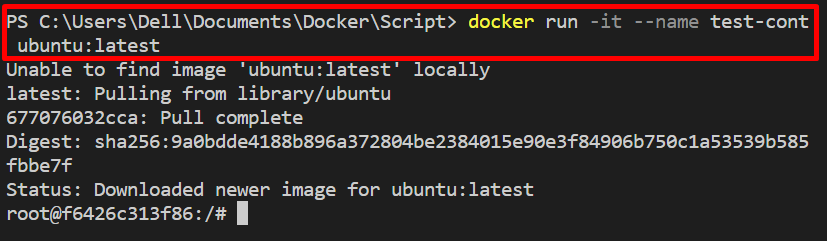
Step 2: Run the Container
Next, run the container in which you want to execute the shell script. We have used the “ubuntu:latest” image to create and start the container. The “-i” flag executes the container interactively, and “-t” assigns the “TTY-pseudo” terminal to the container:
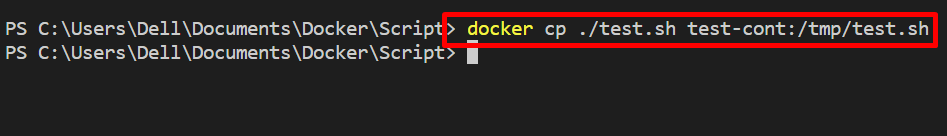
Step 3: Copy Script to Container
Open another terminal Windows, copy the script to container path with the help of “docker cp <path of script> <container-name>:<container’s path>” command:
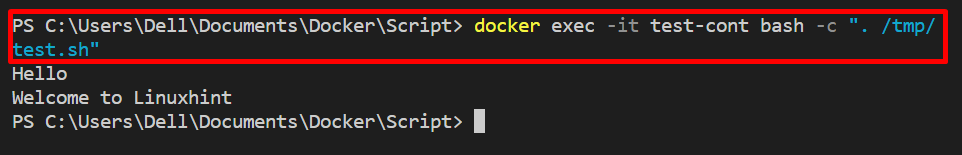
Step 4: Run Shell Script Within Container
Next, run the script within a container using the “docker exec” command as mentioned below:
Here, you can see we have successfully run the shell script in the container:
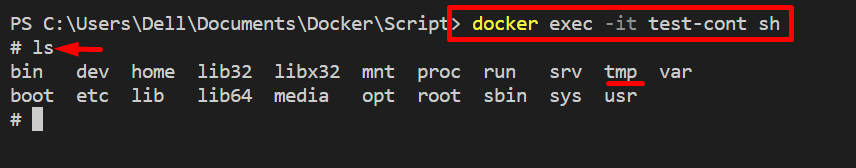
Step 5: Verification
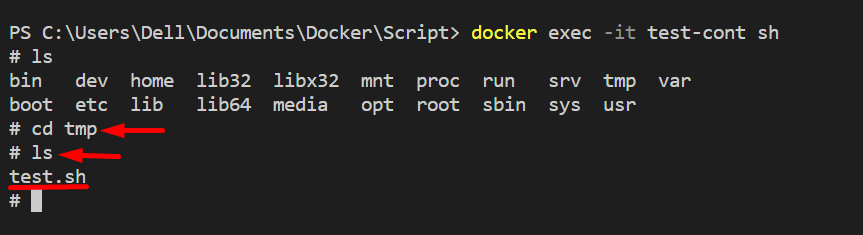
For the verification, open the container’s shell and execute the “ls” command to view files and directories:
ls
Navigate to the “tmp” directory of the container through the “cd” command. After that, execute the “ls” command:
ls
As you can see, the “test.sh” script exists in the “tmp” directory of the container:
This is all about running shell scripts in a container using “docker exec”.
Conclusion
To run the shell script in a container using the “docker exec” command, first, create the shell script and copy it in the running container through the “docker cp” command. After that, run the shell script by utilizing the “docker exec <cont-name> bash -c “<path of script>”” command. This post has demonstrated the technique to run the shell script using the “docker exec” command.