Ubuntu has a graphical user interface for package installers and acts more like a conventional operating system. With Ubuntu, you do not need a terminal to download packages. Ubuntu has three versions: desktop, server, and core.
90% of the operating system market is owned by Microsoft, but Ubuntu comes with its own advantages compared to Windows and macOS. These benefits include the following:
- Free of cost
- More secure than Windows
- Customizable
- Can run from a pen drive and does not need to install
- Comes with Bash support
Many Linux-based laptops have a bad reputation for battery life. There are various reasons for this. Generally, Linux based laptops have less battery life compared to Windows-based. That does not mean that Ubuntu is not a power-efficient operating system, as this distro can manage battery life pretty well if it is fine-tuned.
There are several factors that can harm the battery life in Linux-based laptops. It is good practice to continually identify any issues that may be present in your device’s battery. The Ubuntu Operating System has a built-in app called Power Statistics that can give you information about battery life, remaining capacity, the difference between designed energy and current energy, and more.
If you feel that your battery is draining quickly or behaving abnormally, then there is also a well-known tool that you can use to optimize the battery performance called TLP. TLP is a robust tool to improve and optimize battery life. TLP provides two primary settings, including one for battery and the other for AC consumption. When you turn on your laptop, TLP adjusts its settings according to events. Similarly, if your laptop is using the battery, TLP will adjust its settings accordingly. TLP is a safe application to use, as it does not modify the settings according to CPU load or battery charge level.
To manage the battery life on your Ubuntu laptop, you will need to determine the state of the battery’s health. There are multiple ways to check battery health, but the two main methods are:
- Through Ubuntu’s built-in app Power Statistics
- Through Terminal Commands
Power Statistics Method
The easiest way to check battery performance and capacity is through the built-in Ubuntu app called Power Statistics. This app provides power statistics of any hardware that is connected to your system, for example, a processor and AC adapter.
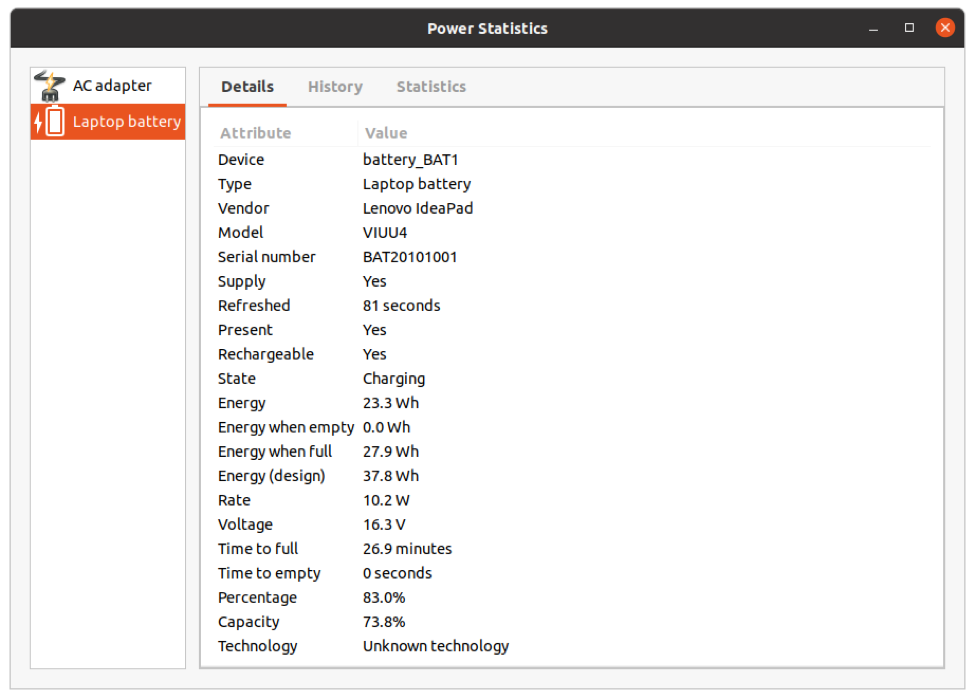
Open the Power Statistics app and pick the “Laptop battery” device, as shown in the following image. You will be presented with various options, including device name, manufacturer name, remaining charge, capacity, and battery status.
The two most important options are:
- Energy When Full
- Energy (Design)
When full, “Energy” is the current capacity of your battery, whereas the “Energy (Design)” is the original battery capacity given by the manufacturer. The larger the gap between the two numbers, the lesser the charge your battery holds. The option “Capacity” tells you the remaining battery capacity in a percentage. You can see these options and more listed in the image below.
Terminal Commands Method
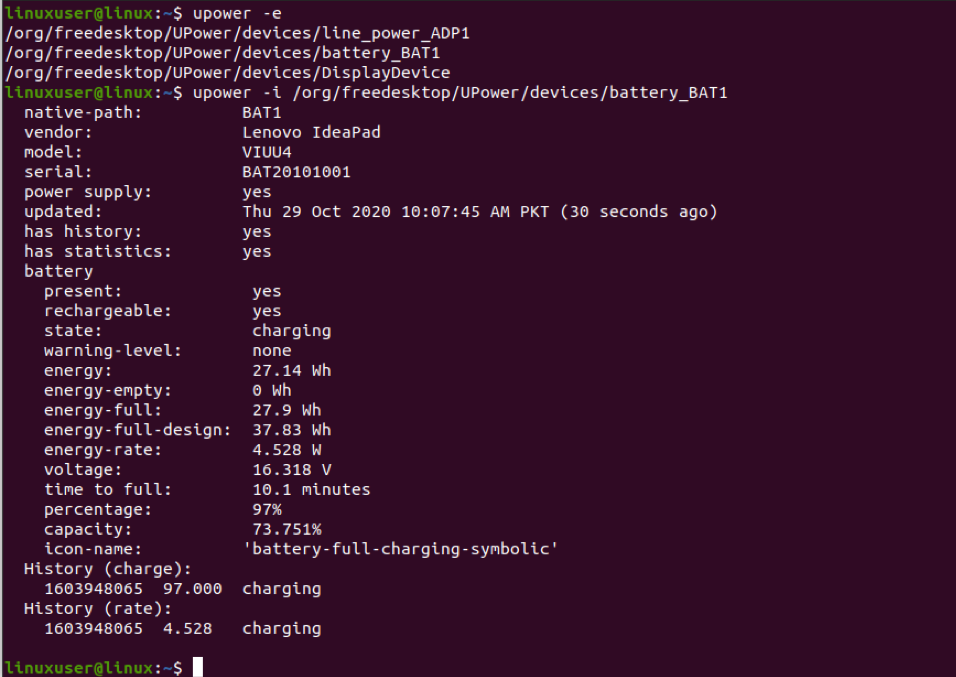
Another option is to check your battery’s device through the Terminal. Open Terminal and enter the following command lines:
The above command is used to find all power device types.
Now, run upower –i and specify the path of the device.
This command will give roughly the same information given by Power Statistics.
Example output:
So, now that you are aware of the health of the battery of your laptop, it is also good practice to optimize the battery of your Linux-based laptop.
Optimizing Battery Life Using TLP
TLP is a command-line tool used to optimize the battery of a laptop. TLP helps to save the battery life of a Linux-based laptop by tweaking the kernel settings to optimize battery performance.
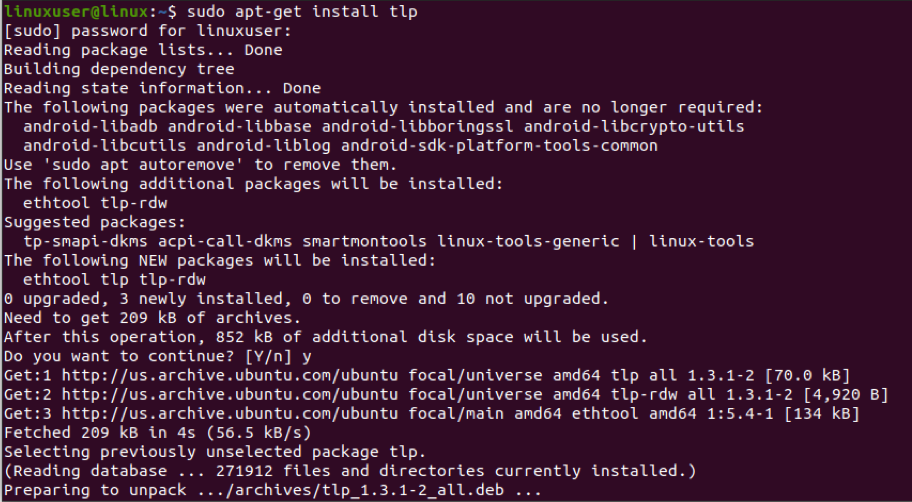
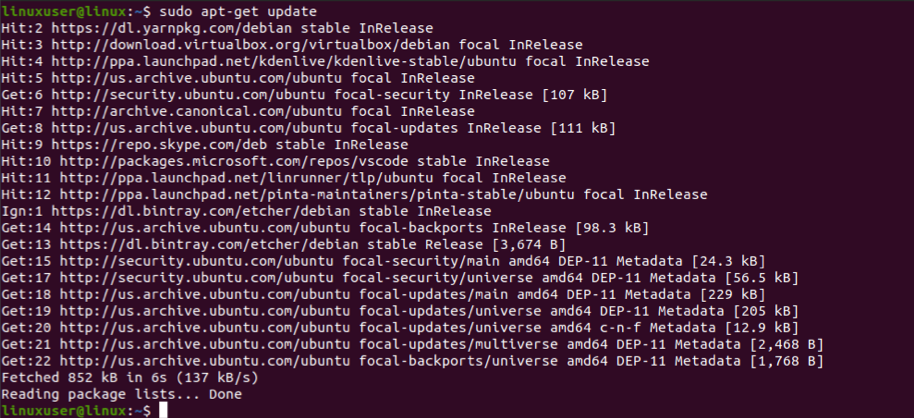
You just have to install TLP to use it. The default settings of TLP are good enough on their own to optimize the battery, but TLP is still highly customizable. To install TLP in Ubuntu, type the following command line in the Terminal:
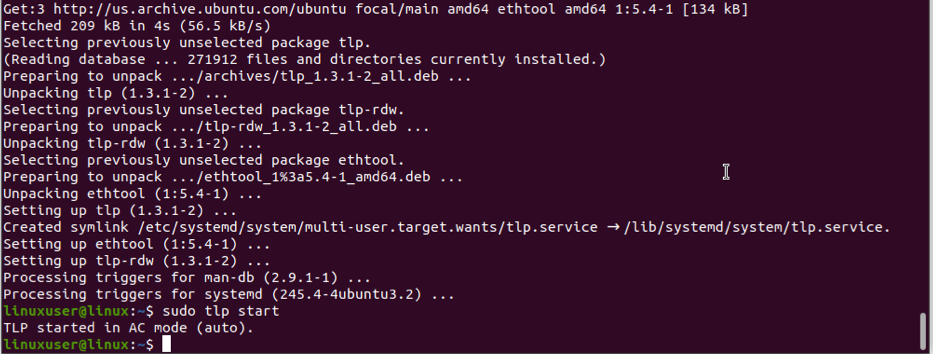
After installing TLP, run the following command to start it:
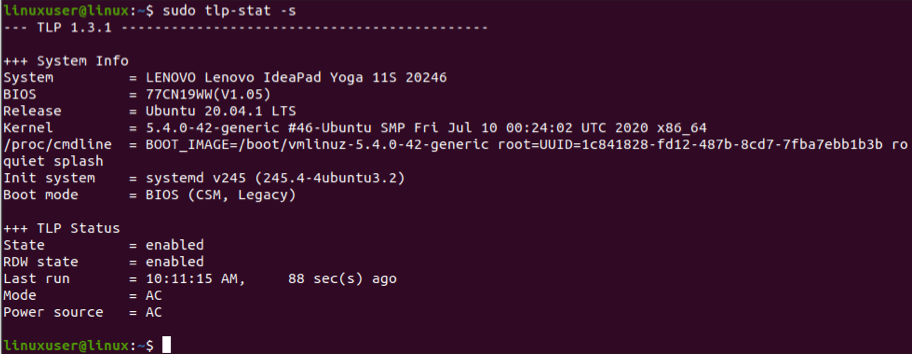
Run the following command to monitor the power usage:
You do not have to adjust or modify any settings after the installation; TLP will take care of it.
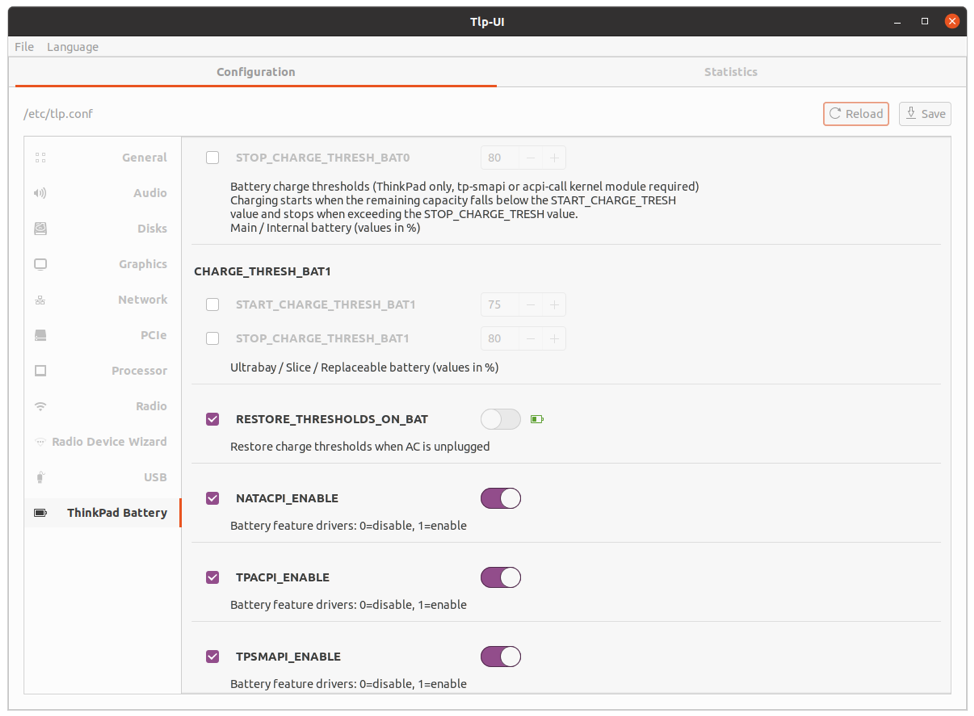
There is a UI-based TLP app that is also available, called TLPUI. TLPUI provides its entire functionality in the graphical user interface, where you can tweak settings and optimize the battery according to your needs.
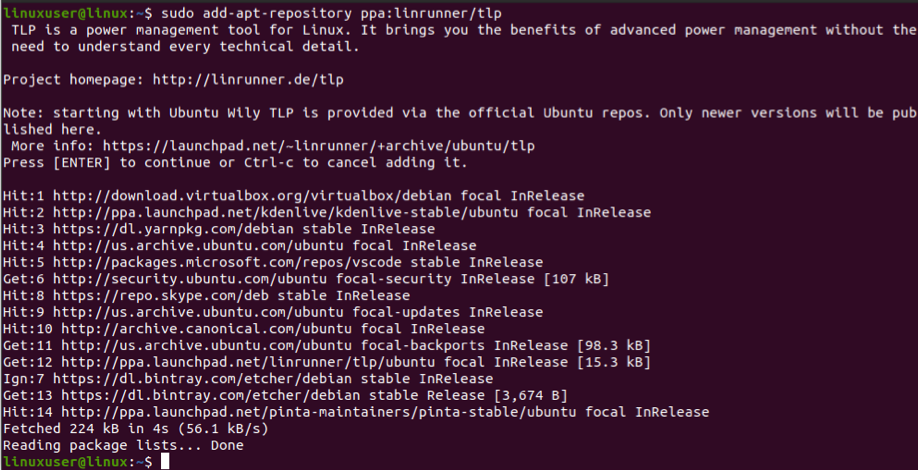
TLPUI does not work without TLP, so you will need to install TLP first. You can do so using the command line, as described above. You will need the latest version of TLP, so type the following command:
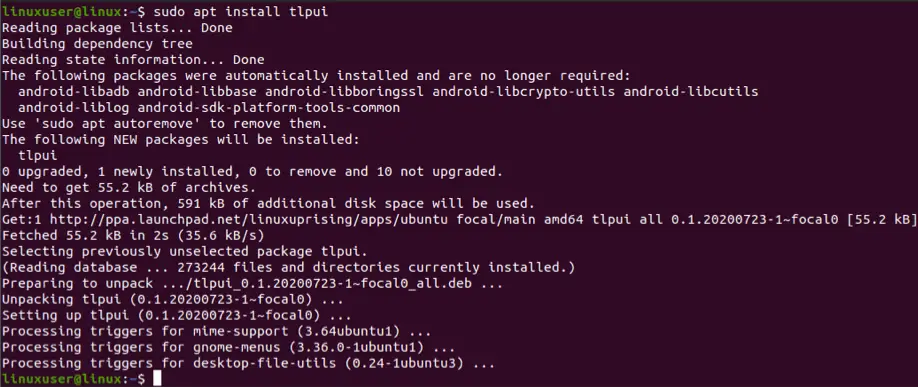
After getting the latest version of TLP, download and install TLPUI using the following command lines:
sudo apt install tlpui
Now, go to Apps and open TLPUI. You will get the following window upon opening TLPUI. You can modify the TLPUI settings quite easily from the graphical user interface.
Conclusion
Hope this helps to manage battery life better for you on Ubuntu