Note: We have explained the procedure explained in this article on a Ubuntu 20.04 LTS system.
Installing Apache2; Step 1: Update
First, we will need to update the system repository index to install the most recent version of Apache2. To do so, launch the Terminal by using the Ctrl+Alt+T shortcut and execute the following command:
Note that, only an authorized user can install, update, or remove the packages from the Linux system.
Step 2: Install Apache2
Next in this step, we will install Apache2 web server. For this, execute the below command in Terminal:
The system might ask for confirmation by providing you with a Y/n option. Hit y and then Enter to continue. After that, the Apache2 web server and its all dependencies will be installed on your system.
Once installed, verify the version of the Apache server as follows:
Firewall configuration
Now, we will need to open certain ports on our system in order to access Apache from outside. First, let’s list the application profiles that we need to give Apache access to. Run the following command to do so:
Here you can see different apache profiles.
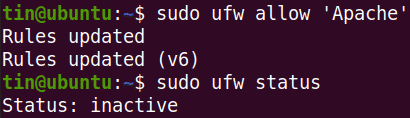
We will use the highly restrictive profile ‘Apache’ to enable network ctivity on port 80.
Now check the status which will show Apache allowed in firewall.
Configuring Apache web server; Verifying Apache service
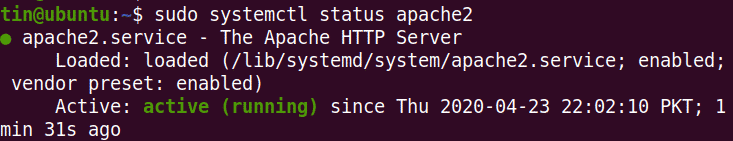
Before moving towards configuration, first, verify if the Apache service is operational. For this, execute the below command in Terminal:
From the above output, you can see the Apache2 service is active and running.
Another approach to verify if Apache is running fine by requesting a web page from the Apache web server. To do so, find your IP address using the following command:
Then open the web browser and access apache welcome page as follows:
Replace the 192.168.72.134 by the IP address of your machine.
By navigating to the above link in the browser, you see the Apache welcome page which is the indication that the Apache server is working properly.
Setting Up Virtual Hosts in Apache
If you have multiple domains that need to be server from the single Apache web server, then you will require to set up virtual hosts. In the following, we will show you how to set up a virtual host in Apache. We will set up the domain name “info.net”. Make sure to replace the info.ne with your own domain name.
Step 1: Create a directory for your domain
In this step, we will create a directory for our domain name. This directory will be used for storing the data on our website.
Run the following command in Terminal by replacing the info.net with your own domain name:
Change the directory ownership to current user:
Assign necessary permissions as follows:
Step 2: Make a sample page for your website
We have setup virtual host and assign necessary permission. Now we, will create a sample page for our website. We will create the sample page using Nano editor, however, any text editor can be used for this purpose.
Copy paste these lines of HML code:
Now use Ctrl+O to save and then Ctrl+X to exit the file.
Step 3: Create a virtual host file
Apache server comes with virtual host file by default. This file is used to serve the contents of the web server. However, we will generate the new virtual host file with the following command:
Now enter the below lines by replacing the info.net by your own domain name.
ServerAdmin admin@info.net
ServerName info.net
ServerAlias info.net
DocumentRoot /var/www/info.net/html
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
</VirtualHost>
Now use Ctrl+O to save and then Ctrl+X to exit the file.
Step 4: Activate virtual host configuration file
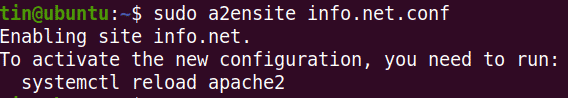
In this step, we will be creating the virtual host configuration file. For this, execute the following command in Terminal:
Now disable the “000-default.conf” default virtual configuration file as follows:
Now restart Apache to activate the new configuration as follows:
Step 5: Test for errors
Once all the configurations are completed, you can test for any configuration errors:
You might receive the following error:
In order to resolve this error, edit the servername.conf file:
Then add this line by replacing the info.net with your own domain name:
Save and exit the servername.conf file and run:
Now again execute:
This time, hopefully, you will not receive any error.
Step 6: Test virtual host
Now the Apache web server is ready to serve our domain. Let’s test this by navigating to the following link in the browser:
Replace the info.net with your domain name.
The following index page shows the Apache server is ready to serve our domain name.
Managing Apache server
In order to manage the Apache server, here are some of the useful commands that you can run in Terminal:
To start the Apache server:
To stop the Apache server:
To stop and then start Apache”
To reload apache server to update the new configurations:
To start Apache at boot:
To disable Apache at boot:
This article has explained in detail the installation and configuration of Apache web server in Ubuntu 20.04. We have also explained setting up a virtual host. Now you can set up multiple domains in the same Apache server. In the end, we have mentioned some commands that can be very helpful in managing the Apache web server.