This blog will illustrate how to install MariaDB using Docker.
How to Install MariaDB Using Docker?
MariaDB is an open-source, universally used MySQL relational DBMS. It is the newest form of the MySQL technology. To install MariaDB using Docker, go through the provided instructions.
Step 1: Pull Image For MariaDB and Start Container
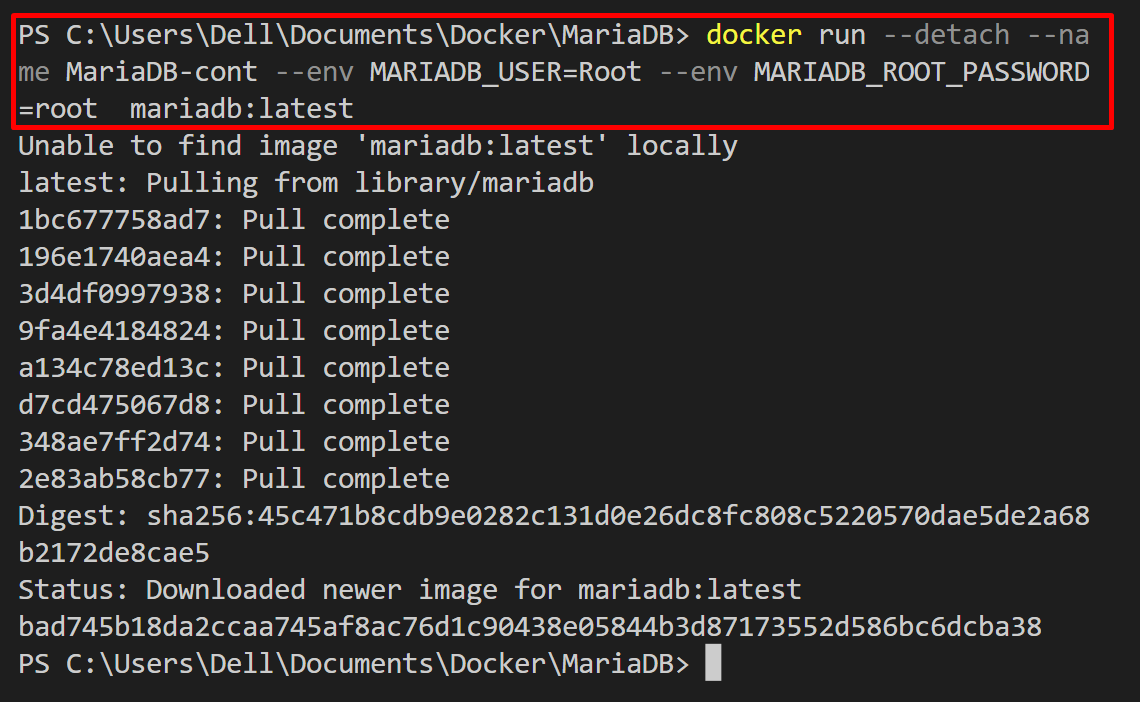
To download the MariaDB official image and execute it to create and start the MariaDB Docker container, utilize the given command:
In the above snippet:
- “–detach” option is used to process the MariaDB container in the backend.
- “–name” specifies the container’s name. For instance, we have set “MariaDB-cont”.
- “–env” option is utilized to define the container’s environment variables.
- “mariadb:latest” is the official Docker image used setup and use MariaDB in the Docker container:
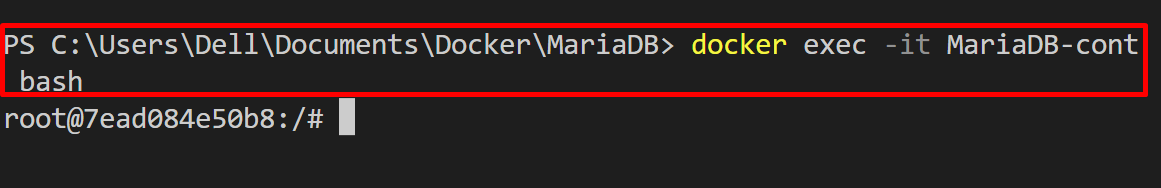
Step 2: Start Container Shell
Next, start the container shell using the “docker exec -it <container-name> bash” command:
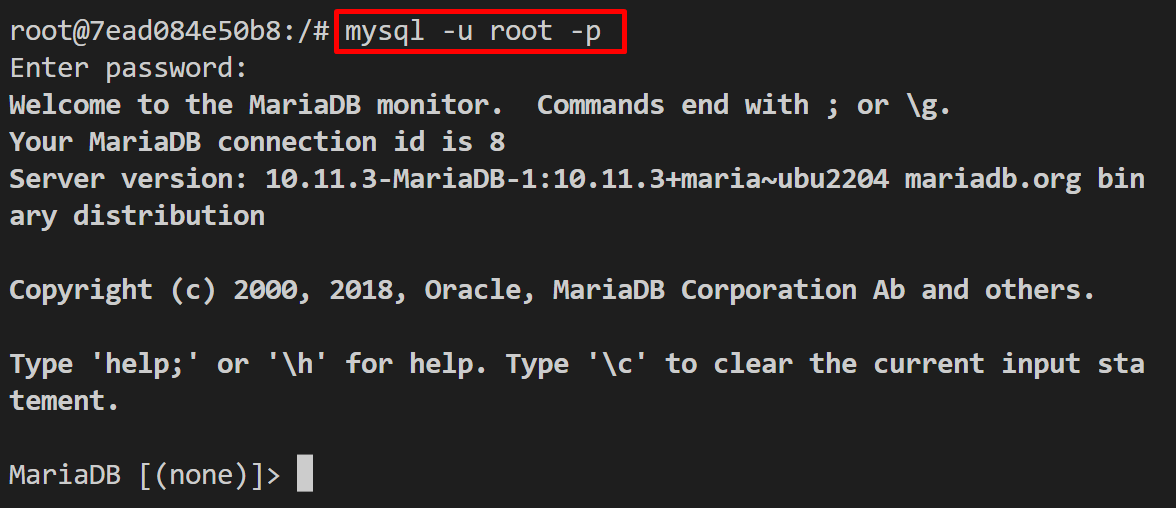
Step 3: Access and Use MariaDB
For the verification, access the MariaDB interface inside the container by executing the “mysql -u root -p” command:
This command will ask you to provide the password, and add the password that you have set in the “MARIADB_ROOT_PASSWORD” environment variable:
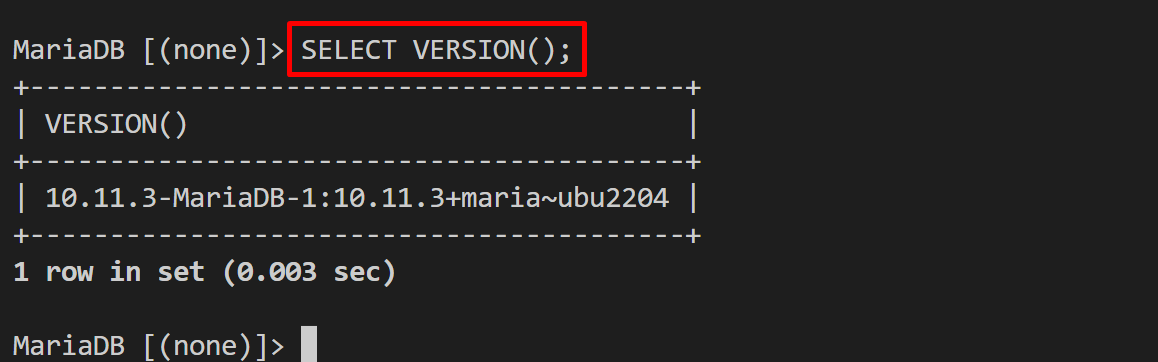
To check the MariaDB version, simply use the provided query:
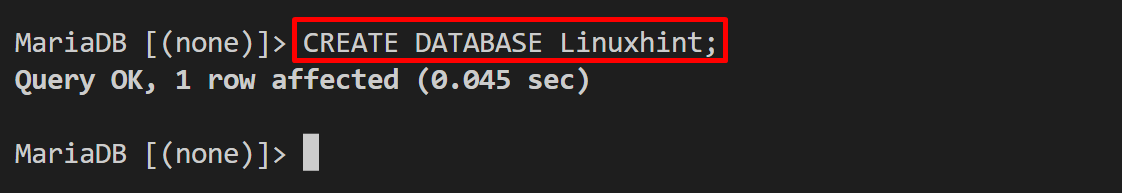
In order to create the database in MariaDB, execute the “CREATE DATABASE <database-name>” query:
That’s how the MariaDB database is installed and used in the Docker container.
Bonus Tip: How to Install MariaDB Using Docker Compose?
Docker compose is a tool that is used to configure and execute multiple containers software, programs, and services. To install MariaDB using the Docker Compose service, follow up the following instructions.
Step 1: Create “docker-compose.yml” File
First, create a file named “docker-compose.yml” file. Next, add the below-mentioned code to the file:
services:
db:
image: mariadb
restart: always
environment:
MARIADB_ROOT_PASSWORD: root
adminer:
image: adminer
restart: always
ports:
- 8080:8080
In the above code block:
- “services” key is used to specify compose services. For illustration, we have configured “db” and “adminer” services.
- “image” is utilized to define the service base image. To install MongoDB, we have utilized the “mariadb” image and “adminer” that also support SQL-based databases.
- “environment” key specifies the environment variables.
- “port” key is used to define the container’s exposed port.
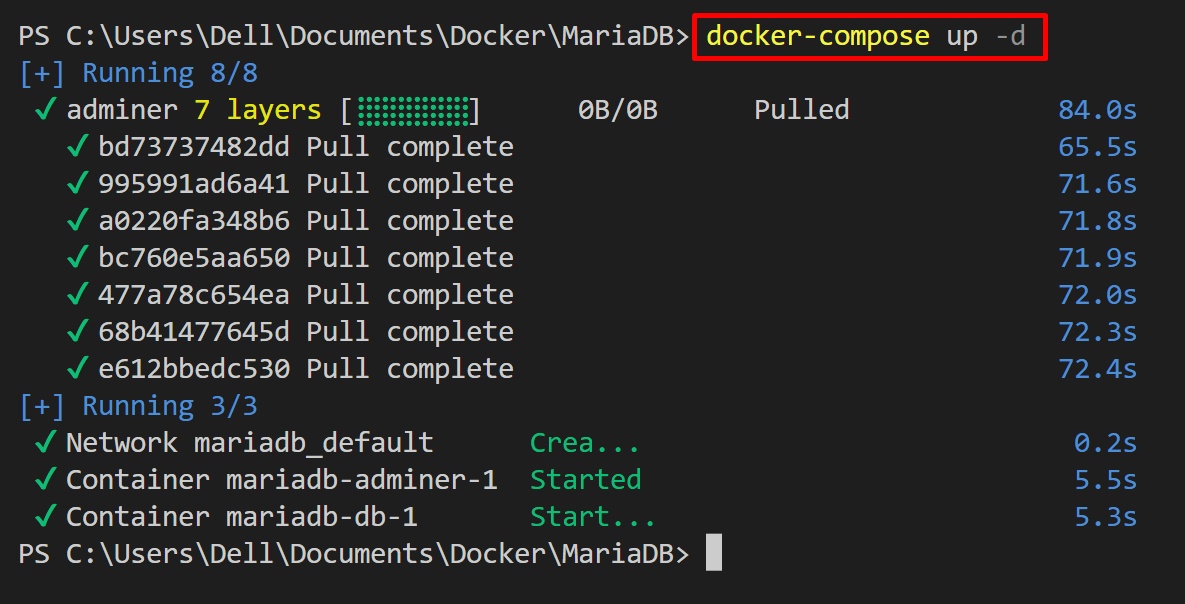
Step 2: Fireup Compose Container
Next, start the compose container using the “docker-compose up” command:
Step 3: Use MariaDB
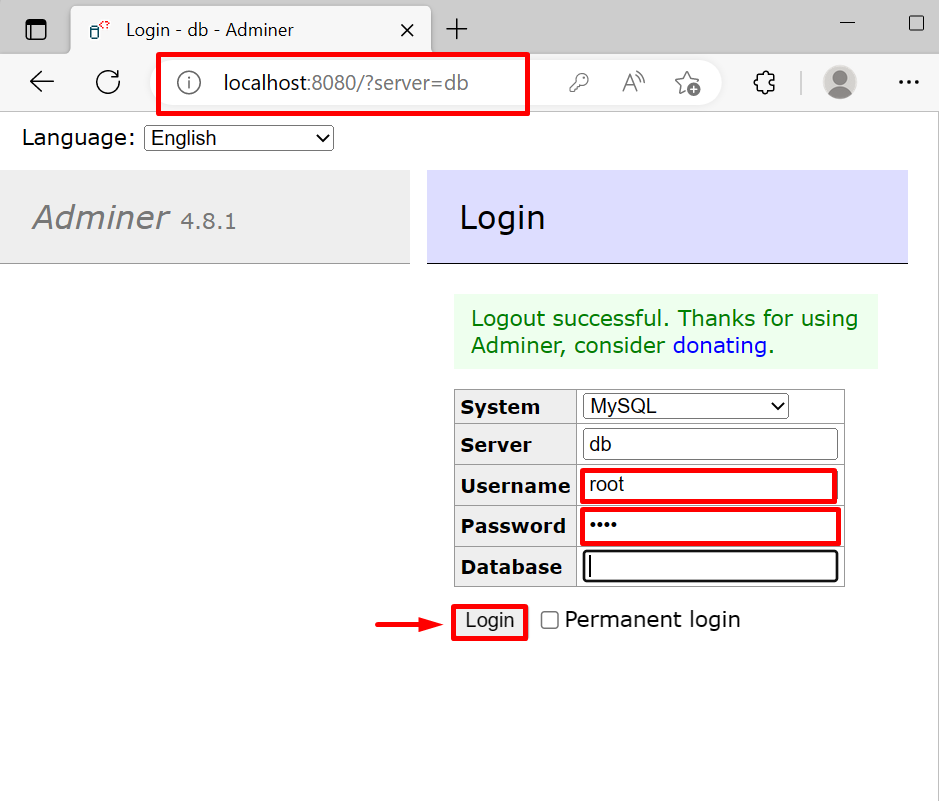
To use MariaDB, open the exposing port “http://localhost:8080/” of the “adminer” service and log in to the MySQL database. Provide the username “root” and password that you have set in the “MARIADB_ROOT_PASSWORD” key in compose file:
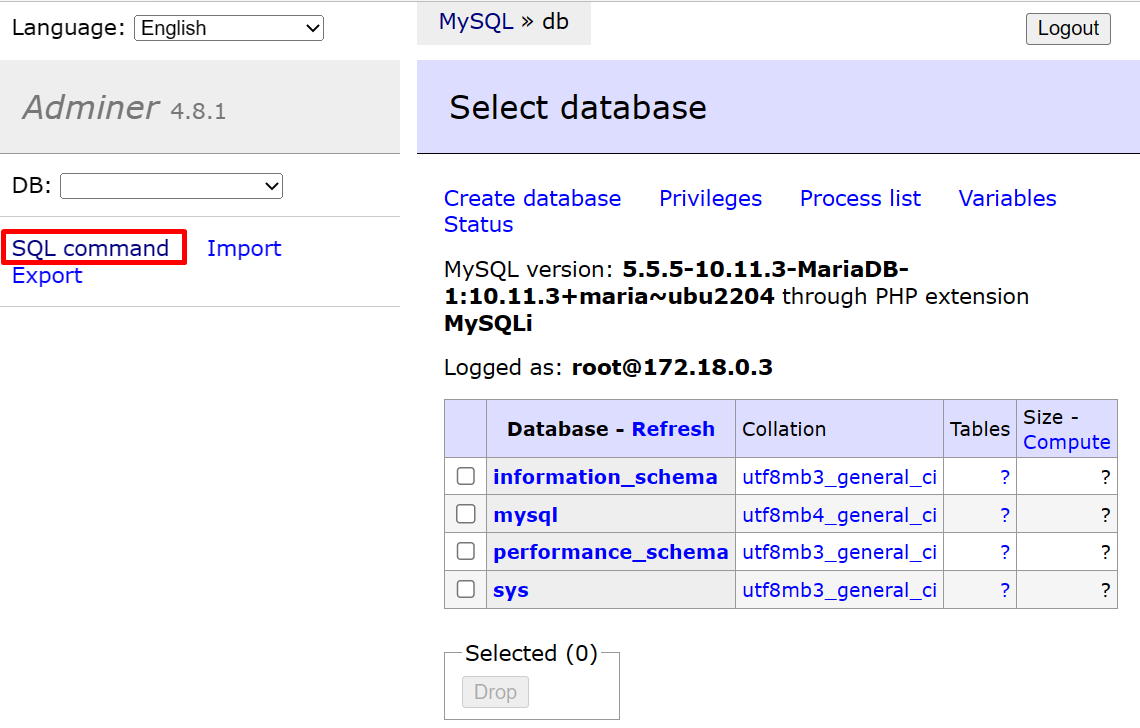
Upon doing so, the MariaDB database interface will appear on the screen. Click on the “SQL command” option to run SQL queries:
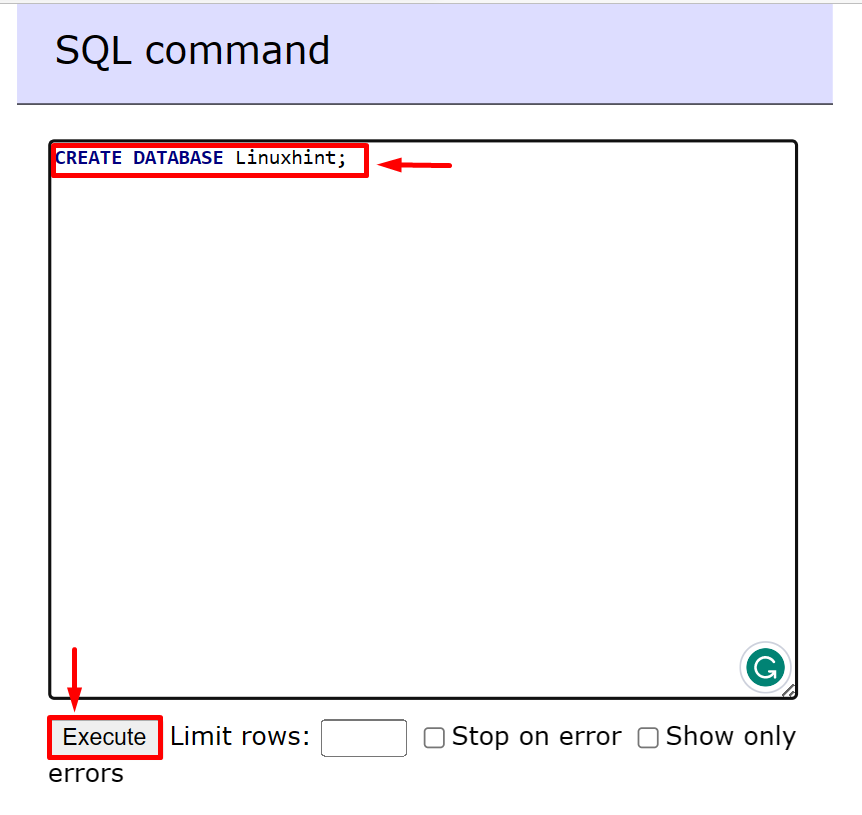
In order to create the new database in MariaDB, use the “CREATE DATABASE <database-name>;” query and hit the “Execute” button:
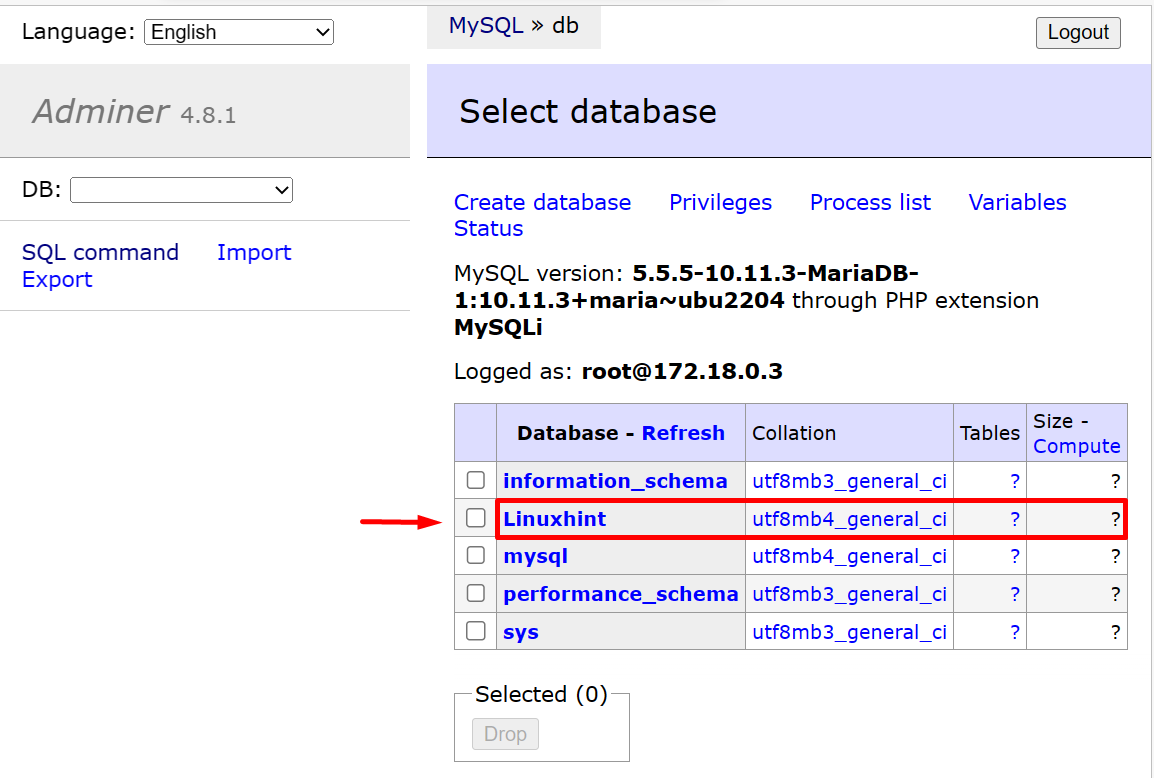
From the below output, you can see that we have successfully created the new database “Linuxhint”:
That’s all about installing the MariaDB database using Docker.
Conclusion
To install MariaDB the improved version of MySQL database, simply use the “docker run –name <cont-name> mariadb:latest” command. Users can also specify the environment variables while executing the command using the “–env” option. To access the MariaDB interface, first, execute the container shell using the “docker exec” command, then run the “mysql -u root -p” command. This article has elaborated on how to install and use MariaDB in Docker.