This article will illustrate the procedure to commit to a running Docker container.
How to Commit a Running Docker Container?
To commit a running Docker container, check out the below-listed steps:
- Display all running containers.
- Select a particular running container.
- Access the running container.
- Make some changes to the container.
- Commit a running container using the “docker commit <container-name> <new-image-name>” command.
- Verify committed changes.
Step 1: View and Select a Running Container
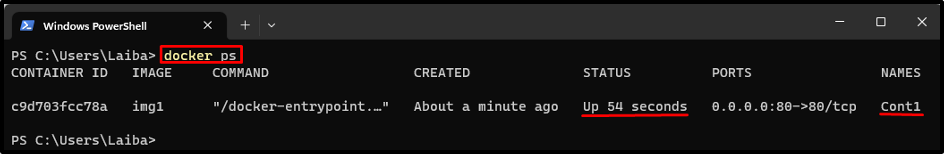
First, display all the running containers and select a specific container:
The above output shows that there is only one running container i.e., “Cont1” and we will use it in upcoming steps.
Step 2: Access Running Container
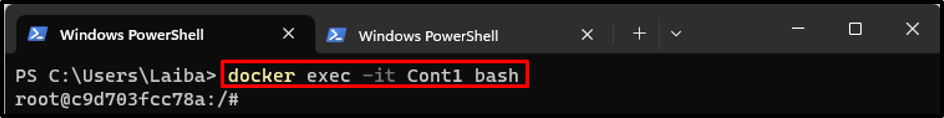
Then, execute the “docker exec -it <container-name> bash” to open the Bash shell inside the running container:
The above-provided command has opened a Bash shell and now users can execute the command within the running container.
Step 3: Make Changes in the Running Container
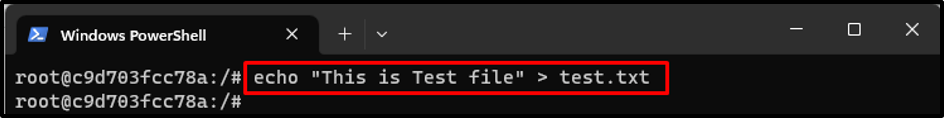
After that, make some changes to the running container. For instance, we have created a new file named “test.txt” file with some content:
The content has been stored in the “test.txt” file.
Step 4: Verification
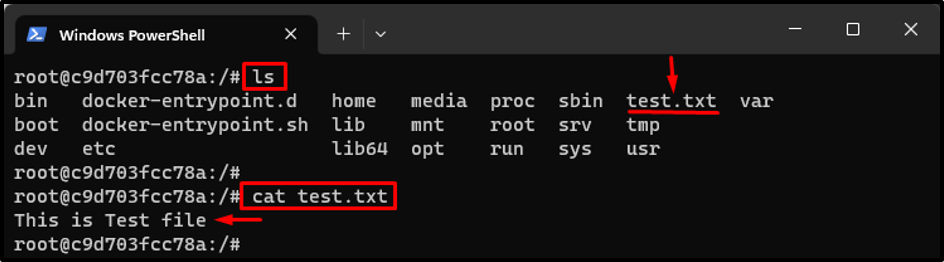
Type out the “ls” command and list all the container’s content to view the newly created file. Then, run the “cat <file-name>” command to view its content:
cat test.txt
In the above output, the newly created file “test.txt” and its content can also be seen in the terminal.
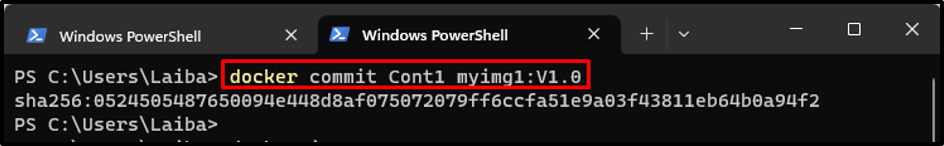
Step 5: Commit the Running Container
Now, keep the current container running and open a new terminal window. Then, enter the “docker commit <container-name> <new-image-name>” command to save the latest changes to a new image:
Step 6: Verify Committed Changes
For the verification, first, list all Docker images to view the new Docker image where the changes have been saved:
The new image i.e., “myimg1” with tag “V1.0” has been created successfully with new modifications.
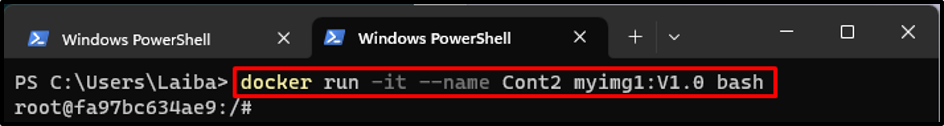
Now, build and start a new container from the newly created Docker image and access it is using the below-listed command:
Here:
- “-it” flag is utilized to start the interactive terminal session in the specified container.
- “–name” sets the container’s name to “Cont2”.
- “myimg1:V1.0” is the Docker image to use for the container.
- “bash” is used to start the bash shell in the container:
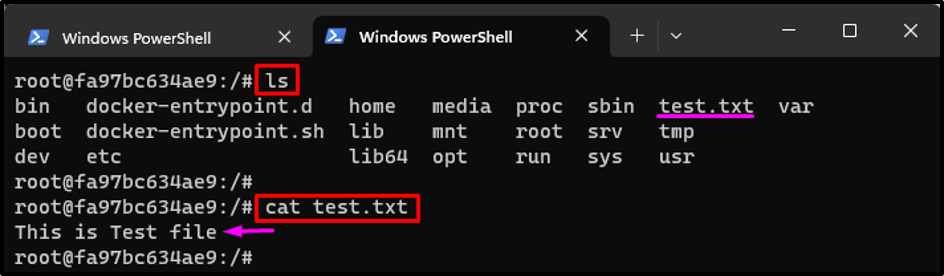
After that, use the “ls” to list the content of the new container and verify whether its content is the same as the previous container. Then, utilize the “cat <file-name>” command to view the file’s content:
cat test.txt
It can be observed that the content of the new container “Cont2” is the same as the previous container “Cont2”.
Conclusion
To commit a running Docker container, first, display all running containers and select a desired one. Then, access the running container and make some changes to it. Next, commit a running container via the “docker commit <container-name> <new-image-name>” command and verify changes. This article has explained the method to commit to a running Docker container.