This lesson includes following topics:
- 1: Introduction to ESP32 OLED Display
- 2: Wiring OLED Display Module to ESP32
- 3: Installing Required Libraries
- 4: Drawing a Progress Bar on OLED Display Using Arduino IDE
- 4.1: Code
- 4.2: Output
1: Introduction to ESP32 OLED Display
An I2C OLED display is a type of organic light-emitting diode (OLED) display that uses the Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) protocol for communication. OLED displays are known for their high contrast ratio, wide viewing angle, and fast response time, making them well-suited for a variety of display applications.
An I2C OLED display typically consists of a small OLED screen and a driver circuit that converts the I2C signals into the appropriate voltages and currents needed to drive the OLED pixels.
LEDs inside the OLED screen illuminate the pixels that display us different images and text. While on the other side the LCD screen uses a backlight for illuminating its pixels. Brightness of these pixels can be controlled pixel by pixel.
Now we will interface ESP32 with an OLED display.
2: Wiring OLED Display Module to ESP32
OLED screens mainly work on two communication protocols. These are I2C and SPI. Among these two SPI (Serial peripheral interface) is faster compared to I2C, but most of the time I2C OLED display is preferred because of a smaller number of wires.
I2C is a two-wire serial communication protocol that allows multiple devices to share a single set of data and clock lines, making it a convenient choice for connecting OLED displays to microcontrollers and other devices
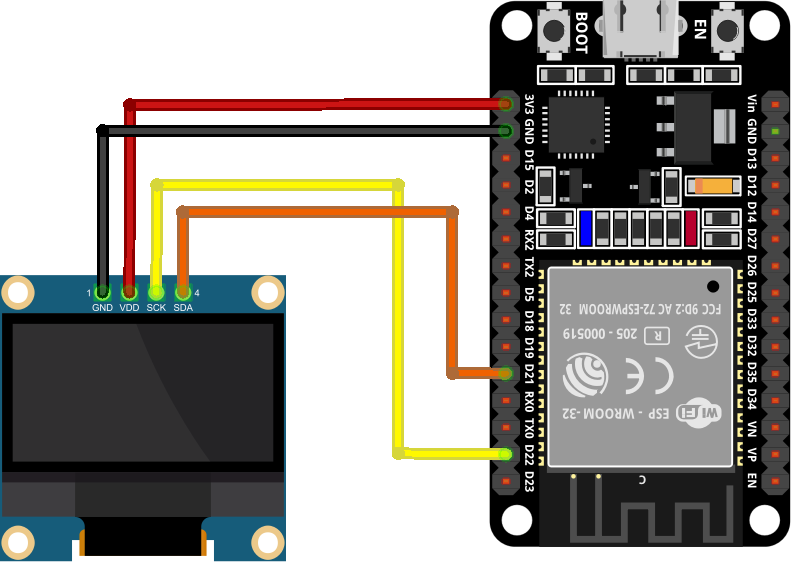
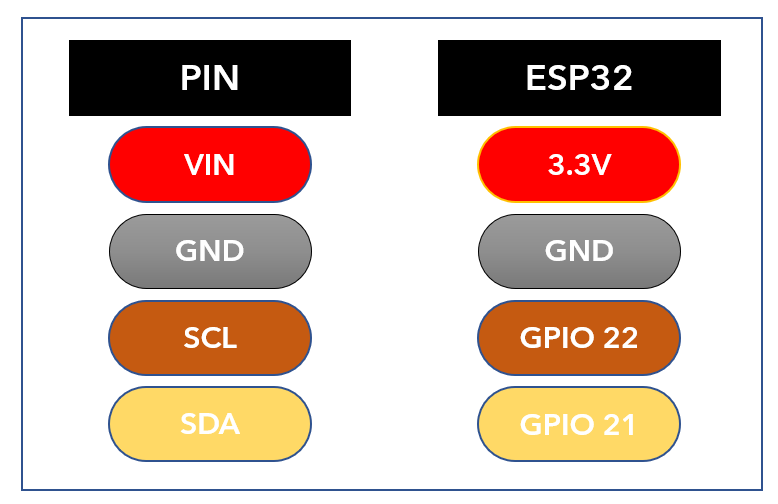
Using I2C OLED two pins SDA and SCL are enough for displaying images and text. The given image shows ESP32 with 0.96-inch (128×64 pixels) OLED screen.
ESP32 pins connection with OLED is as follows:
As we have interfaced ESP32 with an OLED display, now we will install the necessary libraries in the Arduino IDE so we can move forward with shapes displaying on the OLED screen.
3: Installing Required Libraries
For displaying images, we need to install the necessary libraries for OLED display in Arduino IDE. Without using these libraries ESP32 cannot display graphics on OLED.
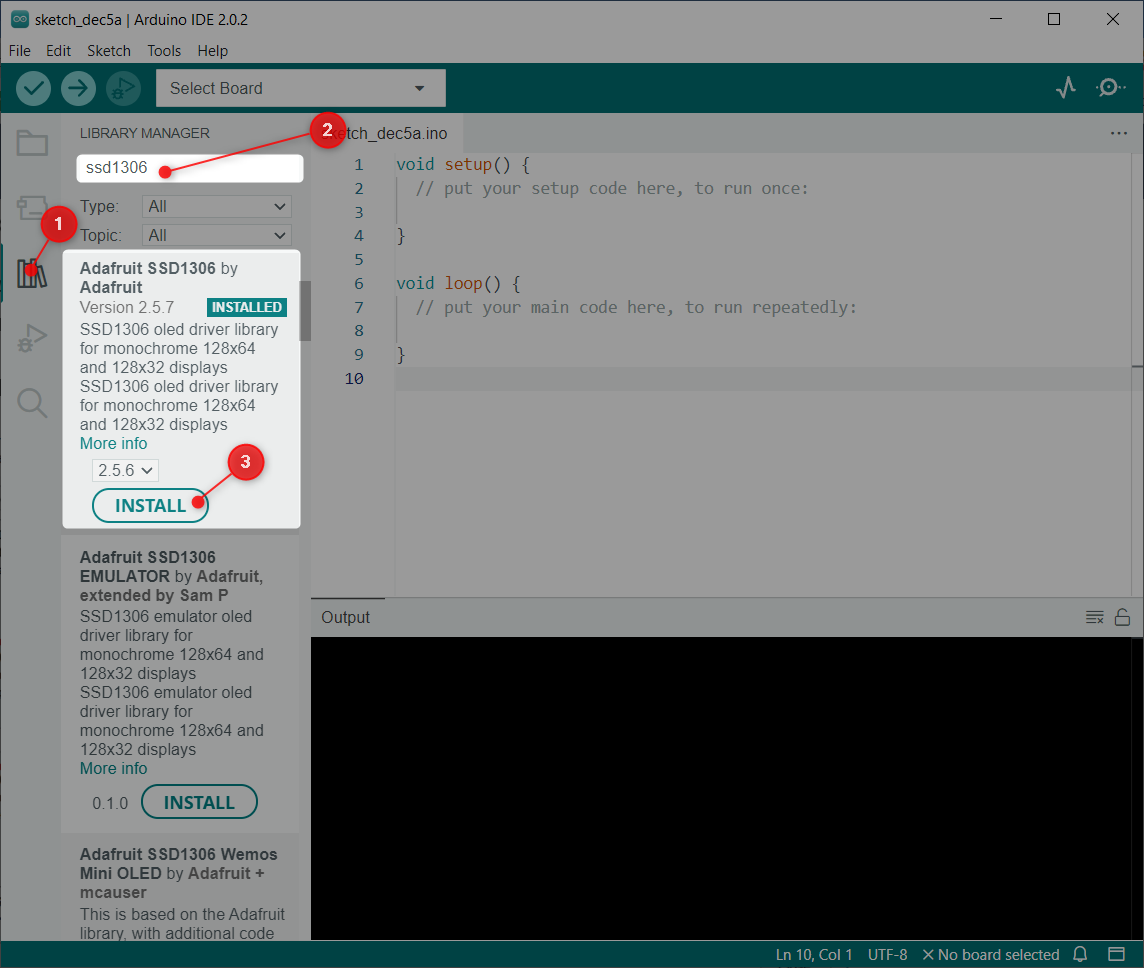
Mainly two libraries from Adafruit are used: SSD1306 and GFX library. First open the Arduino IDE and search the SSD1306 library. Install the SSD1306 OLED library by Adafruit. Other way of installing is going to: Sketch>Include Library>Manage Libraries:
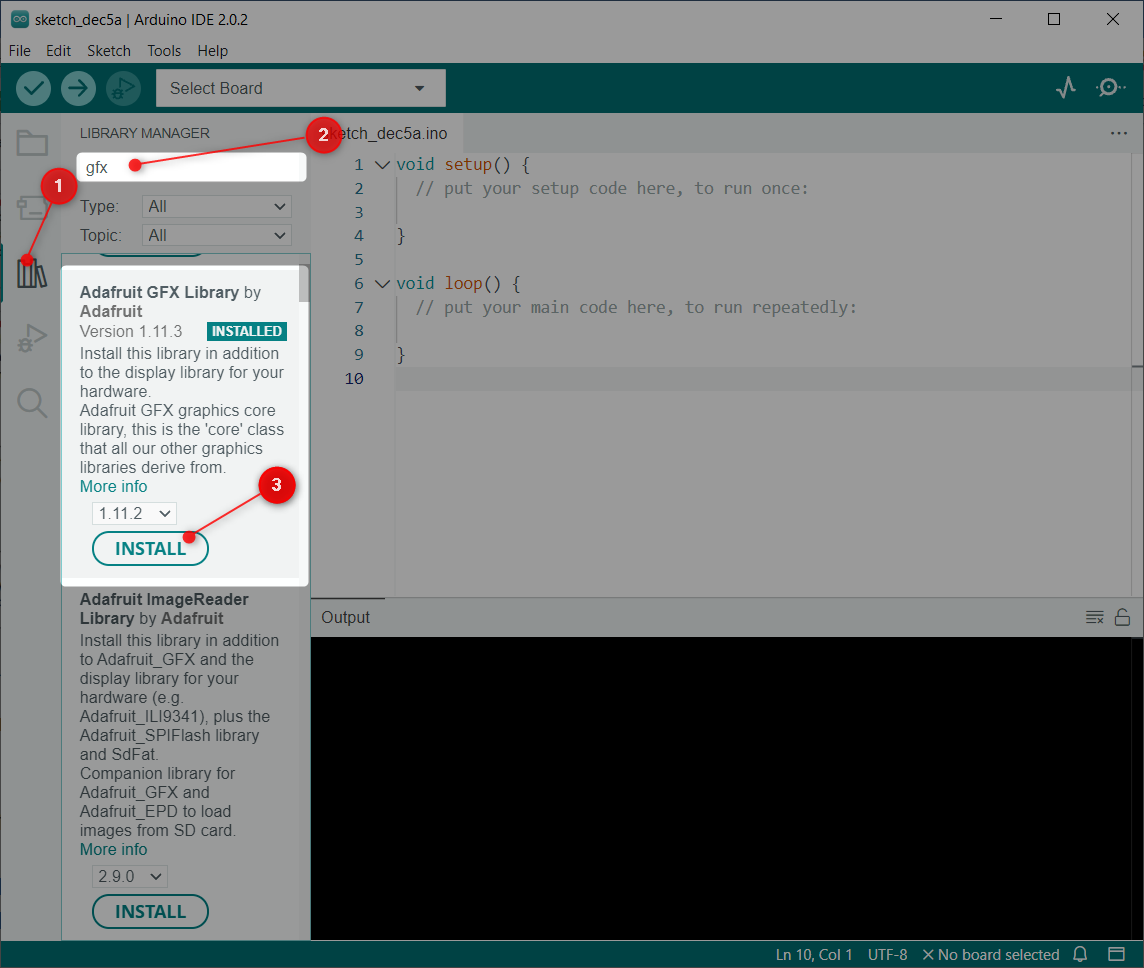
Now install the GFX library by Adafruit:
Now we have installed both libraries. Now we can easily program ESP32 with an OLED display.
4: Drawing a Progress Bar on OLED Display Using Arduino IDE
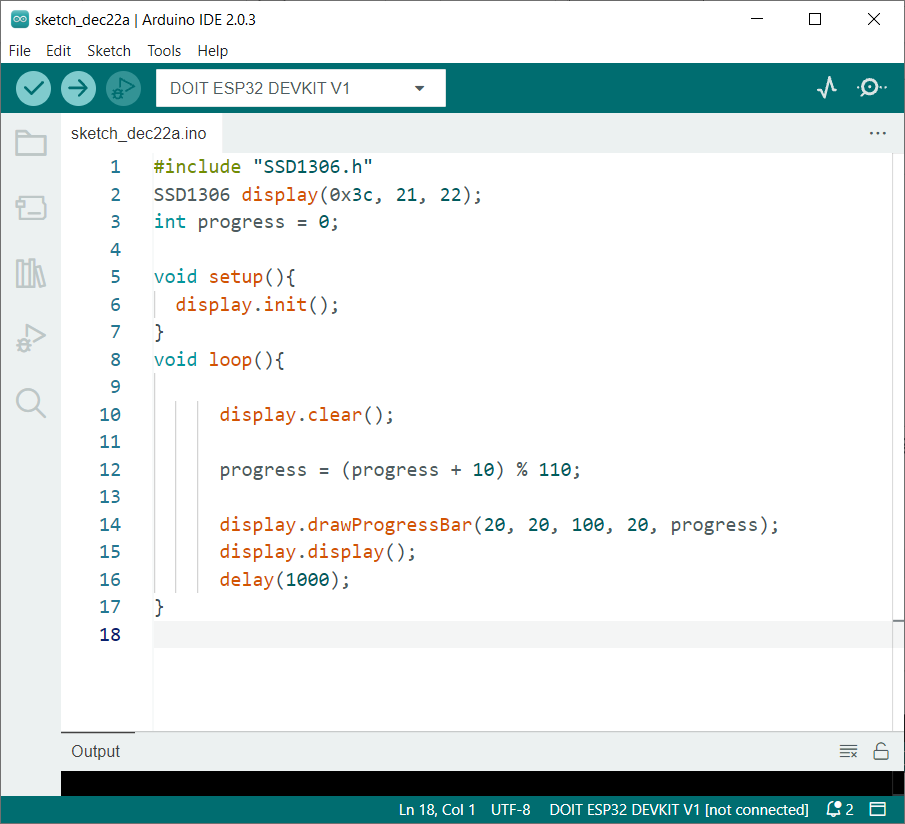
To draw a progress bar on an OLED screen we will be using the display.drawProgressBar(20, 20, 100, 20, progress); function.
This function takes 5 arguments:
- Position of center with respect to x-coordinate
- Position of center with respect to y-coordinate
- Third argument is width of the bar
- Fourth argument is height of progress bar
- Last argument is the actual progress which we pass an integer value between 0 and 100
After defining all these 5 parameters, upload the code to the ESP32 board.
4.1: Code
Open Arduino IDE, connect ESP32 and upload code:
Code started by including the necessary SSD1306 library files. After that we defined the I2C address and the I2C pins for communication.
Remember to check the I2C address first before defining. For checking the I2C address of any device upload the code given in tutorial How to Scan I2C Address in ESP32 Using Arduino IDE.
If you are using more than one I2C device with the same address, you have to change the address of any of them first.
Next in code we initialized the OLED display and defined a progress formula.
Progress formula will calculate the progress and store value in global variable progress. We simply sum the 10 to the current progress value and get the remainder by dividing it with 110 using the modulus operator. Once the progress bar is completed, we will have 110%110 which gives us 0. This will automatically start the bar again from zero.
Next drawProgressBar is called and this function will display the progress bar according to the current value of variable progress. This function will take 5 arguments as explained earlier.
SSD1306 display(0x3c, 21, 22);
int progress = 0;
void setup(){
display.init();
}
void loop(){
display.clear();
progress = (progress + 10) % 110;
display.drawProgressBar(20, 20, 100, 20, progress);
display.display();
delay(1000);
}
4.2: Output
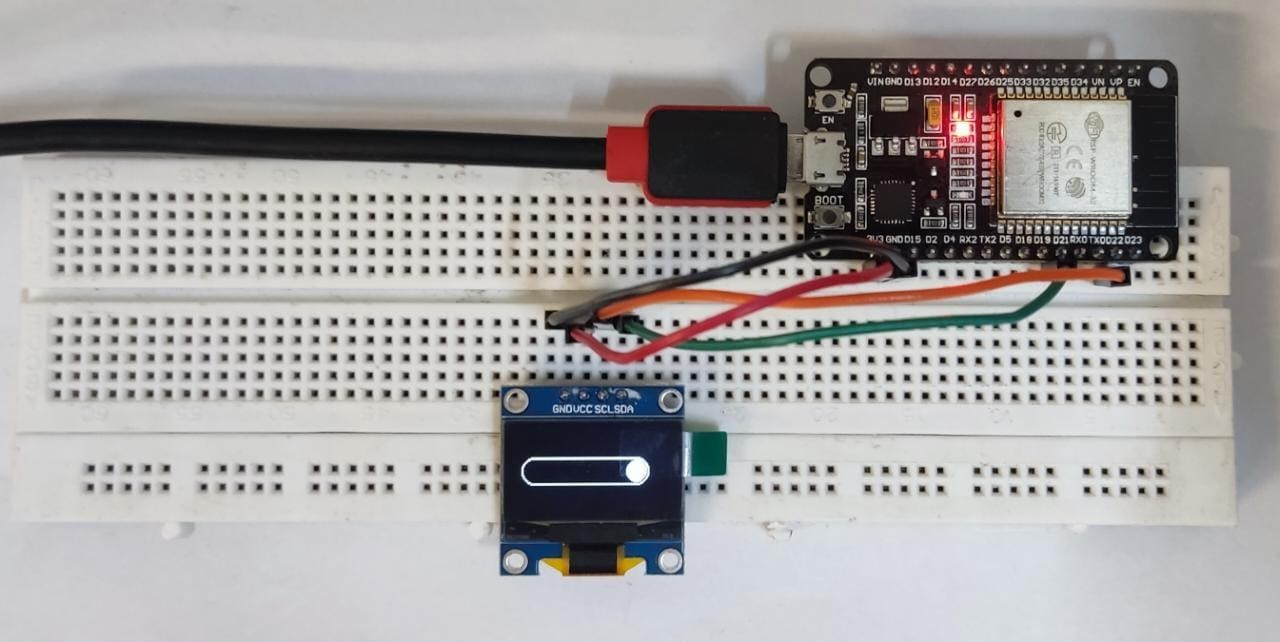
After uploading code in ESP32 below output will appear on the OLED screen. This output shows the progress bar is at 10% which is the initial set position:
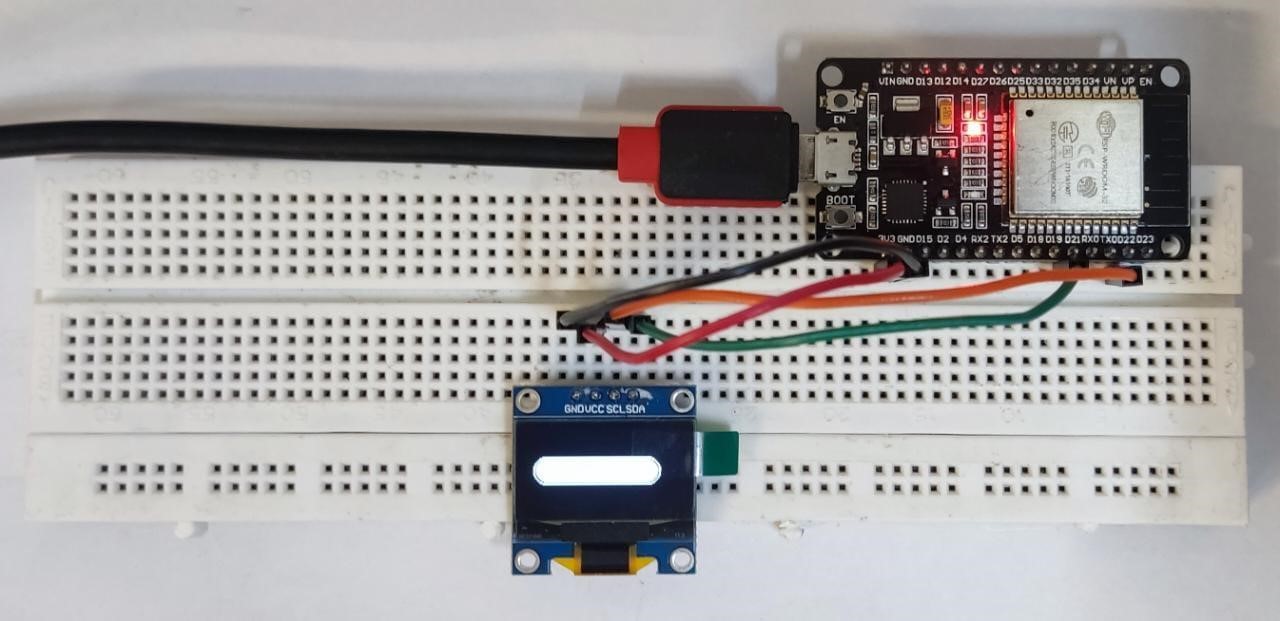
Now the progress bar is at 100% which means a certain task is completed:
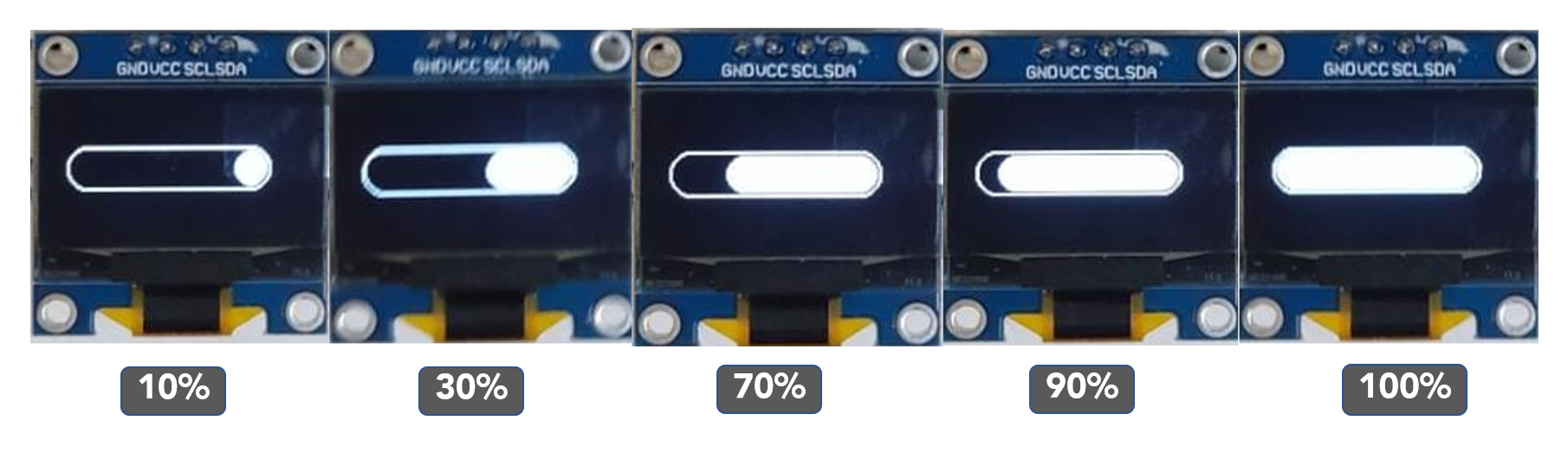
Here are the output stages in between the 0% and 100%. We have set the progress interval to 10:
Conclusion
Progress bar is a great way of displaying real time progress of a project. Using OLED displays with ESP32 we can take real time data and display it over the screen. Using the code given any of the data can be represented in the form of progress bar.