The significant components of Docker are Docker images, Docker containers, Docker registry, and Docker volume. The Docker volumes are the external file system that is used to preserve the data produced by the Docker containers. The Docker volume is entirely independent of the container’s life cycle as it is managed on the host. Therefore, it is also referred to as a backup file system and is easily shareable among other containers.
This blog will demonstrate the method for mounting the Docker volumes with containers.
How to Mount Docker Volumes?
The simple “-mount” or “-v” option is utilized to mount the Docker volume. The “–mount” option specifies the “source volume” and “target dir”. To mount the Docker volume with the container, follow up on the given instructions.
Step 1: Create Docker Volume
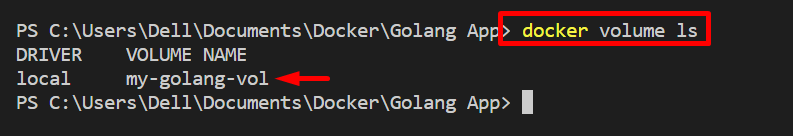
First, create a new Docker volume with the help of the “docker volume create <volume-name>” command as shown below:
After that, verify if the volume is created or not by viewing the list of the Docker volumes:
Step 2: Inspect Docker Volume
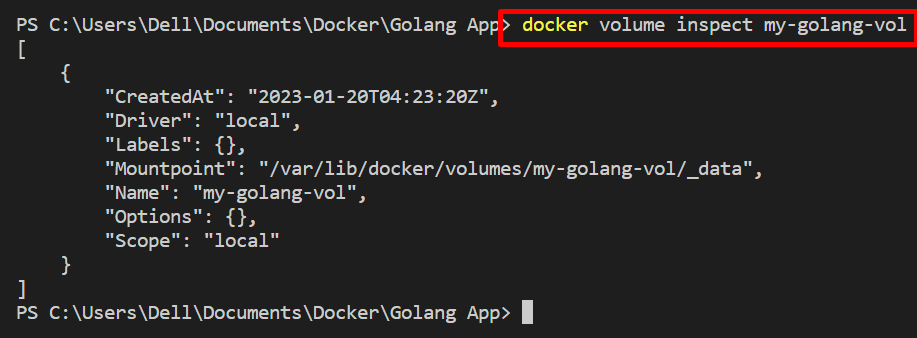
In order to check the details about created volume, inspect the volume through the “docker volume inspect” command:
The above command shows the name, mountpoint, driver details of the Docker volume:
Step 3: Mount the Docker Volume
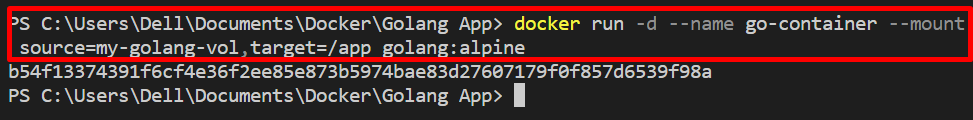
Next, mount the newly created Docker volume with the container through the provided command. This command will run and generate the Docker container using the image:
The description of the above command is as follows:
- “–name” is used to specify the container name.
- “-d” is utilized to execute the container in the background.
- “–mount” is used to mount the volume with the newly generated container.
- “source” variable is used to specify the volume.
- “target” is used to define the destination path.
- “golang:alpine” is an image that creates a new container:
Step 4: Inspect the Docker Container
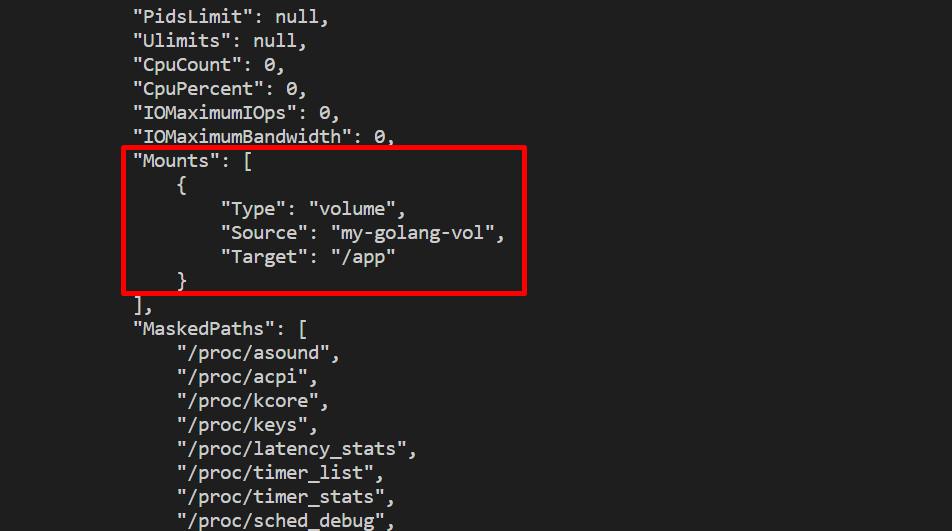
Inspect the Docker container to verify if the volume is mounted or not:
From the below output, you can see that the volume has been successfully mounted with the Docker container:

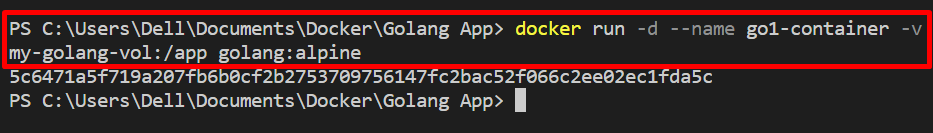
Alternatively, users can utilize the “-v” option to mount a volume with the container, as shown below:
We have demonstrated the procedure for mounting the Docker volumes.
Conclusion
To mount the Docker volume, first, create a new volume. Then, utilize the “docker run -d –name <container-name> –mount source=<volume>,target=<path> <image>” command to mount a newly created volume. This command will create a new container using a specified image and mount the Docker volume with the container. This write-up has demonstrated how to mount Docker volumes.