Sometimes, we come across such a situation where we want to avoid some items or contents between the group of the same items. To specify them manually costs time. So, to avoid time consumption, CSS refers to such effective and efficient properties to make use of them in the code that is quite easily understandable and makes the code manageable. This is done by the CSS “not the first” property.
Not:First-Child Property
This CSS property is used to select all the HTML contents of the same type other than the first one. This property is opposite to the CSS property of “CSS first of type” which is responsible for affecting only the first of most HTML content of the same type. Besides adding a style to all the tags by the inline CSS avoiding the first one, this not:first-child property removed the ambiguity that is created by having the mess of inline CSS that makes the code hard to understand and complicated. We only add a small piece of code in the internal or external CSS by specifying the HTML content where we want to apply this property. Then the first child is automatically affected.
Syntax:
The syntax for the not:first-child property is as follows:
Content_name : not (:first-child) {
Property: value; \\ Any effect that we want to apply on the HTML items other than the first one.
}
Example 1: Not:First-Child of the Paragraph
To elaborate on the concept of not having a first child, we use the <p> paragraphs of the HTML content to apply this property. Paragraphs are the HTML contents that are said to be a bunch of text lines. These lines are sequenced and aligned in such a way to form a paragraph. The code contains the body tag. We use the two simple headings and the three paragraphs that contain the simple text of a few words with them. We use a sample text of Lorem Ipsum.
We just need to see the results of the property. To make it quite simple, only this content is declared. Then, close the tags of the body.
The head section only contains the style tag to make it an internal CSS.
Use the paragraph tag <p> with the not:first-child property to apply all the effects on all the paragraphs except the first one. We add the red font color to the paragraphs. Close all the opened tags.
Save the code with the html extension to the text editor. This extension makes the icon of the file as the default browser. This icon assures that the file is a web page.
Example 2: Not:First-Child on the List
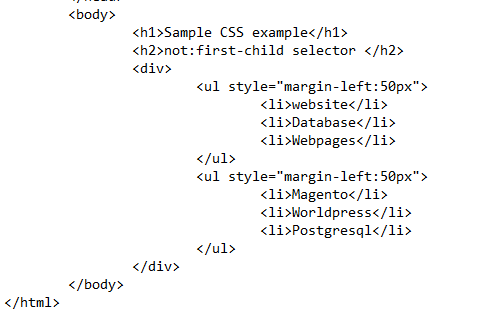
HTML lists are an important way of representing the text. To implement the CSS property of the first-child selector, we use the two lists. To elaborate further, we first need to have the know-how of the HTML lists. Two types of lists are created through the HTML language – an unordered list <ul> and an ordered list <ol>. The way of declaring is the same for both of them. Inside <ul> and <ol>, all the items are written with <li> tags.
Now, coming back to the example, we used two unordered lists. Both lists are declared inside the div. First, consider the HTML body section of the code. Two simple headings, <h1> and <h2>, are declared. Then, the div tag is used to declare a div container. Inside the div, the first <ul> list is declared. An inline CSS for the margin property is added. This margin property is applied on the second div as well.
A margin property is the CSS value of the distance of the object from the border of the background display. For instance, the margin of the list here is declared to create the list at a specified distance.
Both the lists are declared similarly having three list items. Now, close all the tags and head towards the internal CSS. The heading one is applied by the font-color property. Then, the main part of the code not:first-child property is applied.
This property is applied on the <ul> tag, as both lists are unordered. But make sure that these lists lay independently or are present inside any other container. As we know that we declared both the lists inside the div, we need to mention the div with the <ul> tag so that the property is applied on all the lists inside the div except the first one.
Background-color: purple;
Color: white;
Font-weight: bold;
Width: 40%;
}
The div and <ul> are applied with the features of having a background color and the font color. The font weight is set to BOLD. The width of the list is also declared.
Close all the tags. Save the file and implement it on the browser to see the results.
You will see that the first list appears by default without any change applied to it. While the second list is affected by all the values and properties that we applied to the tag of the unordered list in the head section.
Similarly, if we apply any property to all the <ul> tags like we did before but without using the not:first-child property for the lists, what will happen?
Font-style: italic;
}
We set the font style to italic in all the ul of the div. But the values that are written inside the not-first child selector property are applied on all the lists except the first one.
Apply both the styles on the same body code. Save it and implement it. We see that the italic style is applied on all the list items because we did not mention the not:first-child property with them. While the values that have the selector is applied only on the second list.
Conclusion
The CSS not:first-child gives us knowledge regarding the use of CSS properties on all the elements of HTML rather than the first one. The condition to implement this phenomenon is that all the HTML contents must be of the same type, otherwise this effect will not be applied. From the beginning, we talked about the HTML and CSS basic usage. Then, the CSS not:first-child is explained by giving a syntax that is followed by applying this property. Then, we implemented this concept in two different HTML contents: one is the paragraph and the other one is the div container.