CSS Wrap Text Property
This CSS property is a text-related property. The alignment property of the text is used here to adjust the text with the alignment inside any outer container or by using a small area to display independently. It allows the long words or sentences to be fixed in a particular area or container. You can also say that the long words are broken into two or more portions so that they can be wrapped into the next line. We need to apply such tags to minimize the chance of the text wrapping so that the text lies on a single line. All these effects are applied according to the requirements.
To accomplish the wrap text or not wrapping property, we will use a special CSS property which is the white-space property.
White-Space Property
This is the CSS property that assists to control how the line-break CSS property and white-space property are used in any web page creation and design. White-space is the area that is present between the inner HTML content and the boundary of the outer HTML content. This property determines how the white-space or the area inside the HTML element is handled or controlled.
Sometimes, the space is created automatically. We need to remove it, or in other cases, the special CSS effects are applied to manage the white-space inside the element. There is the same approach to apply or remove the CSS wrap text properly.
The basic syntax of the wrap property is:
The value can be any of the previously given values that is given to the white-space property. If the white-space property is provided by the normal value, this means that the white-space around the text is according to the standard chart of normality. The pre-wrap causes the white-space of the left side inside the element. This space is between the text and the outer element, so the left side of the element will have more space with the “pre” text that has the overall space before the text. The pre-line causes a line gap between the text and the outer element boundary.
If we don’t want to wrap the text, the white-space property is not necessary to be applied first. But if the text wrapping is already done and we need to remove it, we use the “nowrap” value to this property.
We will implement this phenomenon in the following examples:
Example 1: Don’t Wrap the Text with HTML Tables
In this example, we will handle the white-space property in the table contents. A table is an HTML container that carries the text and other contents inside it. The table differs from the div container since it has rows and columns in it. A table has two types of tags further in it – the head tag and the body tag. The head part contains the table rows and the body part also contains the table rows to add the table data. Whereas, the html data is entered in the table in the form of rows each inside the heading tag <th> of the body and the <thead> contains only the readings.
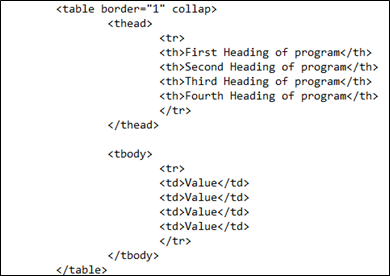
In the example, the table is applied with the border property that is 1 collapse.
<table border= "1" collap>
This border prevents the table cells from getting wrapped. The <tr> and <th> are used to add the items in the table. Close the <thead> tag. These rows contain the heading of the table. Now, use the body <tbody> tag. This section contains the values regarding the heading. All the further rows are entered in the body section. We use the <td> inside the <tr> tag for the data inside the table rows. Close all the tags and save them.
After the HTML body code, we now use the CSS body to add the effects of the white spacing. There is no need to apply the internal CSS as we will directly use the <th> tag like the <h1> and <p> tags. Inside the style tag, the “th” is applied by the white-space effect. We display the text inside as a whole sentence on a single line, so we use the “nowrap” property.
<th {
White-space: nowrap;
} </style>
Now, save the code in the html extension. Execute the file in the browser to see the resultant value.
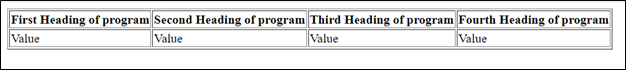
Upon execution, you will see that a table is created with the heading that is declared on the single line, although it is long enough to avail the property of the CSS white-space.
Example 2: Don’t Wrap the Text with the Paragraph
Another example we used here is the paragraph. These two paragraphs contain a single word of several letters. If a sentence is used in the paragraph, it is easy to break the sentence in place between the words. But a single word with numerous characters without space is difficult to hold without wrapping the text.
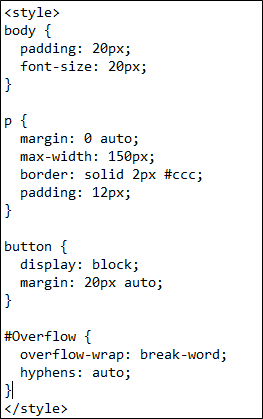
The second paragraph is applied with the CSS id. This id is declared in the head section, making the internal CSS. Both of the paragraphs have a single word with numerous letters. Now, consider the CSS of this code. First, the whole body is applied with a padding effect and a font size.
The paragraph is applied with auto margin value. This value is the distance between the inner content and the outer box. We also added the padding property to both paragraphs. The distance between the paragraph and the border is calculated through this padding value.
The overflow id contains the text wrap property and gives the value to break the words so the text can fit inside the border.
Overflow-wrap: break-word; }
Upon execution, you will see that the paragraph in which we have not applied any class for the white space exceeded the limit that we initiated. Whereas the second paragraph is limited on where we applied the overflow-wrap effect to break the word.
Conclusion
This article is helpful when we need to understand the concept of white-space in the HTML content. If we want to add this white-space in the HTML content value, specifically in the text, the text will be broken into separate words and will utilize two or more sentences. But if we don’t want to wrap the text with the CSS white-space property, the text will be displayed in a single line without a word break. We used two examples to elaborate the CSS “don’t wrap text” property with the table and paragraph.