In this article, I am going to show you how to setup Bluetooth devices on your Raspberry Pi running the Raspberry Pi OS. So, let’s get started.
Things You Will Need:
To follow this article, you will need the following things:
- A Raspberry Pi 3 or Raspberry Pi 4
- A micro-USB (Raspberry Pi 3) or USB Type-C (Raspberry Pi 4) power adapter.
- A 16 GB or 32 GB microSD card with Raspberry Pi OS (with the desktop environment) flashed.
- Network connectivity on the Raspberry Pi
- A laptop or a desktop computer for VNC remote desktop access to the Raspberry Pi.
NOTE:
If you don’t want to access your Raspberry Pi remotely via VNC, you need to connect a monitor, a keyboard, and a mouse to your Raspberry Pi as well. I won’t need any of these as I will be connecting to my Raspberry Pi remotely via VNC. My setup is called the headless setup of Raspberry Pi.
If you need any assistance on flashing the Raspberry Pi OS image on the microSD card, check my article How to Install and Use Raspberry Pi Imager.
If you’re a Raspberry Pi beginner and you need any assistance on installing Raspberry Pi OS on your Raspberry Pi, check my article How to Install Raspberry Pi OS on Raspberry Pi 4.
Also, if you need any assistance on the headless setup of Raspberry Pi, check my article How to Install and Configure Raspberry Pi OS on Raspberry Pi 4 Without External Monitor.
Pairing Bluetooth Keyboard, Mouse, and Audio Devices
On Raspberry Pi OS, the default Bluetooth applet (on the top right corner) will let you connect to a Bluetooth input/output device like a keyboard, a mouse, a headphone, or a speaker.
I don’t have any Bluetooth keyboard, mouse, headphone, or speaker. So, I can’t show you exactly how to connect to one. I do have an Android smartphone. It has Bluetooth. I will show you how to pair it with the Raspberry Pi OS. The process should be similar and easier for a Bluetooth keyboard, mouse, headphone, or speaker.
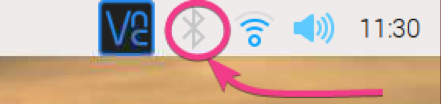
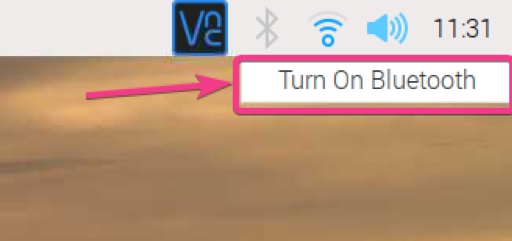
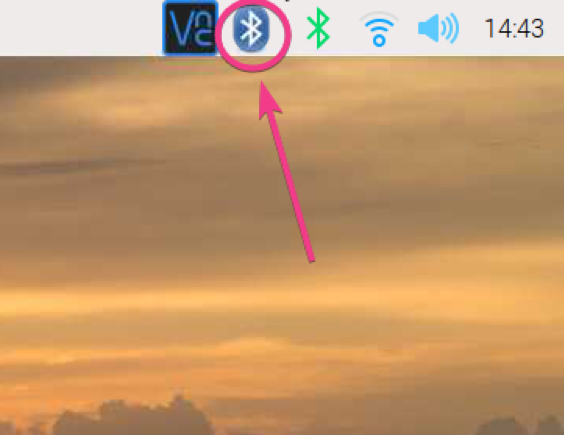
First, right-click (RMB) on the Bluetooth icon ( ) and click on Turn On Bluetooth as marked in the screenshot below.
Bluetooth should be turned on. The color of the Bluetooth icon should be changed to blue.
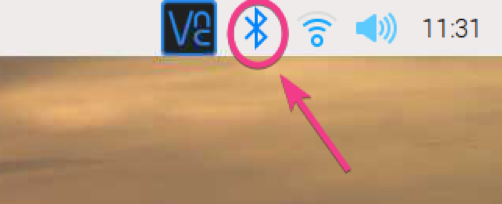
To pair a Bluetooth device, right-click (RMB) on the Bluetooth icon and click on Add Device… as marked in the screenshot below.
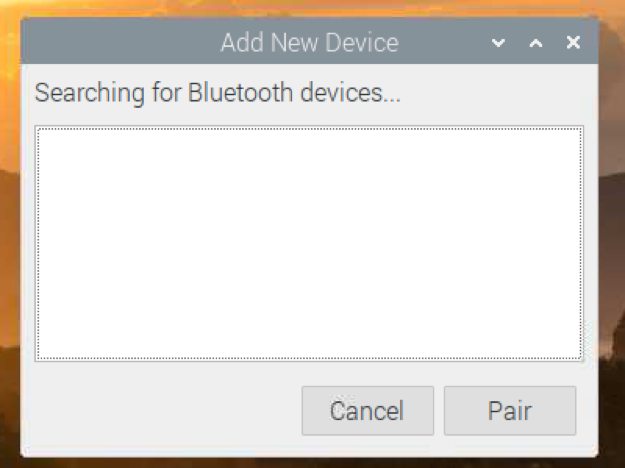
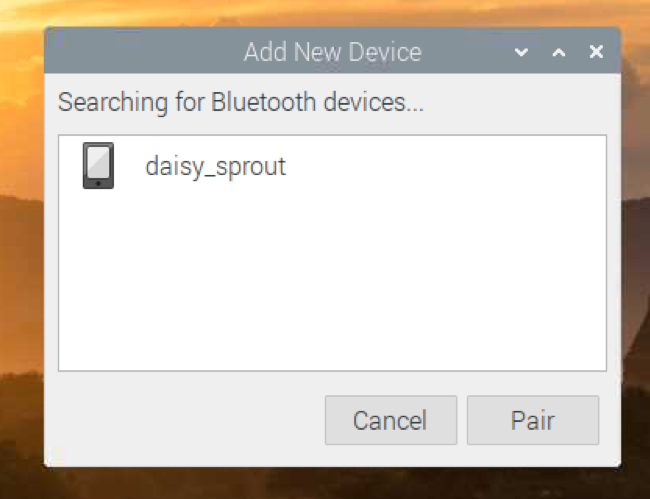
As you can see, it’s searching for a new Bluetooth device.
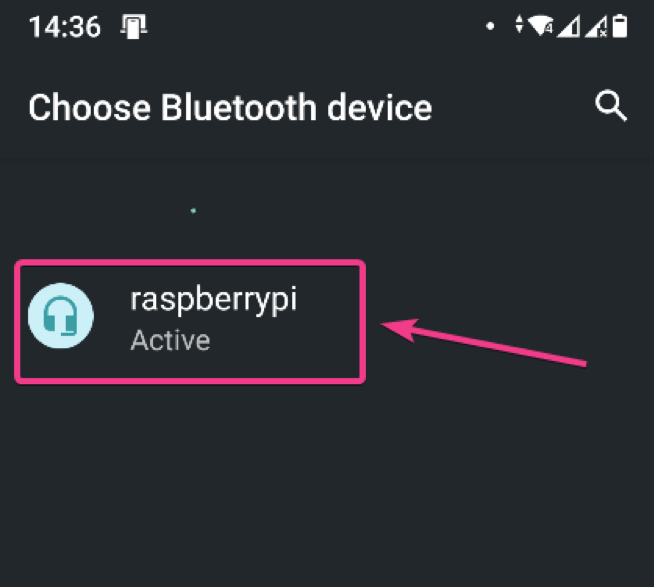
Once I have turned on Bluetooth on my Android smartphone, it detected my device as you can see in the screenshot below.
To pair the Bluetooth device, select the device and click on Pair.
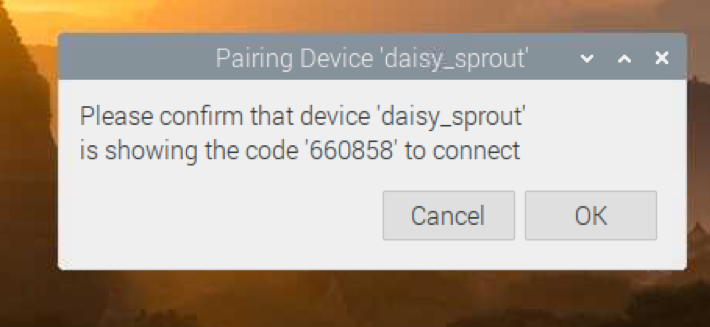
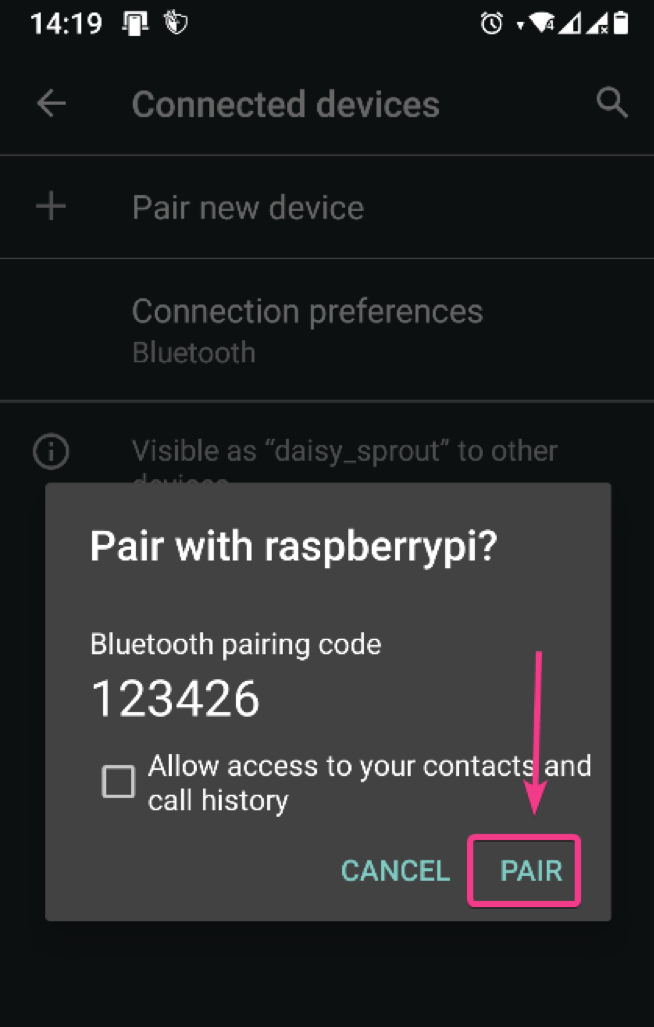
You should see a 6-digit code on the screen.
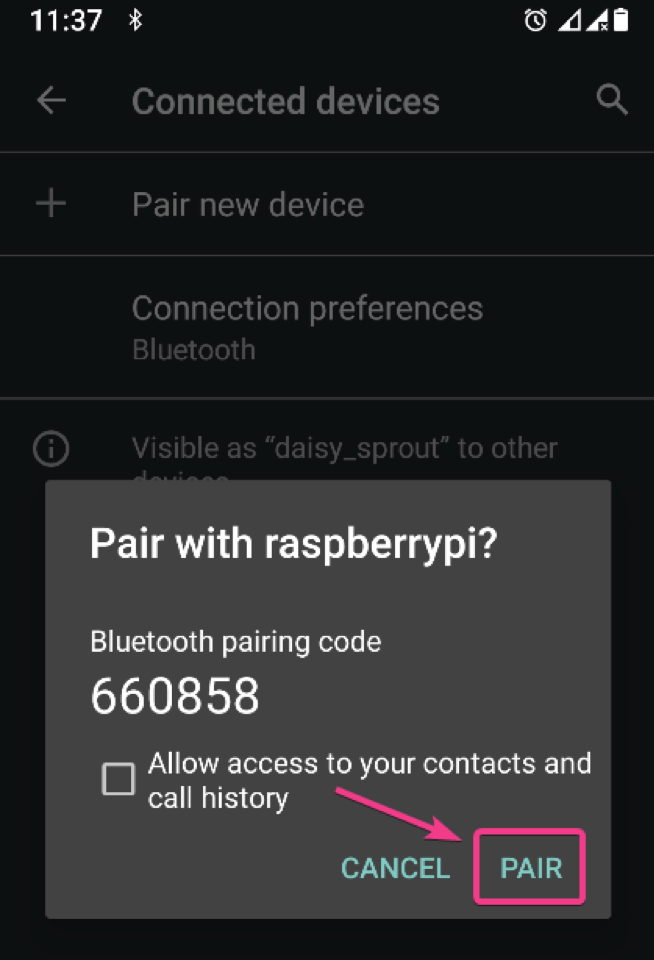
You should also get a pairing request on your phone. Make sure the 6-digit number is the same. If it is, click on PAIR.
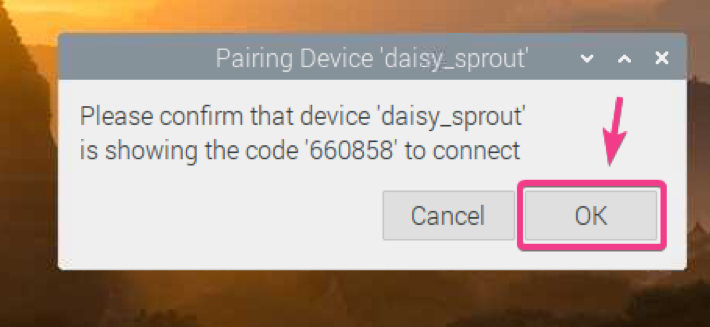
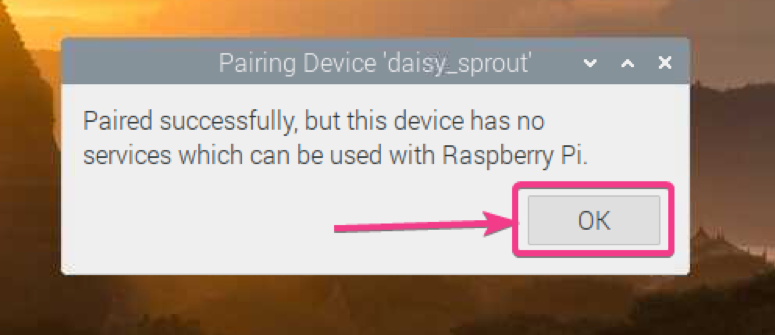
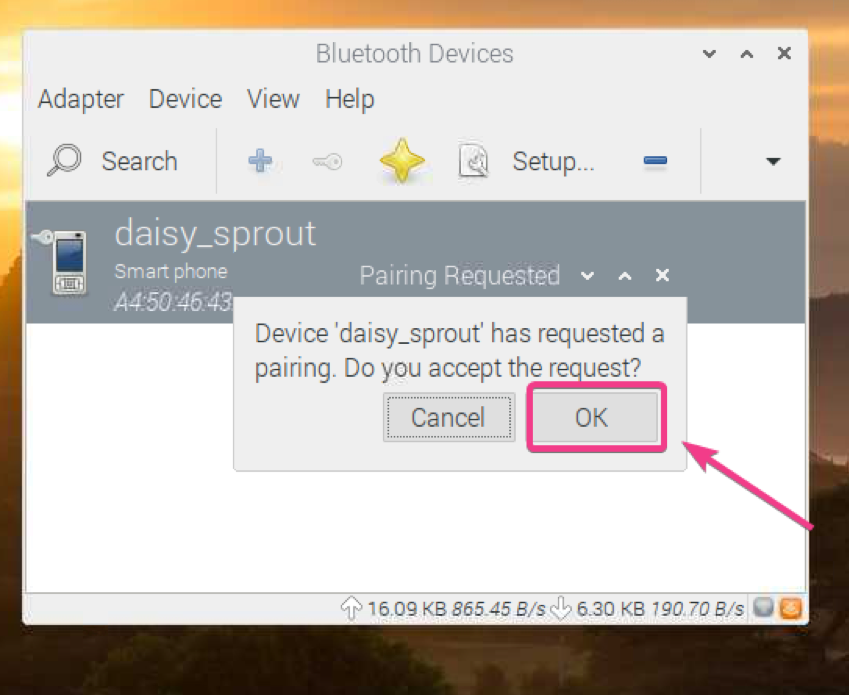
Click on OK.
Your Bluetooth device should be paired. Click on OK.
Making the Raspberry Pi Bluetooth Discoverable:
To connect to some Bluetooth devices, your Raspberry Pi Bluetooth needs to be discoverable by these devices.
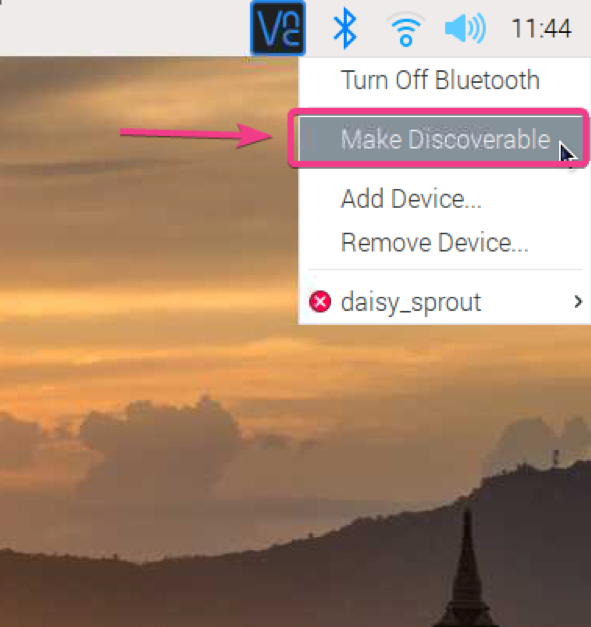
To make your Raspberry Pi Bluetooth discoverable, right-click (RMB) on the Bluetooth icon and click on Make Discoverable as shown in the screenshot below.
The Bluetooth icon should start blinking. It means that the Bluetooth of your Raspberry Pi is now discoverable.
Transferring Files with Bluetooth:
If you want to transfer files from your Raspberry Pi to other devices, or other devices to your Raspberry Pi using Bluetooth, then you need a Bluetooth Manager. There are many Bluetooth managers out there. But in this article, I am going to use Blueman Bluetooth Manager.
Blueman is available in the official package repository of Raspberry Pi OS. So, it’s very easy to install on the Raspberry Pi OS.
First, update the APT package repository cache with the following command:
Update all the existing packages of Raspberry Pi OS with the following command:
To confirm the upgrade, press Y and then press .
The APT package manager should start downloading all the required packages from the internet and install them one by one. It may take a while to complete.
At this point, all the updates should be installed.
For the changes to take effect, reboot the Raspberry Pi with the following command:
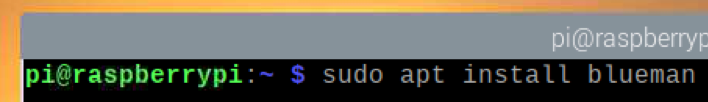
To install Blueman, run the following command:
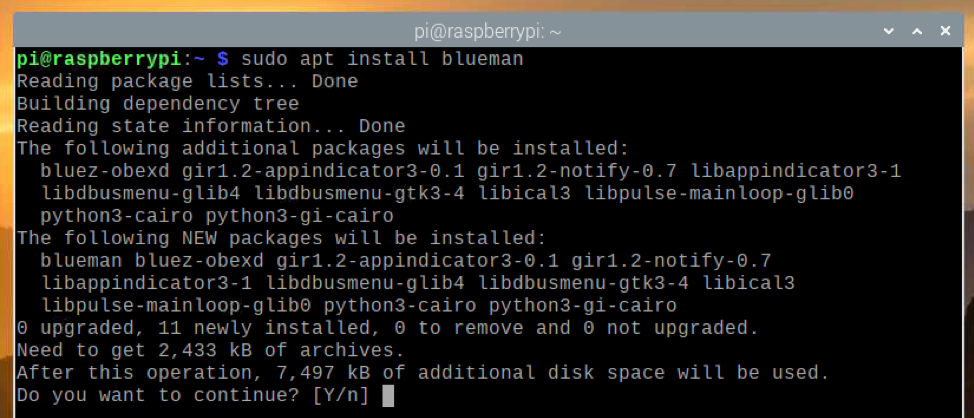
To confirm the installation, press Y and press .
The APT package manager should start downloading all the required packages from the internet and install them one by one. It may take a while to complete.
At this point, Blueman should be installed.
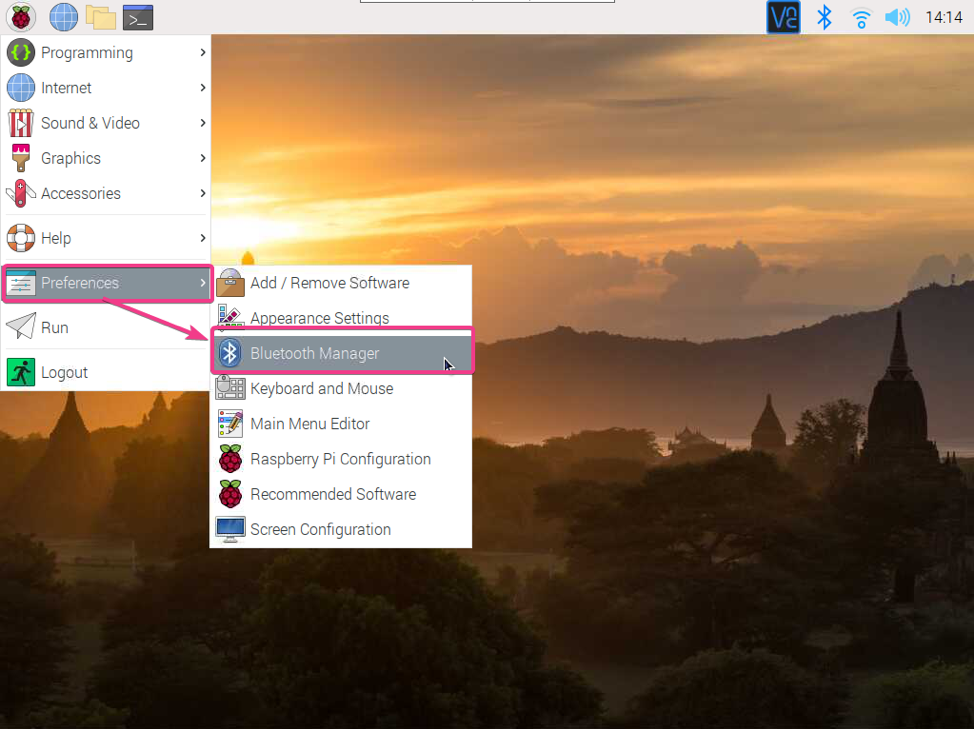
Once Blueman is installed, you can start Blueman from the Raspberry Pi OS Menu > Preferences > Bluetooth Manager.
If Bluetooth is turned off, you should see the following window. Click on Enable Bluetooth to enable Bluetooth.
Blueman should start.
Blueman icon ( ) should also appear in the top menubar.
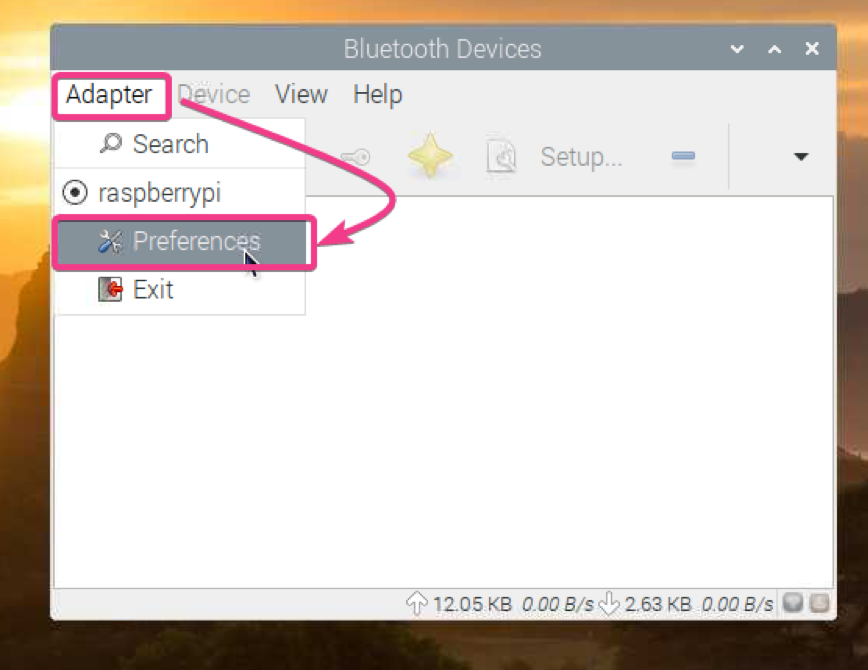
If you want your Raspberry Pi to be visible to other Bluetooth devices, go to Adapter > Preferences from Blueman as shown in the screenshot below.
Then, select Always visible from Visibility Setting.
If you want, you can also set a name for your Bluetooth device in the Friendly Name section.
Once you’re done, click on Close.
To search for a Bluetooth device, click on Search.
Blueman should find your Bluetooth device.
To pair with the Bluetooth device, right-click (RMB) on the device from the list and click on Pair.
Blueman should show a 6-digit number.
You should also get a pairing request on the selected Bluetooth device. If the 6-digit code matches, click on PAIR.
Then, click on Confirm on the Blueman side.
Click on OK.
The device should be paired. Click on OK.
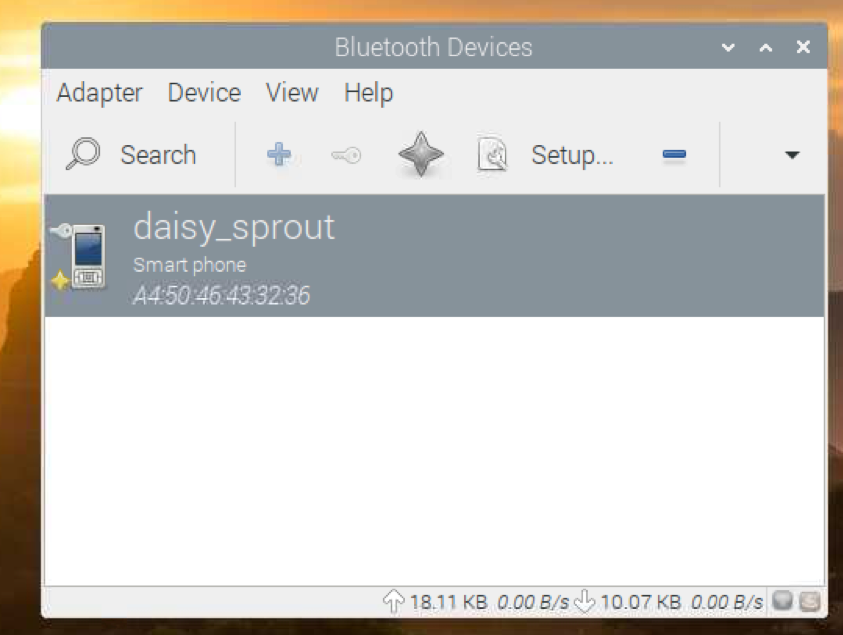
Once the device is paired, it should be listed in Blueman Bluetooth Manager.
To send a file to your Bluetooth device, right-click (RMB) on it and click on Send a File… as marked in the screenshot below.
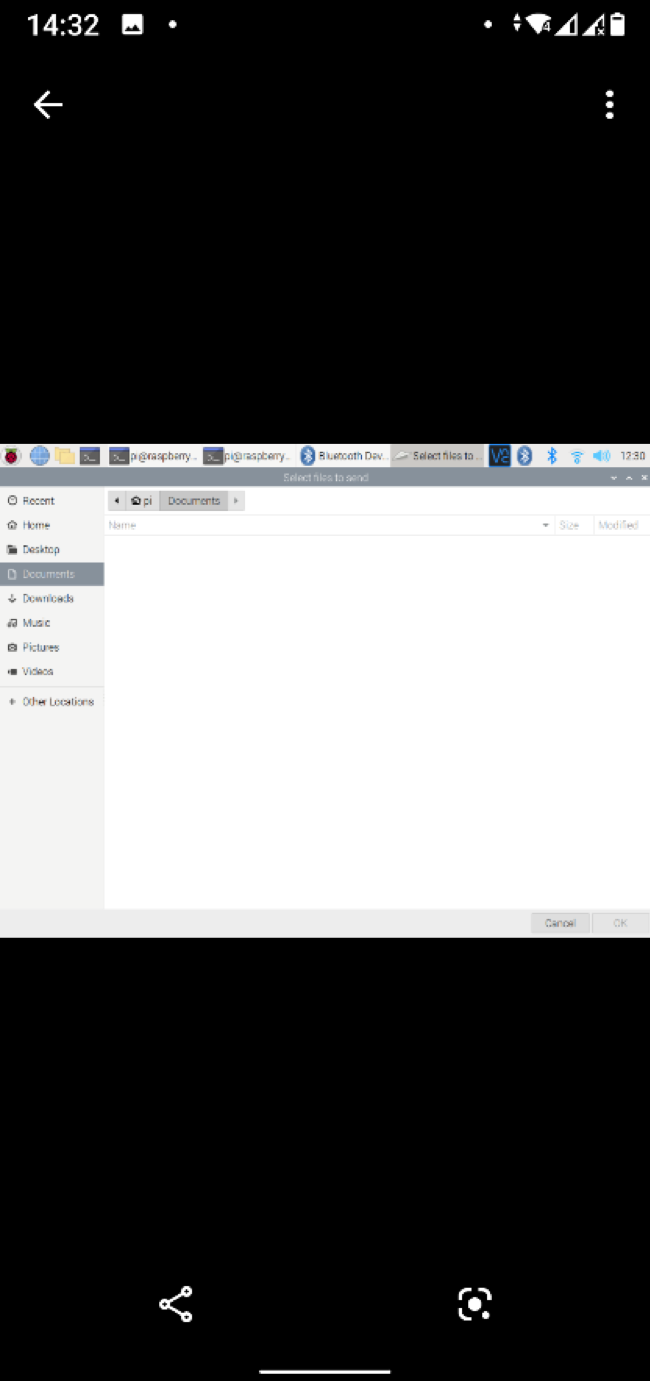
A file picker should be opened. Select the file you want to share using Bluetooth and click on OK.
Blueman should start the file transfer process.
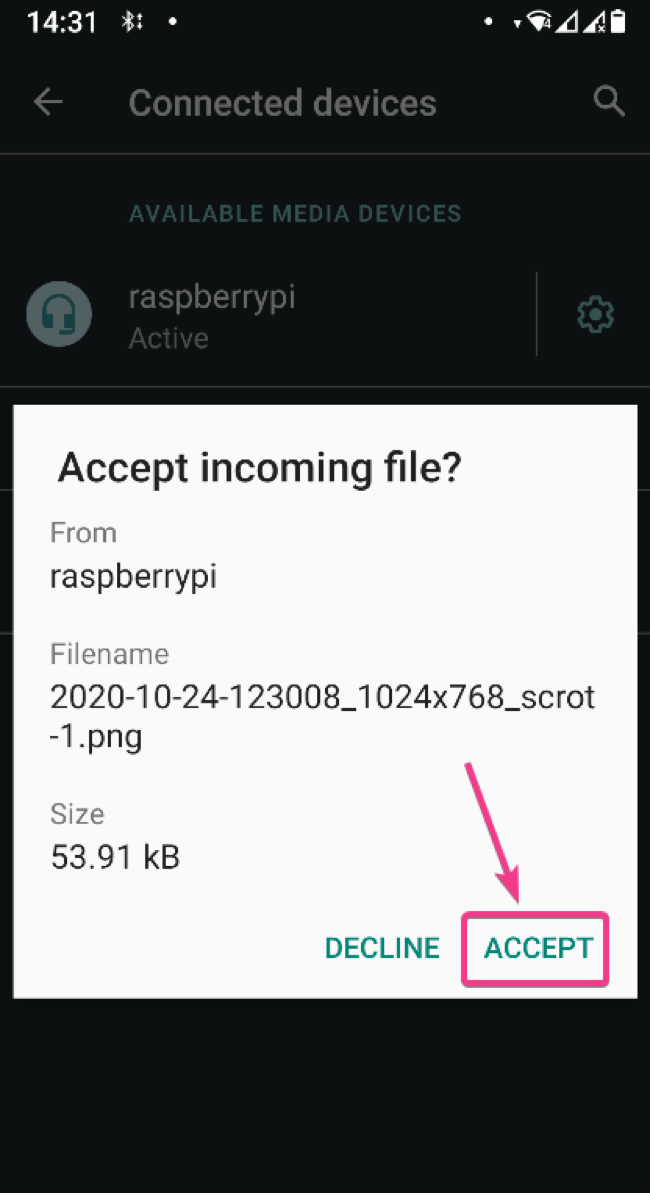
Click on ACCEPT to confirm the file transfer on your receiving Bluetooth device (where you are trying to send the file).
The file should be transferred as you can see in the screenshot below.
I have sent an image to my Android smartphone. As you can see, the image was successfully transferred to my Android device via Bluetooth.
You can also send files from your Android device or other Bluetooth enabled devices to your Raspberry Pi via Bluetooth.
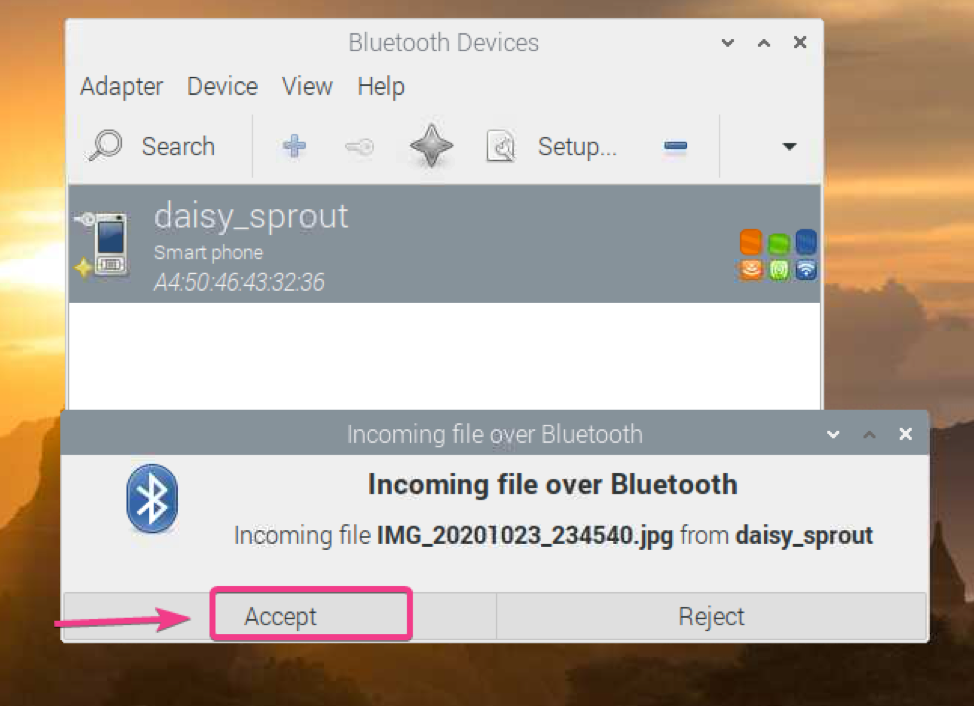
First, make sure your Raspberry Pi Bluetooth is discoverable. Then, share any file from your Bluetooth enabled device and select your Raspberry Pi from the list of receiving devices.
Blueman should ask you whether you want to accept the incoming file over Bluetooth. Click on Accept.
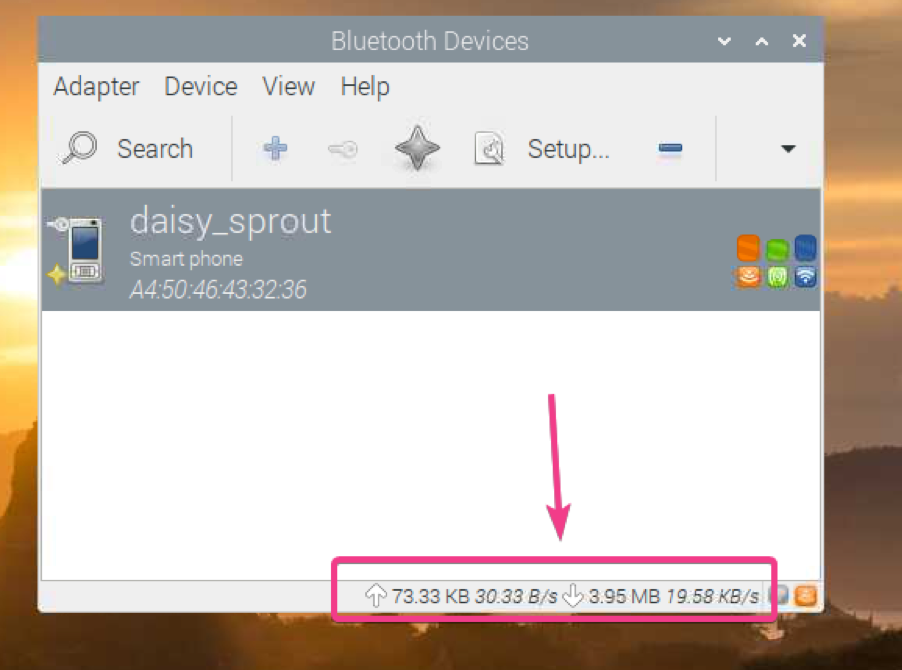
As you can see, the file is being transferred to the Raspberry Pi via Bluetooth.
File transfer statistics should also be displayed on the bottom panel of Blueman as you can see in the screenshot below. You can see that Bluetooth communication is very slow.
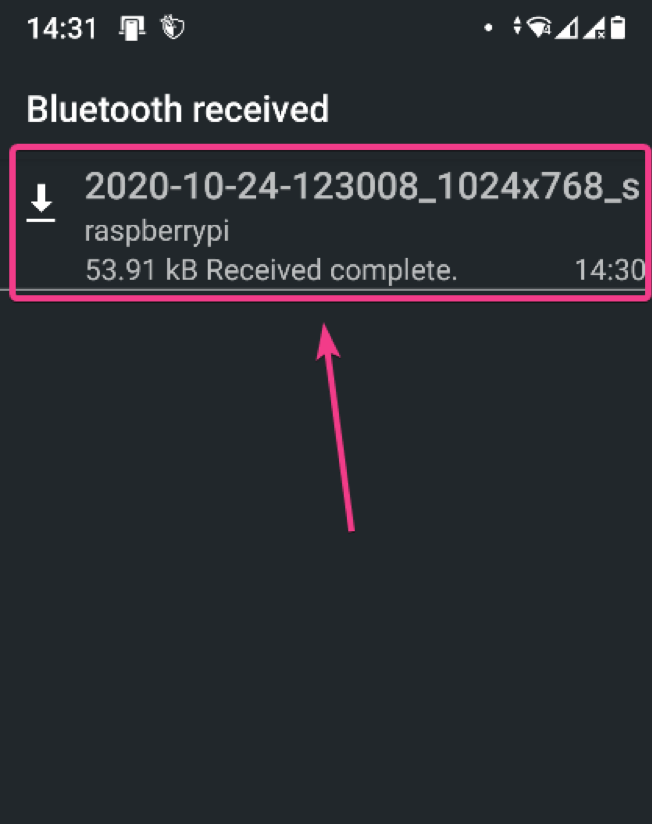
Once the transfer is complete, you should see the following message.
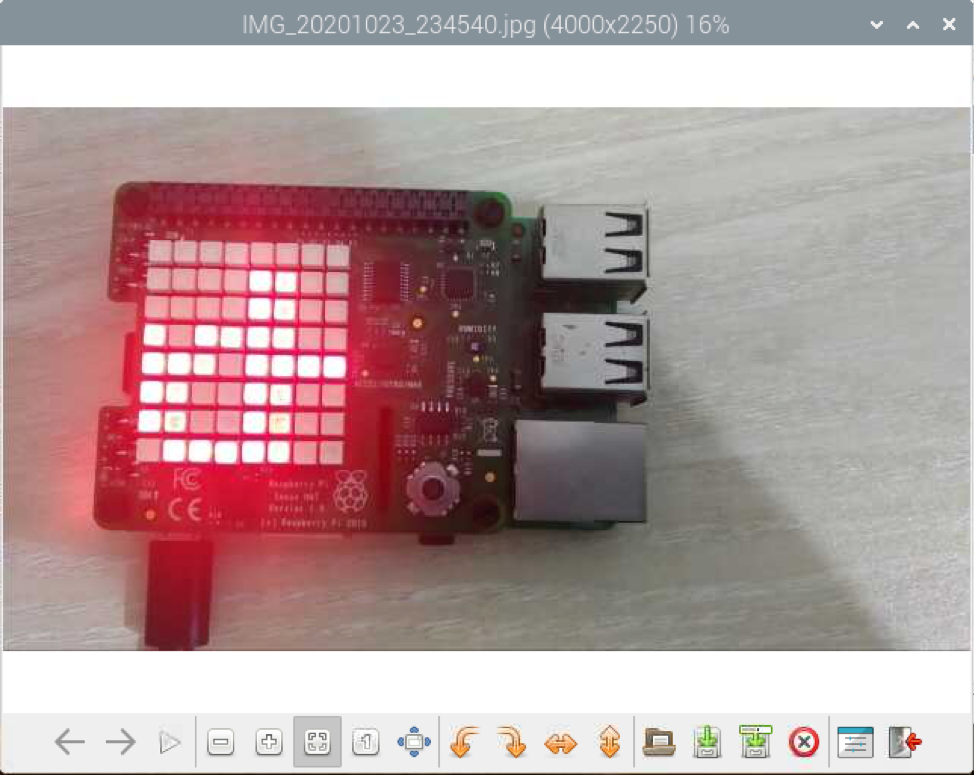
The files transferred to your Raspberry Pi via Bluetooth should be in the ~/Downloads directory of your Raspberry Pi.
As you can see, the file was successfully transferred to my Raspberry Pi from my Android smartphone.
Conclusion:
In this article, I have shown you how to use Bluetooth on the Raspberry Pi single-board computer with Raspberry Pi OS installed. I have shown you how to pair a Bluetooth device on the Raspberry Pi. I have also shown you how to transfer files from your Raspberry Pi to other Bluetooth enabled devices and vice versa.