Docker is a project development and software-sharing tool widely used worldwide. Sometimes, the developer wants to restart Docker cleanly after shutting it down. One of the other reasons is when the user deletes the Container or image, their reference will be saved locally and cannot be removed, which may cause errors or abnormal conditions. Therefore, occasionally developers want to start Docker from scratch with a clean restart.
This post will describe how to restart the Docker instance cleanly.
How to Cleanly Restart the Docker Instance?
To cleanly restart the Docker instance, remove unused containers and images. For this purpose, follow up on the provided instructions.
Step 1: List Down All Containers
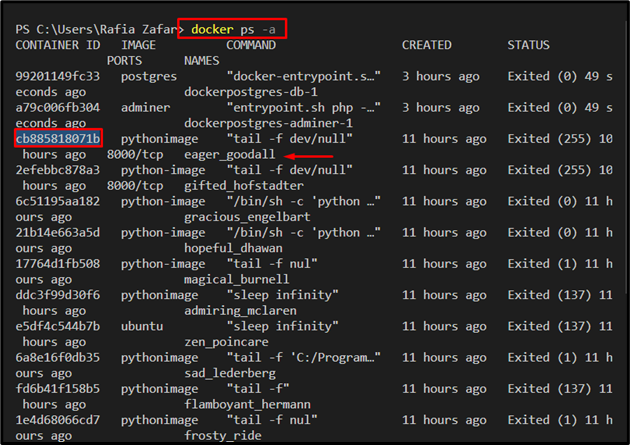
First, list down all the Docker containers with the help of the “docker ps -a” command:
Note the “Container ID” of the Docker container you want to remove:
Step 2: Stop Container
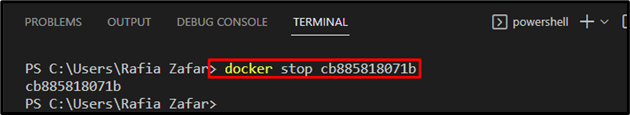
Next, if the container is running, stop the container through the “docker stop <container-id>” command:
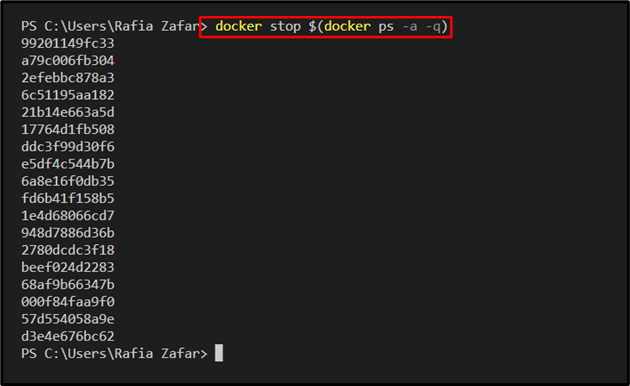
In order to stop all Docker containers, utilize the provided command in the Visual Studio Code Editor terminal. Here, the “-q” option is used to display container IDs only:
Step 3: Remove Container
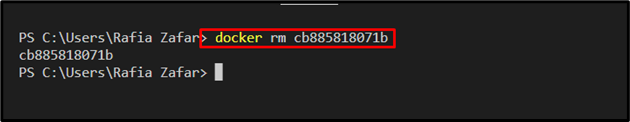
Now, remove the Docker container by utilizing the “docker rm <container-id>” command. Users can also remove Docker containers using the container name:
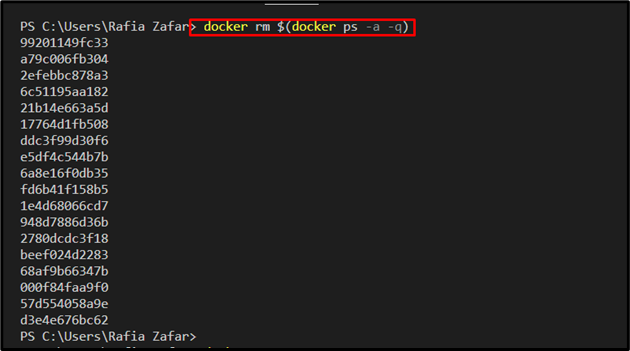
To remove all stopped Docker containers for using the Docker from scratch, check out the provided command:
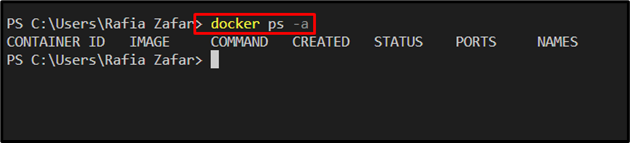
Verify, if the Docker containers are removed or not by viewing the container list:
Step 4: List All Images
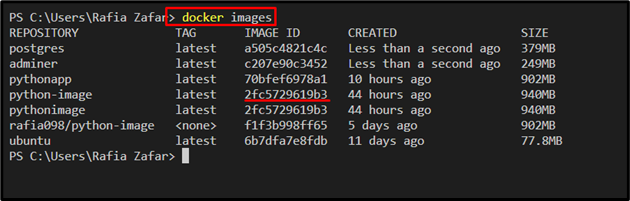
Lastly, remove the Docker image. For this purpose, first, list down all Docker images and note the id of the image you are required to remove:
Step 5: Remove Docker Image
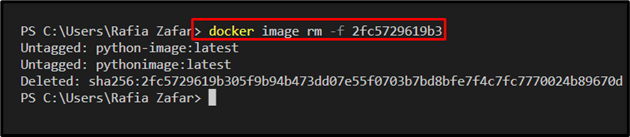
Next, remove the Docker image command using the “docker image rm” command. Here, the “-f” option is used to remove the Docker image forcefully:
This blog has demonstrated how to start the Docker instance cleanly.
Conclusion
To restart the Docker instance cleanly, first, list down all Docker containers. Then, stop the unused or extra containers using the “docker stop” command. After that, remove the Docker containers using the “docker rm <container-id>” command. To remove all stopped containers at once, use the “docker rm $(docker ps -a -q)” command. Next, to remove Docker images, utilize the “docker images rm -f <image-id>” command. This post has explained how to restart the Docker instance cleanly.