Docker containers are a major part of the Docker platform that plays a vital role in project deployment. Docker is a lightweight executable package that allows developers to run and execute projects on many machines by encapsulating all project dependencies, libraries, and source code. Moreover, developers can execute these projects on any system through Docker containers.
This blog will demonstrate the method to run Docker containers in the background through the “docker run” command.
How to Run a Docker Container in the Background Through Docker run Command?
To execute the container in the background with the help of the “docker run” command, the “–detach” option is utilized. For this purpose, look at given instructions.
Step 1: Launch Terminal
From the Windows “Startup” menu, launch your favorite terminal. For instance, we will use the “Git Bash” terminal:
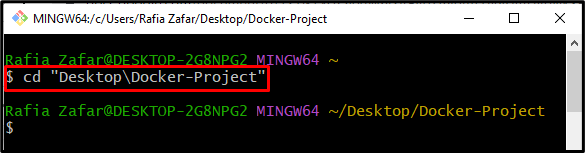
Step 2: Open Project Directory
Navigate to the project directory using the “cd” command. Users can also create a new directory with the help of the “mkdir” command:
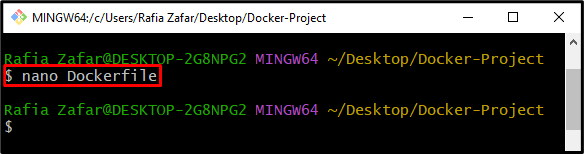
Step 3: Create Dockerfile
Create a new “Dockerfile” using the Nano text editor:
Paste the below-given code in Dockerfile to execute the Golang program:
WORKDIR /go/src/app
COPY main.go .
RUN go build -o webserver .
CMD ["./webserver"]
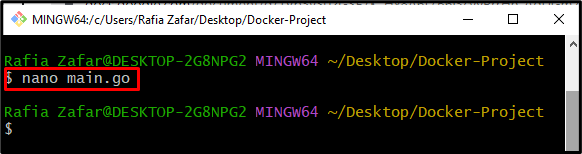
Step 4: Create main.go File
Next, create another file “main.go” in the Nano text editor with the help of provided command:
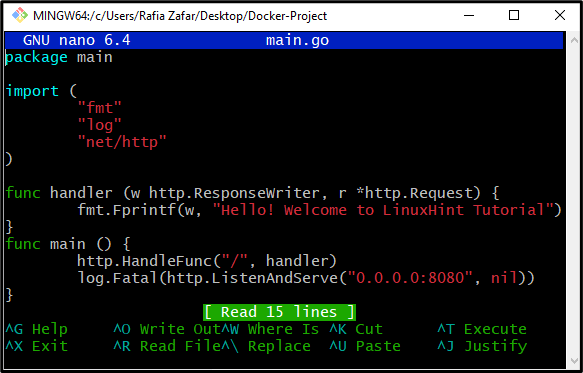
Paste the golang code that will print “Hello! Welcome to LinuxHint Tutorial” when executed on the local host port “8080”:
import (
"fmt"
"log"
"net/http"
)
func handler (w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
fmt.Fprintf(w, "Hello! Welcome to LinuxHint Tutorial")
}
func main () {
http.HandleFunc("/", handler)
log.Fatal(http.ListenAndServe("0.0.0.0:8080", nil))
}
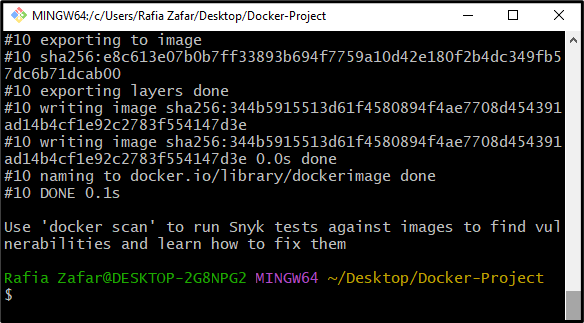
Step 5: Build a New Docker Image
After that, generate the new Docker image through the “docker build” command. Here, the “-i” flag is utilized to build images by name:
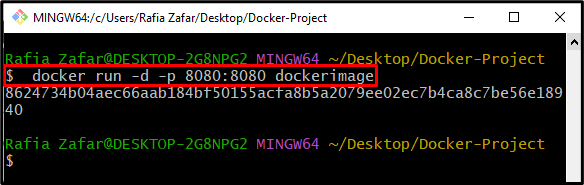
Step 6: Run Container in Background
Now, run the container in the background using the following “docker run” command:
In the above command, the “-p” option is used to define the port number. However, the “-d” option is specifically utilized to run the container in the background:
It can be observed that we have successfully deployed the application on localhost port “8080”:
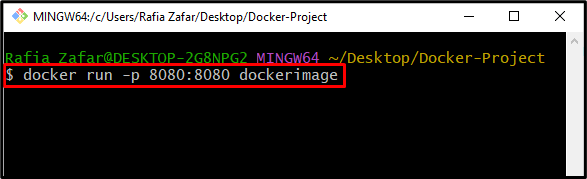
Note: If the container runs normally, the user cannot perform any actions. However, you can complete other tasks when the container runs in the background.
We have demonstrated the procedure for running the container in the background using the “docker run” command.
Conclusion
To run the container in the background, the “docker run” command is utilized along with the “–detach” or “-d” option. To run the container, first, make an image through a simple Dockerfile. Then, run the new Docker image using the “docker run -d <image-name>” command. The command will automatically execute the Docker container in the background. In post has explained the method for executing a container as a background process.