The relationships between the tables are the key feature of relational databases, which is being represented by foreign and primary keys. In this article, we will explain the foreign keys and their working in SQLite.
What are foreign keys?
Foreign keys are the values in a table that indicate the primary key of another table. To understand this let us consider two tables, table A and table B:
|
Table A |
||
| Student Id (Primary_key) | Student Name | Teacher Id (Forign_key) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | 123 |
| 2 | Paul | 453 |
|
Table B |
||
| Teacher ID (Primary_key) | Teacher Names | Subjects allowed |
|---|---|---|
| 123 | Alex | Maths, Physics |
| 453 | Juana | Chemistry, Botany |
Now, in Table A, Student Id is the primary key of that table, and Teacher Id is the foreign key, but in Table B, Teacher ID is the primary key. Teacher ID, which is a foreign key, establishes a relationship between Table A to Table B.
How to check the status of the Foreign key in SQLite
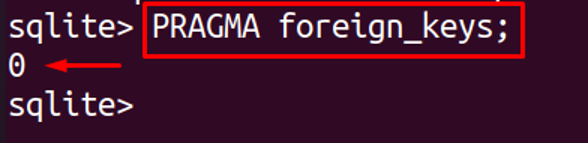
SQLite begin supporting the feature of a foreign key after the release of its version 3.6.19, so to check whether the installed version of SQLite supports the foreign key or not, execute the following command in the SQLite environment:
The output can either be “0” or “1” and if it doesn’t display any output then it means it does not support the foreign keys.
| Output | Result |
|---|---|
| 0 | The foreign keys are disabled |
| 1 | The foreign keys are enabled |
How to enable/disable foreign keys in SQLite
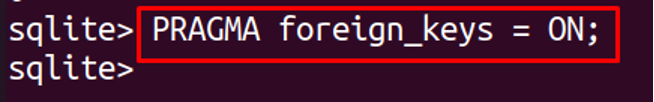
To enable the foreign keys in SQLite, run the following:
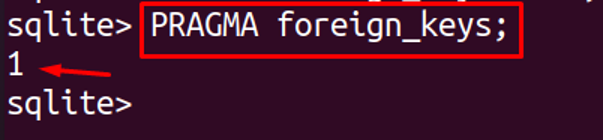
We can disable the foreign keys, by just typing OFF instead of ON in the above command. To confirm that foreign keys are enabled, run the PRAGMA command:
The output shows 1, which means the foreign keys are being enabled.
What is the general syntax of using foreign key
The general syntax of using a foreign key to create a table is:
(
column1 datatype [ NULL | NOT NULL ] PRIMARY KEY,
column2 datatype [ NULL | NOT NULL ] FOREIGN KEY,
...
FOREIGN KEY (column1, column2, ...))
REFERENCES parent_table (column1, column2 ...)
);
The explanation of it is:
- Use the clause “CREATE TABLE” for the creation of a table
- Replace table_name with the name of the table
- Define the columns with their data types, and also define whether the support NULL/NOT NULL values
- Also mentions the columns that hold PRIMARY key and the Foreign key
- Use the statement FOREIGN KEY and mention in () the column names which are foreign keys
- Use the clause REFERENCE and replace the parent_table with the name of parent table and mention its foreign keys
How does a foreign key works in SQLite
To understand the working of foreign keys let us consider an example of a courier service and create two tables, customer_details, and shipment_details which are having the following data:
|
customer_details |
||
| Customer_id | Customer_name | Shipment_id |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | John | 5612 |
| 2 | Paul | 3467 |
|
shipment_details |
|||
| Shipment_id | Status | From (City) | To (City) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5612 | Delivered | London | Manchester |
| 3467 | In process | Bristol | Cardiff |
In the table, customer_details, Customer_id is the primary key and Shipment_id is a foreign key. And in the table, shipment_details, shipment_id is a primary key.
How to add a foreign key in SQLite
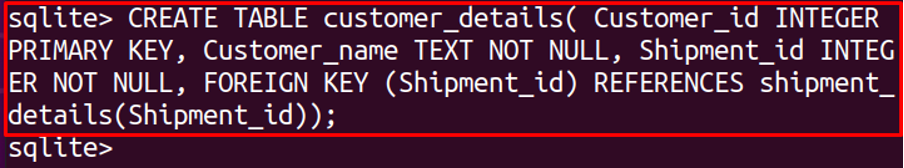
To create a table, customer_details run the following command:
In the above command, we have mentioned the foreign key and primary key and also refer to the table where the foreign key will be available. After the creation of the customer_details table, we will create the shipment_details table as:
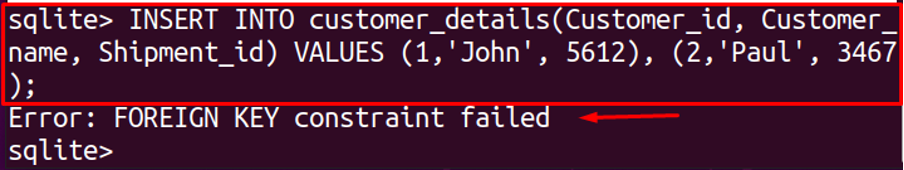
Now to insert values in the customer_details table, use the following command:
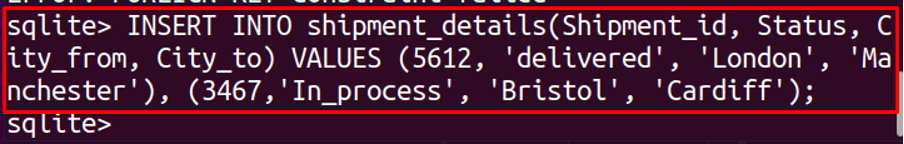
We can see that it generated the error of “Error: FOREIGN KEY constraint failed”, this error is generated because we were referring to the Shipment_id of table, shipment_details, which has no value yet. So, to remove this error, first, we have to edit the data in shipment_details, that we are referring to the foreign key. To insert data in the shipment_details table, run the following command:
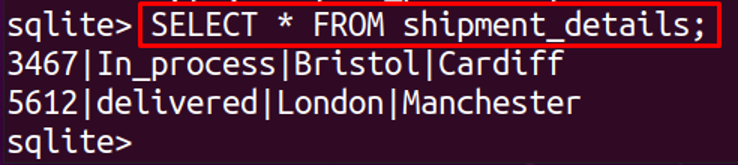
To display the table, shipment_details, run the command:
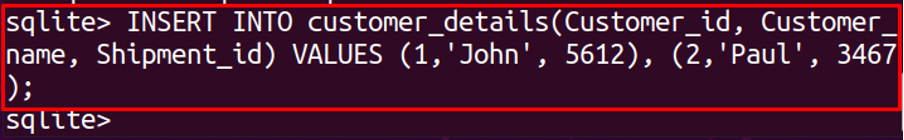
Now, again run the command to insert values in customer_details using the statement:
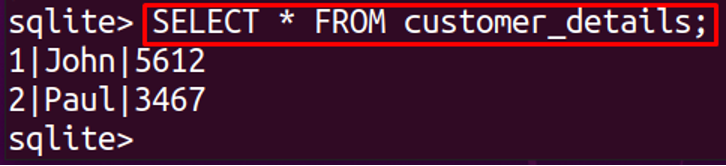
The command has successfully executed without generating the “Foreign key constraint failed” error. To display the table, run the command:
What are the foreign key constraints actions
There are some actions that you can perform on the parent key as a result of which the child key responds. The general syntax is:
REFERENCES parent_table(parent_key_column)
ON UPDATE
ON DELETE ;
An explanation to this syntax is:
- Write the clause of FOREIGN KEY and replace the “foreign_key_column” with the name of your foreign key
- Replace the “parent_table” with the name of the parent table and also “parent_key_columns” with the parent key name
- Write the clause “ON UPDATE” and “ON DELETE”, and replace the “<action>” with the action you want to perform
SQLite supports the actions which are explained in the table:
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Null | When the parent key is deleted, the child key column set to null values |
| Set default | It works the same as the Null action, but instead of setting null values to the child key column, it set a default value |
| No action | When changes are made in the parent key of the parent database, no changes are taken place in the child key |
| Restrict | It does not allow the user to add or delete the values from a parent key |
| Cascade | It passes on the changes which are made in a parent table to the child table |
Conclusion
Relational databases are popular for their feature of providing the relationships between the tables, SQLite, one of the relational databases, also supports this feature. The relationships are established with the help of keys, which are known as foreign and primary keys. In SQLite, the foreign key should be enabled to use it. In this article, we learned what are the foreign keys in SQLite and how they work. We also discussed the constraint actions of foreign keys supported by SQLite.