This writeup is related to the data types and its brief explanation, in which we will discuss all the data types which are supported in SQLite and how they can be used as well.
What is a data type
Data type states the type of values that can be stored in that particular column, the data type not only tells the column which type of values it has to insert but also will restrict the values of other data types to be entered in that column. For example, if we declare a column with an integer data type, then only integer type values can be inserted in the column and it will not allow any string to be entered in that column.
What is the list of data types supported by SQLite
The data types which are supported by SQLite are:
- Null
- Integer
- Real
- Text
- blob
These all data types are described in detail.
- Null: This will store the null values.
- Integer: It will store any integer value which are in whole numbers like 1, 45, 543; or can store the value of eight bytes if its magnitude is considered.
- Real: It will store numbers that are in the form of decimals and also known as floating numbers like 1.2, 4.5, 67.4; or they can store any floating number of magnitude having eight bytes.
- Text: It stores any type of string and there is no limit to storing the string, SQLite supports different types of characters and strings including UTF-8, UTF-16 BE, or UTF-26LE.
- Blob: It is the abbreviation of the Binary Logic Blob which can store the value as it is input, it can also store large files like images and videos and there is no limit to the size of the value in storing blob.
What is affinity in SQLite
Other databases restrict the data types to enter in columns, other than which is assigned to the column at the time of declaration of a table, but in SQLite, it allows every data type to enter on the basis of affinity to some data types. The data types that can be entered in the tables with their affinities are shown in the table:
| Data type | Affinity |
|---|---|
| INT | INTEGER |
| INTEGER | |
| TINYINT | |
| SMALLINT | |
| MEDIUMINT | |
| BIGINT | |
| UNSIGNED BIGINT | |
| INT2 | |
| INT8 | |
| CHARACTER(20) | TEXT |
| VARCHAR(255) | |
| VARYINGCHARACTER (255) | |
| NCHAR(55) | |
| NATIVE CHARACTER (70) | |
| NVARCHAR(100) | |
| TEXT | |
| CLOB | |
| No data type specified | BLOB |
| REAL | REAL |
| DOUBLE | |
| DOUBLE PRECISION | |
| FLOAT | |
| NUMERIC | NUMERIC |
| DECIMAL (10,5) | |
| BOOLEAN | |
| DATE | |
| DATETIME |
How data types are used in SQLite
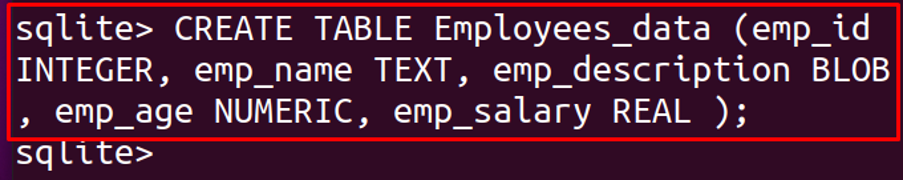
Let us create a table using all the main data types of the SQLite which are INTEGER, REAL, TEXT, and BLOB which are explained above, for example, we create a table, named, Employees_data:
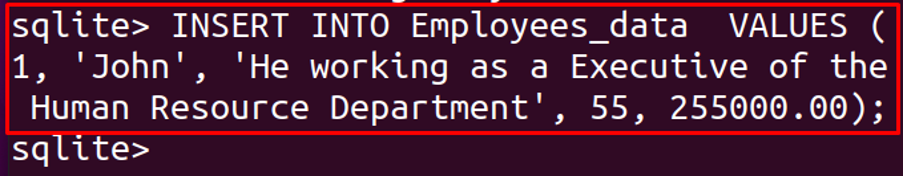
To enter values in the created table, run the command:
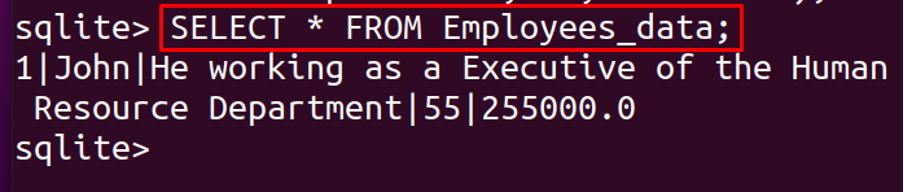
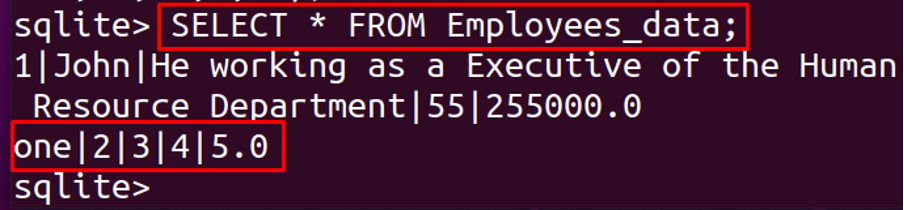
To display the contents of the table, we will execute the following command:
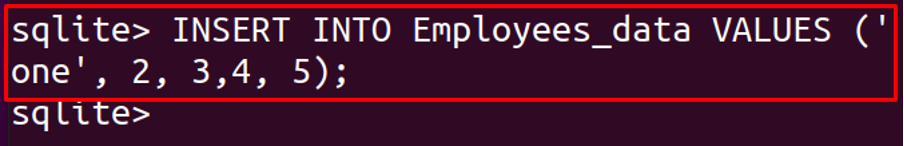
Now we will insert the integers in all the columns of the table and will check whether it generates the error or not.
The command has been executed successfully and all the integers value has been added in all the columns, which means that in SQLite, there is no restriction of inserting a specific data type in the column/rows due to its feature of affinity with other data types, that’s why the value “one” which is in TEXT is inserted in the column which is declared by INTEGER, and the other all values are INTEGER which is successfully inserted in the columns declared with REAL, TEXT, and BLOB data types.
We can display the table, to confirm whether the above statement values are inserted in the table or not:
Conclusion
Data types are very useful for inserting the data in an organized manner as well as it protects the relevant data to be inserted in the column/row. Unlike other databases, SQLite is different as it introduced the concept of affinity in data types, in which any data type can be accommodated by every data type. This writeup is related to the data types and their types in SQLite and it also explains how these data types are used in the SQLite.