To have a clear understanding of how the decode() method works in Python, take a look at its syntax.
Syntax of the decode() Method
The syntax is defined as :
Within this syntax:
- stringVar is the string that has been previously encoded and needs to be decrypted back to the original form.
- encodeFormat defines the encoding format that was used to encode the string initially
- errorMode defines the error-handling mode to use while trying to decode the string into its original form.
Now that you are familiar with the syntax of the decode() method let’s take a look at some examples.
Example 1: Decoding a Simply Encoded String
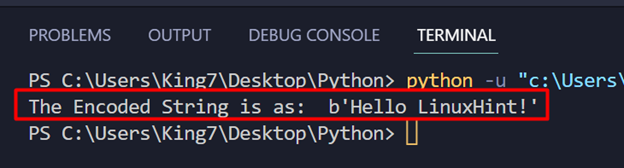
In this example, you are going to try to decode() a string that has been encoded by the encode() method without specifying the encoding format. To do this, first, encode a string using the following code snippet:
encodeStr= stringVar.encode()
Let’s print out the encoded string using the following line:
The program, at this time, gives the following output:
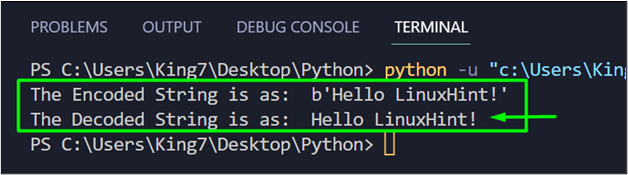
After that, apply the decode() method and print it on the terminal using the print method:
print("The Decoded String is as: ",stringDec)
When you execute the code now, it will produce the following result on the terminal:
You have successfully used the decode() method to the original non-encoded string in Python.
Example 2: Decoding a String With Specific Encoding Format
To demonstrate the working of the decode() method on a string that has been encoded with a specific encoding format, take the following lines of code:
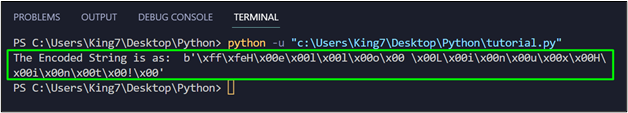
encodeStr= stringVar.encode(encoding="utf16")
print("The Encoded String is as: ",encodeStr)
At this point, when this code snippet is executed, it will produce the following output on the terminal:
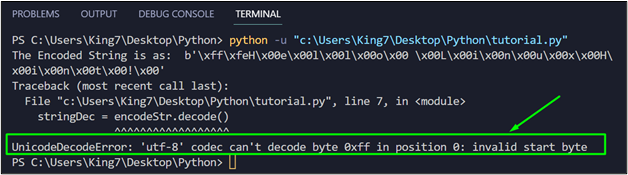
If you try to apply the decode() method with specifying the encoding format:
print("The Decoded String is as: ",stringDec)
It will produce the following error on the terminal:
Therefore, the correct code for decoding this string is as:
print("The Decoded String is as: ",stringDec)
This time around, when the complete code snippet is executed, it will produce the following result on the terminal:
You have successfully decoded a string which had been encoded with a specific encoded string.
Conclusion
The decode() method in Python is used to decode a string that has been encoded with a specific format. This method takes two arguments which are both options, the first one is the encoding type, and the second one is the error-handling mode. If no arguments are provided, then the decode() method sets the encoding format to “utf8”.