In this article, we’ll explore “Python networking” and cover everything to get started with network programming using Python. This blog’s content is as follows:
- What is Python Networking?
- How to Get Started With Python Networking?
- Socket Programming With Python.
- Examples of Networking in Python.
What is Python Networking?
“Python networking” refers to the use of the Python programming language to build applications that can communicate over a network. In a network, devices share resources and information by connecting to one another. Python networking allows these devices to communicate with each other using various protocols, including “HTTP”, “FTP”, “SMTP”, and more.
Python networking is a powerful tool that can be used to build a wide range of network applications, including “web servers”, “chat applications”, and more. It’s also used in data analytics for extracting and analyzing web data.
How to Get Started With Python Networking?
To get started with “Python networking”, it’s important to have a basic overview of Python. If you’re new to Python, we recommend starting with a beginner’s guide to Python programming before diving into networking.
Once you have a good grasp of Python programming, you can start learning about networking concepts like “socket programming”, “web scraping”, and more. There are plenty of resources available online to help you learn these concepts, including tutorials, video courses, and more.
Socket Programming With Python
“Socket programming” is a key concept in Python networking. It’s a low-level networking interface that makes it possible for two devices to communicate over a network. With socket programming, you can build powerful network applications like “chat servers”, “file transfer applications”, and more.
In order to learn how to program sockets in Python, you’ll need to understand the following concepts:
Socket
Sockets are the endpoints of communication links between two devices that provide a two-way flow of information between them. The device is identified by an Internet Protocol (IP) address and a Port Number.
Client-Server Model
There are two types of devices in socket programming: “clients” and “servers”. A “server” listens and responds to incoming requests from clients, and a “client” sends requests to servers.
TCP vs UDP
There are two main transport protocols used in socket programming – “TCP” and “UDP”. “UDP” is a simple, non-connection-oriented protocol, whereas “TCP” is reliable, connection-oriented.
Blocking vs Non-Blocking Sockets
Socket programming can be either “blocking” or “non-blocking”. With “blocking” sockets, the program waits for a response from the other device before continuing. With “non-blocking” sockets, the program continues to run as long as a response is received.
Socket Methods
Python’s socket module provides several methods for creating and manipulating sockets. These methods include the following:
- socket()
- bind()
- listen()
- accept()
- connect()
- send()
- recv()
Examples of Networking in Python
Following are examples of networking in Python:
Example 1: Creating a Simple “Client-Server” Communication Program Using the “socket” Module
Let’s first create the server-side code.
Server-Side Code
Overview of the following code snippet:
server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
host = socket.gethostname()
port = 12345
server_socket.bind((host, port))
server_socket.listen(1)
print('Waiting for a client connection...')
client_socket, addr = server_socket.accept()
print('Connection established with:', addr)
message = 'Welcome to the server!'
client_socket.send(message.encode())
client_socket.close()
Client-Side Code
Now, the client-side code is created. Here is an example code:
client_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
host = socket.gethostname()
port = 12345
client_socket.connect((host, port))
message = client_socket.recv(1024)
print(message.decode())
client_socket.close()
In the above server-client code:
- The “client-server” communication program is created using the built-in “socket” module in Python.
- The “server” waits for a client connection, generates a welcome notification to the client, and then closes the connection.
- The “client” creates/establishes a connection with the server, retrieves the welcome message, and then closes the connection.
Output
To execute the above client-server communication code in Python, first, open the code editor and copy the server and client code into two separate Python files, such as “server.py”, and “client.py”. After that, open two terminal windows or command prompt windows.
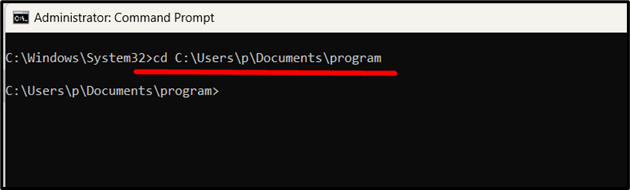
In the first terminal window, navigate to the directory where the “server.py” file is saved using the “cd” command, as follows:
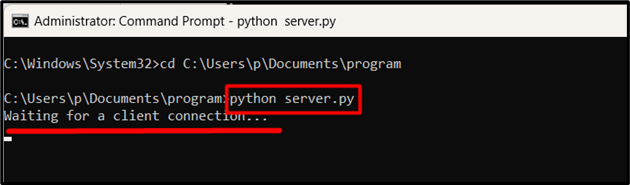
Now, execute the “server.py” file by running the following command:
Here is the output snippet:
The server will start running and wait for a client connection.
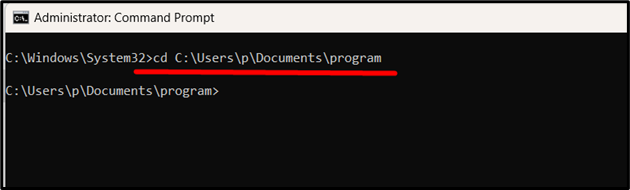
Now, open the second terminal. Here, navigate to the directory where the “client.py” file is saved using the “cd” command:
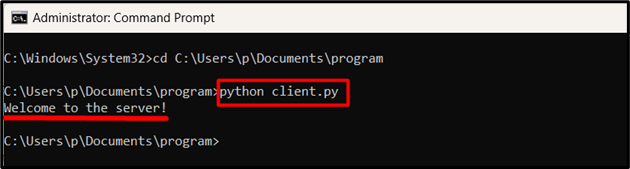
Here, execute the “client.py” file by running the following command:
Following is the output snippet:
The client will now connect to the server and receive the welcome message from the server.
Note: In the first terminal window where you executed “server.py”, you will see the message “Connection established with: <client_address>” displayed. A server will also close a client’s connection after sending a message.
Example 2: Sending an HTTP Request Using the “requests” Module
Here is an example code:
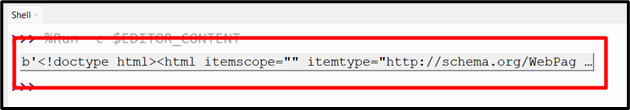
response = requests.get('https://www.google.com')
print(response.content)
In the above code, the “requests” module is used to send an “HTTP GET” request to “https://www.google.com” and print the response content.
Output
The above snippet shows the response content of the specified site.
Example 3: Resolving a Hostname to an IP Address Utilizing the “socket” Module
Following is an example code:
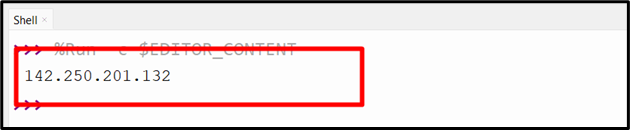
hostname = 'www.google.com'
ip_address = socket.gethostbyname(hostname)
print(ip_address)
The above code snippet uses the “socket” module to resolve the hostname “www.google.com” to its corresponding IP address and prints it.
Output
The above snippet displays the IP address of the specified site.
Conclusion
“Python Networking” allows developers to create server and client applications, send and receive data over the network, and manage network protocols effortlessly. Several networking-specific libraries, such as the popular “requests”, “Scapy” libraries, and “socket”, etc. are used in Python.