Python provides several modules and functions for handling input and output operations related to files, such as io, shutil, and many more. In Python, the “io” module supports several modules and functions for dealing with binary data, Unicode data, and string data.
The outcomes of this tutorial are:
- What is the Python IO Module?
- BytesIO Class of IO Module in Python
- StringIO Class of IO Module in Python
What is the Python IO Module?
In Python, the “io” module provides various sets of classes and functions for managing files related to input and output operations. One of the advantages of utilizing the “io” module is that it allows us to extend its functionality to enable writing to Unicode data. We can also use various classes and functions of the “io” module for Unicode encoding and decoding.
Python offers the IO module for handling stream and buffer operations in various ways. There are two useful classes within the IO module, such as “BytesIO” and “StringIO”, which can be accessed using the “io.BytesIO” and “io.StringIO”.
Let’s get started with the BytesIO class!
BytesIO Class of IO Module in Python
The “BytesIO” class in Python provides a stream-like interface for handling binary data in memory. This class is used to treat bytes data as a file-like object that enables read and write operations on the bytes without using the physical file. To get more understanding, have a look at the following code:
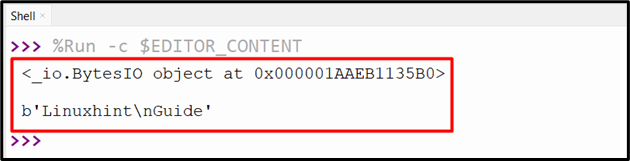
bs = io.BytesIO(b'Linuxhint\x0AGuide')
print(bs, '\n')
print(bs.getvalue())
bs.close()
In the above example code:
- First, import the “io” module.
- Then, use the “io.BytesIO()” constructor that takes the binary data as an argument and creates the BytesIO object.
- Next, print the BytesIO object on the console utilizing the “print()” function.
- To retrieve and print the content of the BytesIO object, use the “getvalue()” method.
- Finally, utilize the “close()” method to close the BytesIO object.
As you can see, the BytesIO object, along with its value, has been created and printed on the console:
StringIO Class of IO Module in Python
In Python, the “StringIO” class is similar to the “BytesIO” class, and it is used to treat strings as file-like objects rather than bytes. This class delivers methods for reading from and writing to an in-memory buffer. For further understanding, let’s have a look at the below examples:
Example 1: Creating and Reading Data from File Object
Check out the below-provided code to create a file object and read data from it:
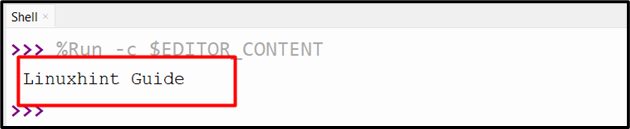
str1 = 'Linuxhint Guide'
file1 = io.StringIO(str1)
file2 = file1.read()
print(file2)
Here:
- Initially, imported the “io” module and then used the “io.StringIO()” constructor to create the file-like string object.
- Next, invoked the “file.read()” method to read the newly created data and display it to the console using the “print()” function.
Output
The data has been created and displayed successfully on the console.
Example 2: Writing Data to File Object
Let’s take an example for writing a string to the newly created file object:
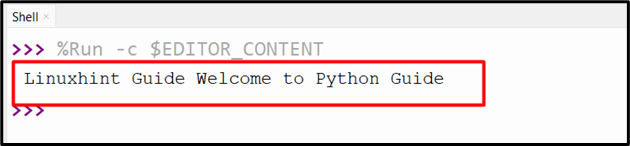
str1 = 'Linuxhint Guide'
file1 = io.StringIO(str1)
file2 = file1.read()
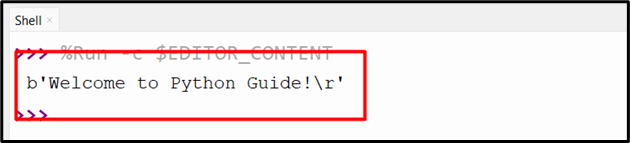
file1.write(' Welcome to Python Guide')
file1.seek(0)
file3 = file1.read()
print(file3)
According to the above-provided code:
- First of all, added the “io” module.
- Then, use the “io.StringIO()” function to create an in-memory buffer object (file object) by taking the string as an argument.
- Next, apply the “read()” method to read the contents of the object named “file1”.
- Afterward, utilized the “write()” method to write or append the string to the existing content in the in-memory buffer or file object.
- To shift the file handler/pointer to the start of the file, invoke the “seek()” method.
- Finally, use the “read()” method to read all the content of the file and display it to the console using the “print()” function.
It can be seen that the string has been successfully written to the string file-like object:
Example 3: Using “io.open()” Method to Read a File
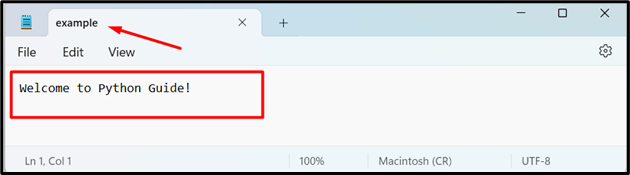
The “io.open()” method can also be used to read the data from the file that is similar to the file object. Here is the snippet of the file along with its original content:
To read data from the file using the buffered read, the below example is used in Python:
f1 = io.open("example.txt", "rb", buffering = 5)
print(f1.read())
f1.close()
In the above code:
- The “io” module is imported/added at the start.
- Then, use the “io.open()” method to open the file in a binary module for reading the data from the file.
- Next, pass the “rb” mode and “buffering=5” parameters to this particular method. These parameters specify the mode and the buffer size to be used for reading the file. Here based on the buffer size, data will be read in chunks of 5 bytes at a time.
- Lastly, the “read()” method is used to read the entire content of the file, and the “close()” method is utilized to terminate/close the file.
Output
The data has been read successfully.
Conclusion
In Python, the “IO” module is used to provide several functions and classes for handling and performing input/output operations on data. There are two main classes of the “Input/Output” module, such as BytesIO and StringIO. The “BytesIO” class is used to handle and manipulate the binary data, and the “StringIO” class is used to work with string data. In this guide, we have delivered a complete overview of the Python IO module using numerous examples.