Installation of Prerequisites
Let’s get started with the implementation of converting a dictionary to a yaml document. For this, you need to have the Python, pip, and yaml already installed and configured on your windows system. If you don’t have any one of these packages set up at your end, don’t worry. Here is a modest description of the ways you can install each one of these. Open your Windows Command Prompt using the “Run as Administrator” option and the black screen will show as follows:
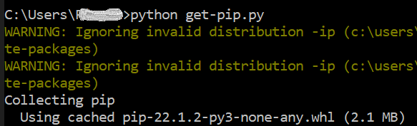
After the full configuration of the Python’s latest version at your end, make sure to download the official pip file from the bootstrap site named “get-pip.py”. Make sure to save it within the same directory where you installed your updated Python package. Numerous articles exist about how to download this “pip” file. If you don’t want to use them, just run the following code:
curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py -o get-pip.py
If not, you can simply use the “python” instruction along with the name of a pip file “ge-pip.py” and press the Enter key to install it as follows. First, it starts collecting the data:
Then, the collected package of “pip” is installed.
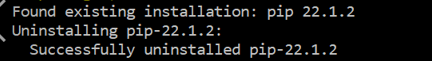
If it’s already been installed on your system, this command will uninstall its previous version. You can understand that in our situation, it has already been found and uninstalled successfully.
After that, it will be installed successfully on your system and the command prompt displays the following output:
You can see the installed version of pip at the command prompt using the version command.
To install the “yaml” package at your end, you need to use the installation command starting with the keyword “pip” and ending with the keyword “PyYAML” in the command prompt.
You will see that the system will start collecting the “yaml” package as per the process bar.
After a few seconds of collection, it starts installing the “YAML” package automatically.
Within a few seconds, the “YAML” package will be installed at our end. You can see the installed version of YAML on your screen as “PyYAML-6.0”.
Now, you need to open the Python console at the same command prompt using the simple “python” instruction as we used within the following image:
Example 01: Dictionary to YAML
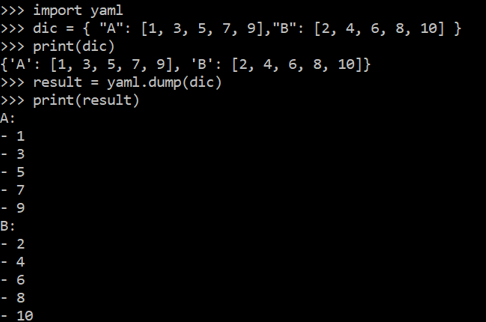
Let’s get started with the first example of “yaml” in the Python console. Within this example, we convert a simple Python dictionary to a yaml file since this “yaml” came up with the “dump” function. We initialize this code example with the use of the “import” statement to import the “yaml” package in the Python console. After that, we initialize a dictionary named “dic” with a total of 2 key-value pairs in it. Each of its keys contains a list of 5 values as its value pair.
After that, we use the print() function of Python to print the dictionary “dic”. The very next line displays the dictionary in a key-value pair format. After this, we use the “yaml” package to call the “dump” function to convert the “dic” dictionary to “yaml” file format and save the result to the “result” variable. Lastly, we use the “print” function once again to print out the “result” variable that holds the yaml file in it.
The very next line displays the conversion of a dictionary to a yaml file format on our Python console screen. You can tell that the outcome is poles apart from the output of a simple dictionary. The keys and their values are all displayed at the separate and single lines as per the yaml file format, i.e. “-“ for the values.
Example 02: YAML to Dictionary
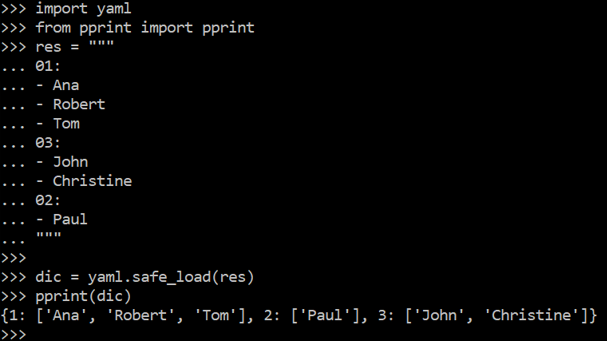
Let’s take a look at the example of converting some yaml file format data to a dictionary. For this, you need to import the “yaml” package first at the start of this code. After that, you need to import the “pprint” package in this code using its library to use the pprint() function via the “import” keyword. This “pprint()” function is mainly designed to print out the converted yaml files to dictionaries. So, we import the “pprint” package and initialize the yaml file at the next line.
This document starts with the “res” variable followed by the “=”, started and ended at the triple double inverted commas. In the very next line, we use the keys 01, 02, and 03 followed by the values starting with the “-“ character. The safe_load() function is used with the yaml package to convert the yaml file to dictionary “dic”. The pprint() function uses the “dic” variable to display the converted dictionary from the yaml file format on your screens.
Conclusion
This article’s introduction covers a brief explanation and usage of Python along with the dynamic nature of the “YAML” language. Within this article, we discussed the use and installation of pip followed by the YAML and discussed two of the examples to convert the Python dictionary to a yaml file format and vice versa. This is completed with the usage of the yaml’s “dump” and “safe_load” functions. Both the examples are quite simple and easy to learn.