JSON or JavaScript Object Notation is a widely utilized format for storing and exchanging/sharing data. It is very difficult to work/deal with JSON data as it is often nested and complex. In order to make it a simple, flattened, or more manageable format, the “pandas.json_normalize()” method of the “Pandas” module is used in Python.
This blog presents a thorough tutorial on the “pandas.json_normalzie()” method using numerous examples and via the following content:
- What is the “pandas.json_normalize()” Method in Python?
- Normalizing JSON Data Using “pandas.json_normalize()” Method
- Normalizing JSON Data Using “pandas.json_normalize()” Method With “max_level” Parameter
What is the “pandas.json_normalize()” Method in Python?
The “pandas.json_normalzie()” method is used to normalize semi-structured JSON (JavaScript object notation) data into a flat table. The syntax of “pandas.json_normalize()” method is shown below:
In the above syntax:
- The “data” parameter specifies the data that can be a dictionary, a nested dictionary, or a list of dictionaries.
- The “max_level” parameter is used to indicate the maximum level or depth of the dictionary to normalize. By default, it normalizes all the levels.
- The “record_path” parameter is used to indicate the path to the record of the JavaScript Object Notation, which should be flattened.
- The other parameters are optional and can perform certain operations when passed to the function.
Example 1: Normalizing JSON Data Using “pandas.json_normalize()” Method
The below code is used to normalize the nested dictionary JSON data:
input_json = [{"name": "Joseph", "id_no": "1234"},{"name": "Lily", "id_no": "1453"},{"name": "Anna", "id_no": "1932"},
{"name": "Henry", "id_no": "1567"},{"name": "David", "id_no": "1354"}]
print(input_json, '\n')
print(pandas.json_normalize(input_json))
In the above code:
- The “pandas” module is imported, the JSON data is created, and stored in the variable “input_json”.
- The “pandas.json_normalize()” method takes the JSON data as a parameter and normalizes it.
Output
The JSON data has been normalized to the maximum level.
Example 2: Normalizing JSON Data Using “pandas.json_normalize()” Method With “max_level” Parameter
The following code is used to normalize the JSON data based on the level of the normalization:
input_json = [
{
"id_no": 18012,
"name": "Joseph",
"grades": {"english": 22, "sports": 30},
},
{"name": "Henry", "grades": {"english": 38, "sports": 60}},
{
"id_no": 18043,
"name": "Anna",
"grades": {"english": 31, "sports": 190},
},
]
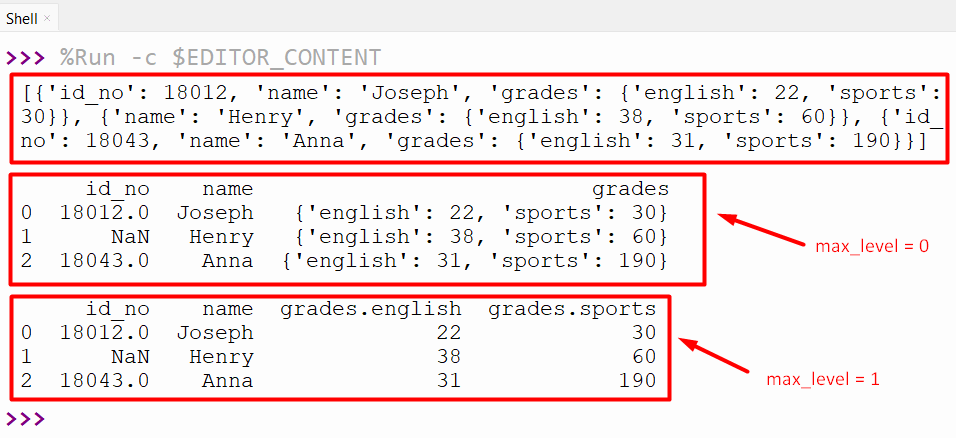
print(input_json, '\n')
print(pandas.json_normalize(input_json, max_level=0), '\n')
print(pandas.json_normalize(input_json, max_level=1))
In the above code:
- The “pandas.json_normalize()” method takes the JSON data and the “max_level=0” parameter value as an argument to normalize the JSON data at level “0”.
- The “pandas.json_normalize()” method is used again to normalize the JSON data at level “1” by assigning the parameter value “max_level=1”.
Output
The JSON data has been normalized according to the specified levels, such as “0” and “1”.
Conclusion
In Python, the “pandas.json_normalize()” method of the “pandas” module is utilized to normalize semi-structured JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) data into a flat table. This method is used with various parameters such as “max_level” to normalize the data based on the passed level value. This write-up has delivered a detailed guide on Panda’s JSON normalize method using numerous examples.