The “Pandas” library provides a powerful data structure named “DataFrame”, which can store tabular data with columns and rows in Python. Many operations can be performed on DataFrame, such as adding or removing data, adding or removing indexes, sorting columns, and others. To access or select specific rows based on some conditions, such as index values, labels, or conditions, several methods are used in Python.
This tutorial will explain a detailed guide on selecting Pandas DataFrame rows based on the index.
How to Get the Pandas DataFrame Rows Based on Indexes in Python?
The following methods are used to get the Pandas DataFrame rows based on the index:
Method 1: Get the Pandas DataFrame Rows Based on Index Using “DataFrame.iloc[]”
The “DataFrame.iloc[]” method selects rows and columns by accepting the index or position value as an argument. This can be used to get the Pandas DataFrame rows based on the index value. Let’s understand it via the following examples:
Example 1: Get Single Row Based on Index Using “DataFrame.iloc[]”
The following code is used to get the single row based on the DataFrame index:
data_value = {'Name':["Anna","Lily","Joseph","Henry"],'Age':[19,21,14,22],'Sex':['F','F','M','M'],'Height':[5.6,4.6,7.1,6.5]}
df = pandas.DataFrame(data_value)
print(df, '\n')
print(df.iloc[2])
In the above code:
- The “pandas” and “numpy” modules are imported.
- The “pandas.DataFrame()” takes the dictionary data as an argument and retrieves the Pandas DataFrame.
- The “df.iloc()” method gets the specified DataFrame row by taking the index value as an argument.
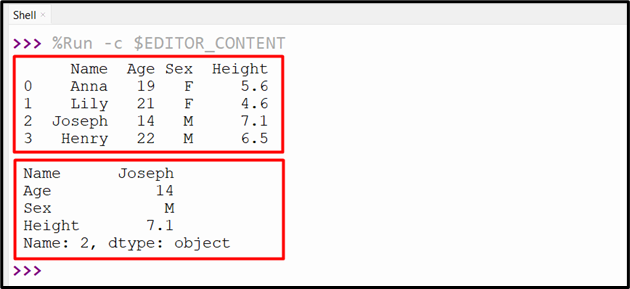
Output
The DataFrame row placed at index “2” is returned to the console.
Example 2: Get Multiple Rows Based on Index Using “DataFrame.iloc[]”
The below code is used to return the multiple rows based on the index:
data_value = {'Name':["Anna","Lily","Joseph","Henry"],'Age':[19,21,14,22],'Sex':['F','F','M','M'],'Height':[5.6,4.6,7.1,6.5]}
df = pandas.DataFrame(data_value)
print(df, '\n')
print(df.iloc[[0,3]])
In the above code:
- The “df.iloc[]” method takes the multiple index value as an argument and returns the DataFrame rows based on that index.
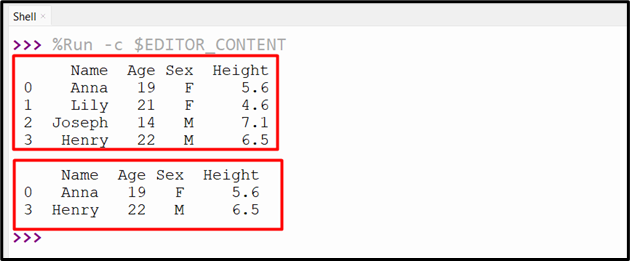
Output
The multiple rows have been retrieved based on the multiple index value.
Example 3: Get Multiple Rows Based on Index Range Using “DataFrame.iloc[]”
We can also get multiple rows based on the specific index range. Here is an example:
data_value = {'Name':["Anna","Lily","Joseph","Henry"],'Age':[19,21,14,22],'Sex':['F','F','M','M'],'Height':[5.6,4.6,7.1,6.5]}
df = pandas.DataFrame(data_value)
print(df, '\n')
print(df.iloc[1:5],'\n')
print(df.iloc[:1],'\n')
print(df.iloc[:3],'\n')
print(df.iloc[-1:],'\n')
In the above code:
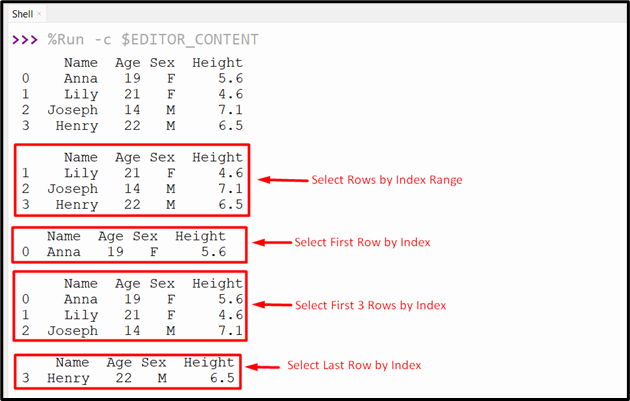
- The “df.iloc[]” method is used multiple times to get Pandas DataFrame rows based on the specific index ranges.
- The “df.iloc[]” method is used to get the first, last and first three rows of Pandas DataFrame.
Output
Method 2: Get the Pandas DataFrame Rows Based on Index Using “DataFrame.loc[]”
The “DataFrame.loc[]” method is used to select rows based on the index by accepting label(s) or a Boolean array as an argument. Let’s utilize this method to get the Pandas DataFrame rows based on the index value.
Example 1: Get Single Row Based on Index Label Using “DataFrame.iloc[]”
The below example is used to get a single row based on the index label:
data_value = {'Name':["Anna","Lily","Joseph","Henry"],'Age':[19,21,14,22],'Sex':['F','F','M','M'],'Height':[5.6,4.6,7.1,6.5]}
df = pandas.DataFrame(data_value,index=['a','b','c','d'])
print(df, '\n')
print(df.loc['c'])
In the above code:
- The “pandas” module is imported.
- The “pandas.DataFrame()” function takes the dictionary data and index labels as arguments and retrieves the Pandas DataFrame.
- The “df.loc[]” method takes the index label “c” as an argument and retrieves the DataFrame rows.
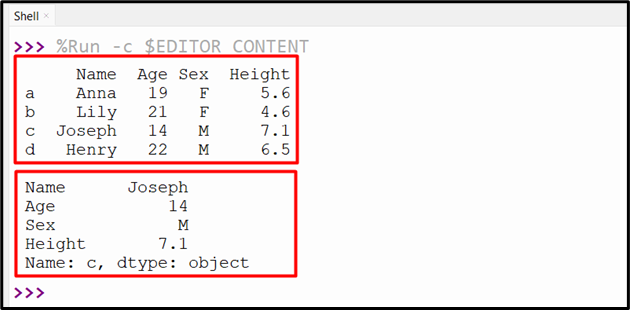
Output
The DataFrame row based on the index label has been retrieved.
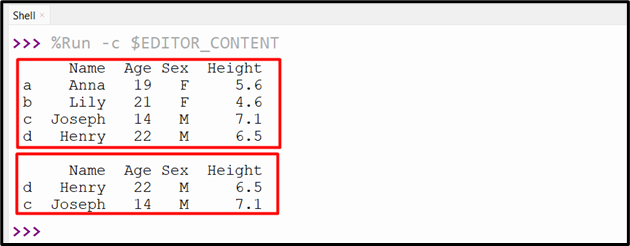
Example 2: Get Multiple Rows Based on Index Label Using “DataFrame.loc[]”
Let’s overview the below code:
data_value = {'Name':["Anna","Lily","Joseph","Henry"],'Age':[19,21,14,22],'Sex':['F','F','M','M'],'Height':[5.6,4.6,7.1,6.5]}
df = pandas.DataFrame(data_value,index=['a','b','c','d'])
print(df, '\n')
print(df.loc[['d','c']])
In the above code:
- The “df.loc[]” method takes the multiple index labels such as “d” and “c” as an argument and retrieves the specified DataFrame rows.
Output
The multiple rows have been retrieved successfully.
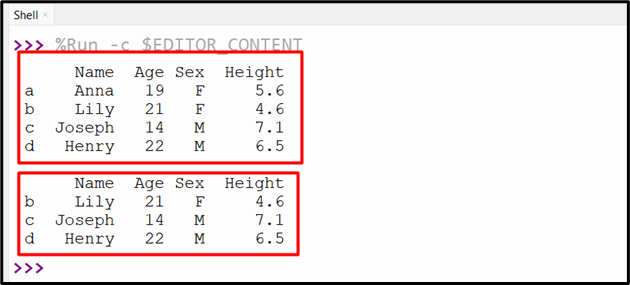
Example 3: Get Rows Between Index Labels Using “DataFrame.loc[]”
Here is the code to get rows between index labels:
data_value = {'Name':["Anna","Lily","Joseph","Henry"],'Age':[19,21,14,22],'Sex':['F','F','M','M'],'Height':[5.6,4.6,7.1,6.5]}
df = pandas.DataFrame(data_value,index=['a','b','c','d'])
print(df, '\n')
print(df.loc['b':'d'])
In the above code:
- The “df.loc[]” method takes the index range “b:d” as an argument and retrieves the multiple rows based on the specific range.
Output
The multiple rows have been retrieved successfully.
Conclusion
The “DataFrame.iloc[]” and the “DataFrame.loc[]” methods of the “Pandas” module are used to get the Pandas DataFrame rows based on the index. The “iloc[]” method takes the index integer value, and the “loc[]” method accepts the index label to get the single or multiple rows of DataFrame. This Python guide presented a detailed tutorial on selecting Pandas DataFrame rows based on the index value using numerous examples.