Machine learning algorithms or any data structure like DataFrame in Python are used with different types of data, such as numerical and categorical variables. Numerical variables are values that can be measured or counted, while categorical variables are values that belong to a specific category, such as color, gender, or occupation. Sometimes, we need to convert categorical values to int values to perform some numerical operations on the category’s values of DataFrame. In Python, various methods are used to accomplish this task.
This blog explains a comprehensive tutorial on converting categorical values of Pandas DataFrame to integers values using multiple examples.
How to Convert Categorical Values to Integers in Pandas?
To convert categorical values to integers in Pandas DataFrame, the below methods are used in Python:
Method 1: Convert Categorical Values to Integers Using “DataFrame.replace()”
The “replace()” method converts the categorical values of the Pandas DataFrame column to integers. Let’s overview the below code to understand this:
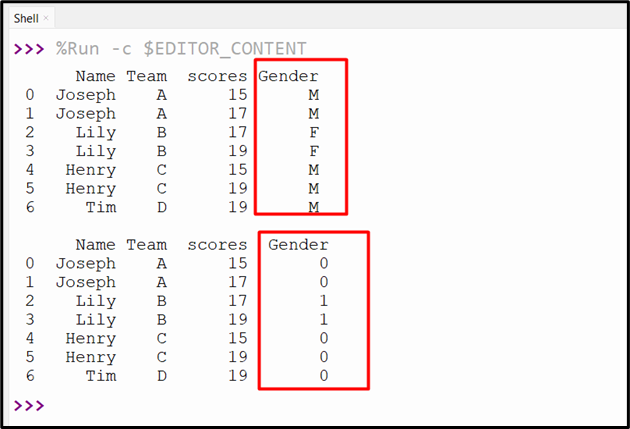
df = pandas.DataFrame({'Name': ['Joseph', 'Joseph', 'Lily', 'Lily', 'Henry', 'Henry', 'Tim'],'Team': ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'C', 'C', 'D'],'scores': [15, 17, 17, 19, 15, 19, 19],'Gender': ['M', 'M', 'F', 'F', 'M', 'M', 'M']})
print(df, '\n')
df['Gender']=df['Gender'].replace(['M', 'F'],[0, 1])
print(df)
In the above code:
- The “pandas” module is imported, and the DataFrame is created.
- The “df.replace()” method is used to replace the categorical values of the “Gender” column with integers “0” and “1”.
Output
The categorical values of the specified column have been converted to int values.
Method 2: Convert Categorical Values to Integers Using “pd.factorize()”
The “pandas.factorize()” method retrieves the numeric representation of the specified array in Python. This method can be utilized to convert the DataFrame categorical values to integers.
Example 1: Convert Single Categorical Column Values of DataFrame to Integers
Let’s examine the below code:
df = pandas.DataFrame({'Name': ['Joseph', 'Joseph', 'Lily', 'Lily', 'Henry', 'Henry', 'Tim'],'Team': ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'C', 'C', 'D'],'scores': [15, 17, 17, 19, 15, 19, 19],'Gender': ['M', 'M', 'F', 'F', 'M', 'M', 'M']})
print(df, '\n')
df['Gender']=pandas.factorize(df['Gender'])[0]
print(df)
In the above code:
- The “pandas” module is imported.
- The “pandas.DataFrame()” method creates a DataFrame with multiple columns.
- The “pandas.factorize()” method is used to convert the “Gender” column values into numeric or integers values.
The DataFrame column value has been converted into integers values.
Example 2: Convert Multiple Categorical Column Values of DataFrame to Integers
We can also utilize the “pandas.factorize()” method along with the “apply()” method to convert the entire or multiple DataFrame columns into integer values. Here is an example code:
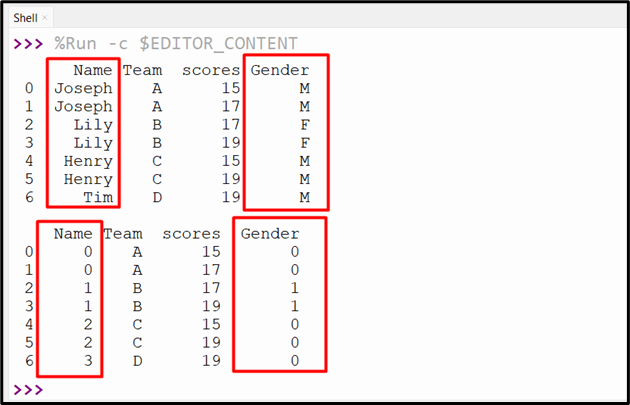
df = pandas.DataFrame({'Name': ['Joseph', 'Joseph', 'Lily', 'Lily', 'Henry', 'Henry', 'Tim'],'Team': ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'C', 'C', 'D'],'scores': [15, 17, 17, 19, 15, 19, 19],'Gender': ['M', 'M', 'F', 'F', 'M', 'M', 'M']})
print(df, '\n')
df[['Name', 'Gender']] = df[['Name', 'Gender']].apply(lambda x: pandas.factorize(x)[0])
print(df)
In the above code:
- The “df.apply()” method takes the “lambda” function as an argument and applies this function to each specified column’s values.
- The “pandas.factorize()” method is defined in the lambda function to convert the specified column values to integer values.
Output
The categorical values of the multiple columns have been converted/transformed into integers.
Method 3: Convert Categorical Values to Integers Using “LabelEncoder()”
The “LabelEncoder()” method can also be used to convert the value of the non-numerical label to numeric labels. This method is utilized to convert the DataFrame categorical values to integers using the below code:
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
df = pandas.DataFrame({'Name': ['Joseph', 'Joseph', 'Lily', 'Lily', 'Henry', 'Henry', 'Tim'],'Team': ['A', 'A', 'B', 'B', 'C', 'C', 'D'],'scores': [15, 17, 17, 19, 15, 19, 19],'Gender': ['M', 'M', 'F', 'F', 'M', 'M', 'M']})
print(df, '\n')
df['Gender']=LabelEncoder().fit_transform(df['Gender'])
print(df)
Here in this code:
- The “pandas” module and the “LabelEncoder” method from the “sklearn” module are imported.
- The “LabelEncoder()” method is utilized along with the “fit_transform()” method to convert the categorical values to integers and fits the transformed/modified values.
Output
The categorical values of the column “Gender” have been converted into integers.
Conclusion
The “DataFrame.replace()”, “pandas.factorize()”, and the “LabelEncoder()” methods are used to convert categorical values to integers in Pandas DataFrame. These methods can efficiently convert the non-numerical values of specified DataFrame columns to integers. This article provided a detailed guide on converting the categorical values to int using various examples.