This guide will cover the following examples:
- Reset the Sequence Value
- Change the Minimum Values of the Sequence
- Change the Maximum Values of the Sequence
- Change the Caching Size of the Sequence
- Set the Size and Order of the Cache Sequence
- Set the Sequence to Generate Descending Values
- Change the Increment Value of the Sequence
- Alter the Sequence to Enable Cycle Option
- Alter the Sequence to Disable Cycle Option
- Alter the Sequence to Modify Multiple Options
Reset the Sequence Value
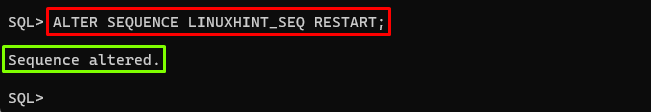
To reset the sequence value or to restart the sequence value from its starting value the “ALTER SEQUENCE” command with the “RESTART” clause can be used. The example is given below:
In the above command, “LINUXHINT_SEQ” represents the sequence name.
Output
The output shows that the sequence has been reset.
Change the Minimum Values of the Sequence
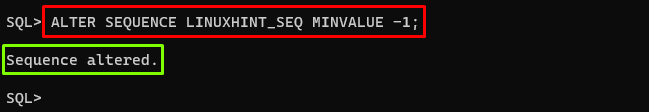
When a sequence is created in Oracle, by default its minimum value is set to 1. The “ALTER SEQUENCE” command with the “MINVALUE” clause can be utilized to change the minimum value of the sequence. The example is given below:
In this example, the new minimum value is -1.
Output
The output showed the minimum value has been changed.
Change the Maximum Values of the Sequence
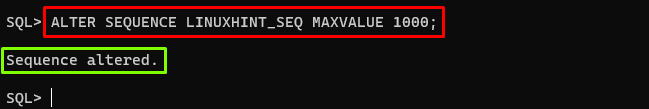
By default, the maximum value of an Oracle sequence is “10^27 – 1”, which is the largest possible value for a 38-digit decimal number. To change the maximum sequence value, the “ALTER SEQUENCE” command with the “MAXVALUE” clause can be used. The example is provided below:
In the above example, the new maximum value will be 1000.
Output
In the screenshot, it can be seen that the maximum value has been changed.
Note: In the above example, the sequence will stop generating values after it reaches 1000, and any attempts to generate a value beyond that point will result in an error.
Change the Caching Size of the Sequence
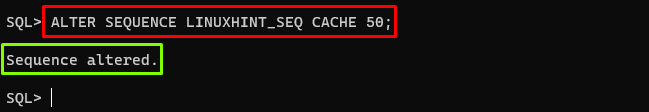
The cache size decides the number of sequence numbers that are pre-allocated and stored in memory for faster access. To change the cache sizing of the sequence, use the “CACHE” clause with the “ALTER SEQUENCE” command. An example is given below:
In the above example, the cache size of the sequence is set to 50. It means the sequence number 50 will be pre-allocated at a time for faster access.
Output
The output depicts that the cache size has been changed.
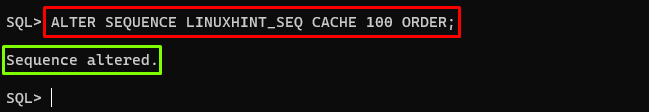
Set the Size and Order of the Cache Sequence
To set the sequence cache size and generate the sequence numbers in order, use the “ORDER” and “CACHE” clauses with the “ALTER SEQUENCE” command. Here is an example:
In this example, the new cache size value will be 100.
Output
The output displayed that the changes have been made to the sequence.
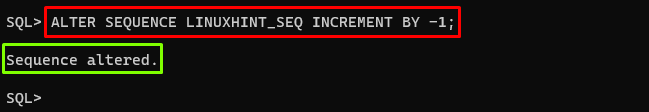
Set the Sequence to Generate Descending Values
The interval between sequence numbers is determined by the increment number. The increment value is set to 1 by default, which means that the next number in the series is returned each time when the sequence is called. When the increment is set to -1, the sequence generates integers in descending order.
To set the sequence to generate descending values, use the “INCREMENT BY” with the “ALTER SEQUENCE” command and set the value to -1. The example is given below:
In this example, the value is -1, which means each time the sequence is called, the previous number in the sequence is returned.
Output
The output depicts that the sequence has been set to generate descending values.
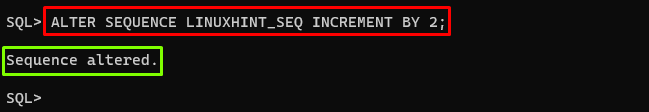
Change the Increment Value of the Sequence
To change the increment value of the sequence, use the “INCREMENT BY” with the “ALTER SEQUENCE” command and set the value accordingly. The example is provided below:
In this example, the value is 2, which means each time the sequence is called, the next number in the sequence will be incremented by 2.
Output
The output displayed that the sequence has been altered accordingly.
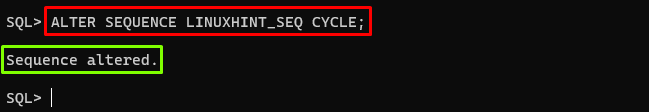
Alter the Sequence to Enable Cycle Option
When the cycle option is enabled for a sequence, the sequence will wrap around and start again from the beginning (MINVALUE) once it reaches the maximum value (MAXVALUE). To enable this option, use the “CYCLE” clause with the “ALTER SEQUENCE” command. The example is given below:
Output
The output displayed the cycle option has been enabled.
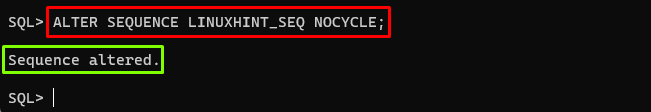
Alter the Sequence to Disable Cycle
When the cycle option is disabled for a sequence, the sequence will stop generating values once it reaches its maximum value (MAXVALUE) or minimum value (MINVALUE), depending on the order of generation. To disable this option, use the “NOCYCLE” clause with the “ALTER SEQUENCE” command. The example is provided below:
Output
The output showed that the cycle option has been disabled.
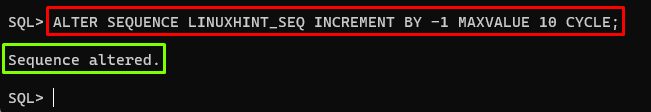
Alter the Sequence to Modify Multiple Options
Type the given command to set the sequence to have a negative increment by -1, a maximum value of 10, and a cycle option enabled:
Output
The output showed that the changes had been made to the sequence successfully.
Conclusion
In Oracle, the “ALTER SEQUENCE” command allows you to change the attributes of a sequence by resetting the sequence value, changing the minimum and maximum values, increment value, caching size, ordering, and enabling or disabling the cycle option. These changes are helpful in many kinds of circumstances, such as when you need to alter the starting value of a sequence or adjust the caching size for better performance. This post has explained various use cases of the ALTER SEQUENCE command using practical examples.