Prerequisite:
You have to complete the following tasks before practicing this tutorial:
A. Run the following command from the terminal to create an SQLite file named “shop.db” that contains the database content:
B. Run the following SQL statement to create a table named “items”. The table contains three fields and a primary key:
id TEXT PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT NOT NULL UNIQUE,
price INTEGER NOT NULL);
C. Run the following SQL statement to insert multiple records into the “items” Three records are inserted into the table:
VALUES
('p-01', 'Pen', 10),
('p-02', 'Pencil', 15),
('p-03', 'Rular', 30);
Different SQLite Commands to Access the SQLite Database
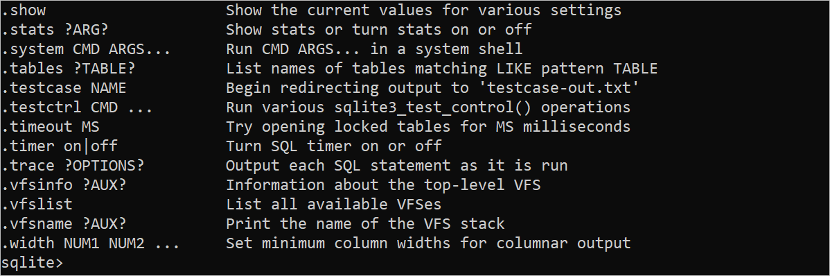
You can get the list of all necessary SQLite commands by executing the following command:
Some portions of the output of the “.help” command are shown here. The uses of the commonly used SQLite commands are shown in the next part of this tutorial.
1. Check the Main Database Path
Run the following SQLite command to check the current database name with the path information and read-write permission:
According to the output, the “shop.db” SQLite database file is stored in the /home/fahmida path.
2. Check the List of the Tables in the Database
Run the following SQLite command to check the list of the tables of the current database:
One table named “items” is created in the “shop.db” database file that is shown in the output.
3. Display the Formatted Structure of the Table
The “.header” SQLite command is used to enable or disable the header option of the output. Run the following SQLite command to enable the header part of the output:
The “.mode” SQLite command is used to define the looks of the output. Run the following command to display the column-based output:
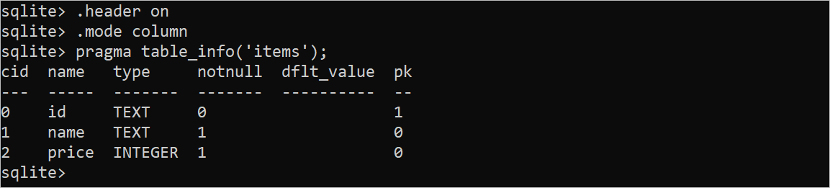
Run the following command to display the structure of the “items” table in tabular form:
The structure of the “items” table is shown in the following output:
4. Display the Table Content in Tabular Format
Three records are inserted in the first part of the tutorial. If the column mode for the output is not set before, run the following SQLite command:
Run the following SQL command to retrieve all records from the “items” table:
The following output appears after executing the commands. Three records of the “items” table are shown with the table header:
5. Display the Table Content with Specific Width
If no column width is set for the output, each column value is displayed with 10 characters wide by default. If the content of the column is too long, the value is shortened. The “.width” command of SQLite is used to set the custom width of the column in the output.
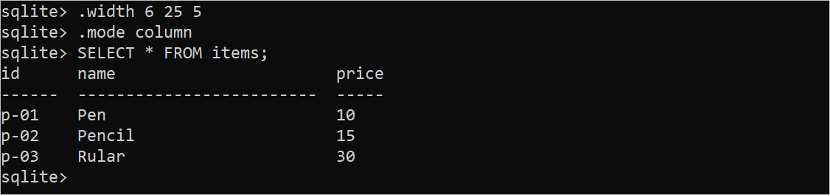
Run the following SQLite command to set the width of the first column to 6 characters, the second column to 25 characters, and the third column to 5 characters:
Run the following SQLite command to set the mode of the output to the column:
Run the following SQL command to read all records from the “items” table:
The following output shows the records of the “items” table based on the width that is set by the “.width” command.
6. Display the Table Content in CSV Format
The content of the SQLite table can be displayed in the CSV format using the “.mode” and “.separator” commands.
Run the following SQLite command to print the output in the list format:
Run the following SQLite command to print the output by separating the columns with a comma (,):
Run the following SQL command to read all records from the “items” table:
The output of the commands is printed in the CSV format.
7. Write the Output into the File
In the previous examples, the output of the commands is printed in the terminal. But the output can be saved into a file using the “.output” SQLite command.
Run the following command to print the output into the “items_data.txt” file:
Run the following SQLite command to print the output by separating the columns with a comma (,):
Run the following SQL command to read all records from the “items” table:
No output is printed here because the output of the SELECT command is written in the “items_data.txt” file:
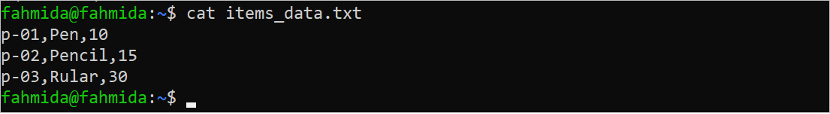
Run the following command to check the content of the “items_data.txt” file:
According to the output, the “items_data.txt” file contains the records of the “items” table.
8. Terminate from the SQLite
Run the following command to exit from the sqlite3:
Conclusion
The methods of opening a new or existing SQLite file and performing different types of database operations using the SQLite commands are shown in this tutorial.