Using Docker Compose, you can create multiple containers and add local or official images such as “Nginx”. Inside a Docker Container, you can install packages, add or remove various settings of that specific container. In this post, we will talk about how to use Nginx with Docker Compose.
To use Nginx with Docker Compose, you need to install and enable Docker and Docker Compose on your system. Follow the post to proceed with the installation procedure.
How to install Docker on CentOS
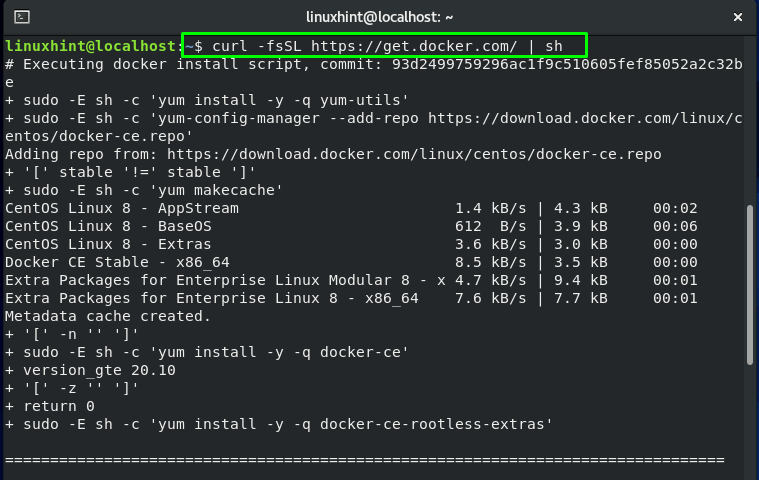
Firstly, press “CTRL+ALT+T” to open the terminal. After that, execute the below-given command for adding the official Docker repository and downloading its latest version:
The above-given error-free output signifies that Docker is successfully installed on your system. Now start the Docker service using the “systemctl” command:
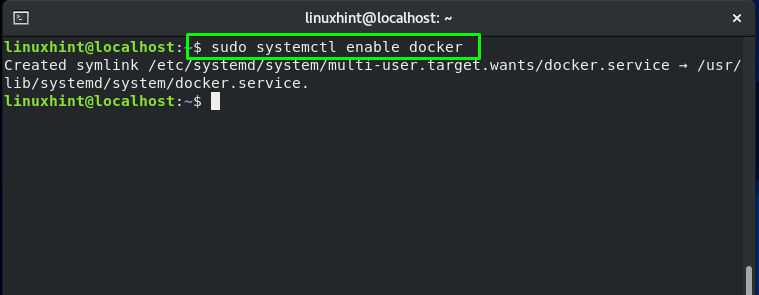
To ensure that the Docker service runs at every server reboot, utilize this command in your terminal:
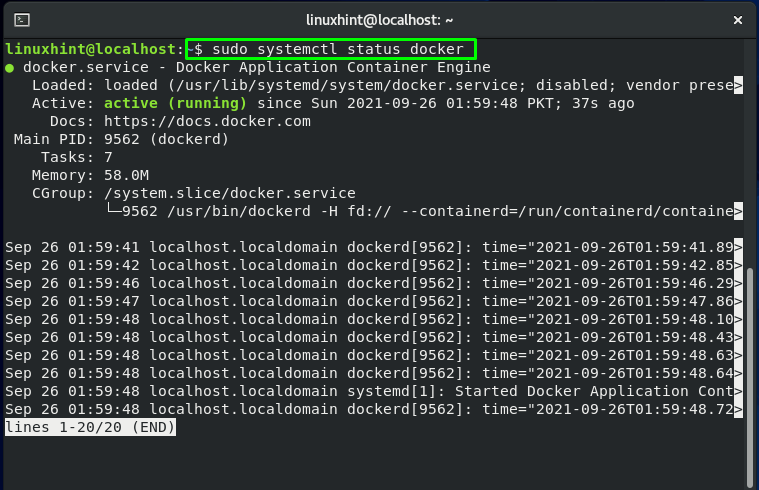
Now, verify if the Docker is running on your system or not:
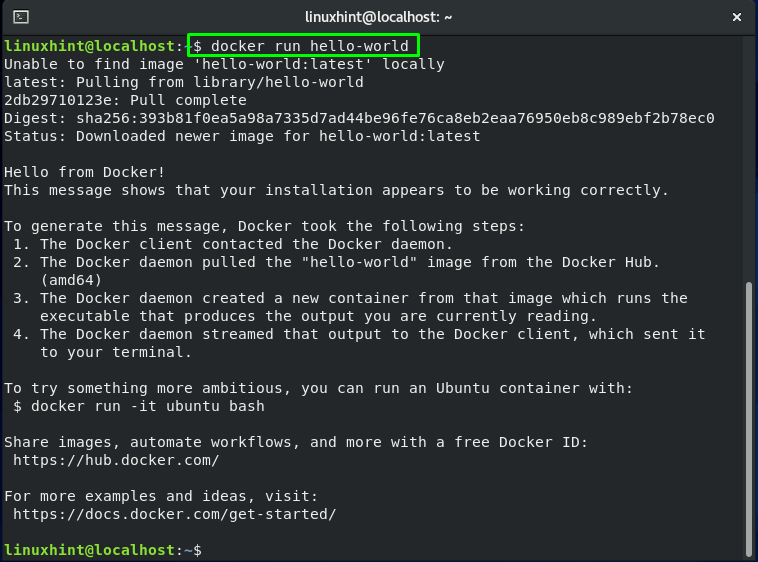
Or you can also pull an image such as “hello-world” from the Docker Hub globally:
How to install Docker Compose on CentOS
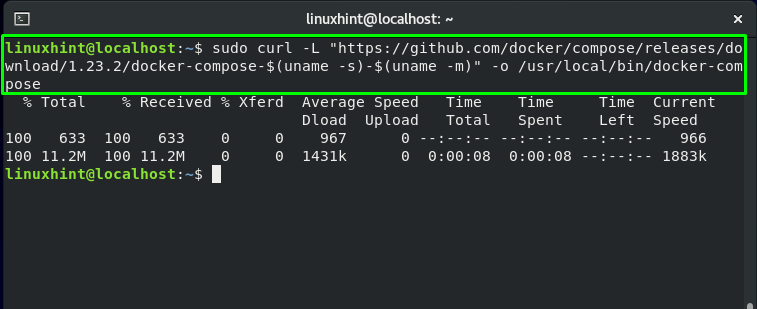
You can install Docker Compose on our system, by executing the below-given command:
This command will download the latest version of Docker Compose and store it in the “/usr/local/bin/docker-compose” directory:
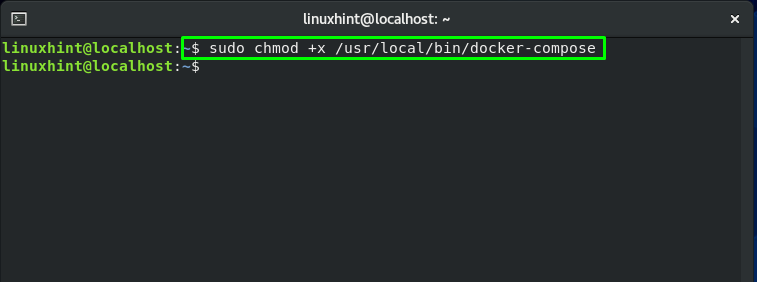
Now, we will set the permission of the downloaded docker-compose with the help of the “chmod” command. The execution of the below-given will make the docker-compose file binary executable:
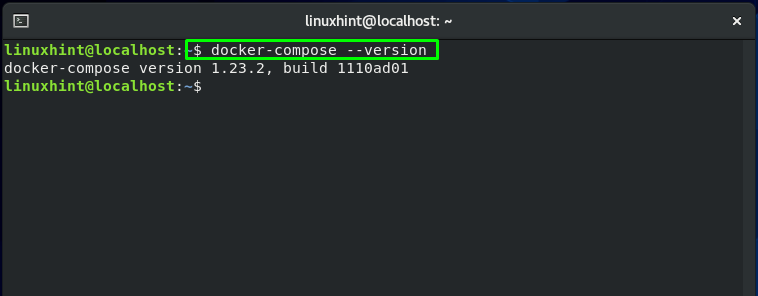
Check out the version of the installed Docker Compose. This action will also verify the existence of Docker Compose on your CentOS system:
How to use Nginx with Docker Compose
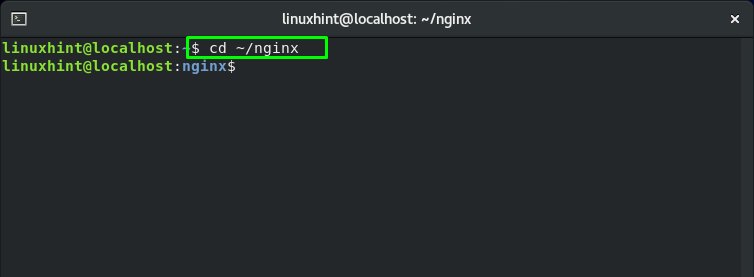
In this section, we will demonstrate how you can use Nginx with Docker Compose. For this purpose, firstly, we will create a “nginx” directory using the “mkdir” command. The “mkdir” command is utilized for creating single or multiple directories in a Linux-based system such as CentOS. Execute the below-mentioned command for creating a “nginx” directory in your system:
Now, move into the “Nginx” Directory with the help of the “cd” command:
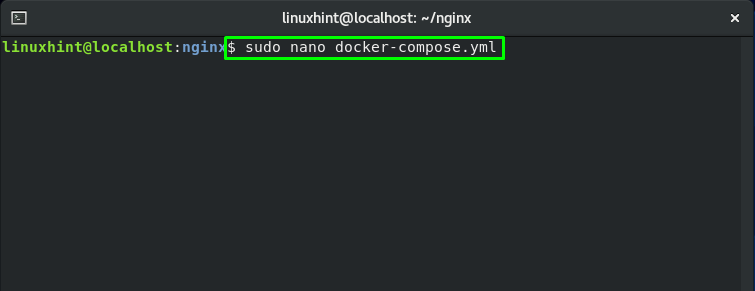
Utilize your nano editor to create a “docker-compose.yml” file:
Now, add the following lines of code in the opened “docker-compose.yml” file:
image: nginx
These lines will add the “Nginx” image to the Docker Container:
Next, press “CTRL+O” to save the content in the docker-compose.yml file:
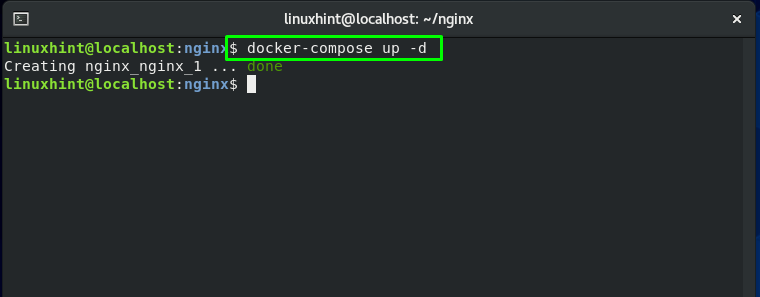
Now, execute the “docker-compose up” to start Nginx as a background process in our system:
Here, the “-d” option is added to activate the detached mode. This mode will execute the containers in the background:
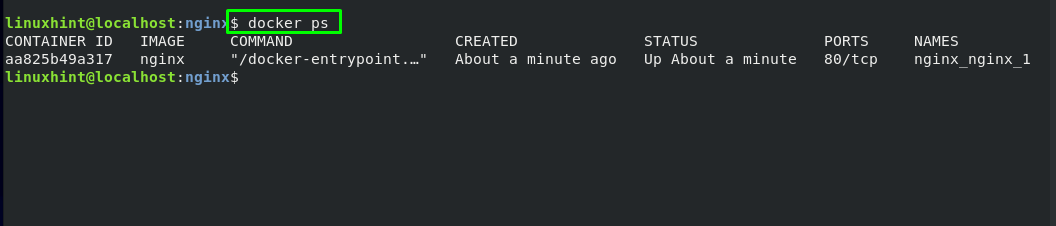
To verify if Nginx is running as a background process, list the Docker images by executing the “docker ps” command:
From the output, note the CONTAINER ID of the Nginx image on your system:
Now, verify if the “Nginx” is running on your system by browsing “http://localhost” in your browser:
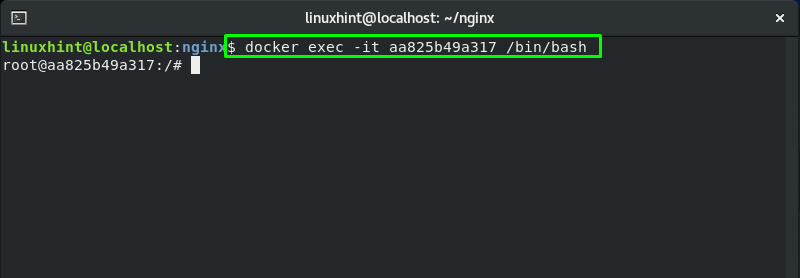
If you want to add, modify or remove something inside your Nginx container, then utilize its CONTAINER ID that can be retrieved from the above-given “docker ps” command.
In our case, the CONTAINER ID is “aa825b49a317“. Now, we will execute the “docker exec” command for starting a shell inside of your Nginx container:
Here, the “-t” option is added for opening a terminal and the “-i” option for making it interactive. Whereas “/bin/bash” will open a bash shell in the running Nginx container:
To exit the current Nginx Container shell, type exit in the terminal:
Conclusion
Docker-compose is a command-line utility that permits its user to deploy multiple Docker containers and applications with a single command. You can link multiple containers together and deploy an application in Docker. Docker Compose utilizes a “.yml” file for defining a stack. In this post, we have shown you how to install Docker and Docker Compose on CentOS. Moreover, we have also demonstrated to you how to use Nginx with Docker Compose.