It results in establishing an empty link that stays until it reaches the inactive timeout value. Flooding a server with such empty connections will trigger a denial-of-service (DoS) condition that results in a LAND attack. The article provides a brief overview of the LAND attack, its purpose, and how to prevent it with timely detection.
Background
A LAND attack aims to make a device unusable or slow it down by overloading the system’s resources so that no authorized users can use it. Most of the time, the purpose of these attacks is to target a specific user to limit his access from making outgoing network connections. Land attacks can also target an entire enterprise that prevents outgoing traffic from reaching the network and restricts the incoming traffic.
Land attacks are comparatively easier to carry out than obtaining remote administrator access to a target device. Due to this reason, these kinds of attacks are popular on the internet. They can be both intentional or unintentional. One of the main reasons for LAND attacks is an unauthorized user intentionally overburdening a resource or when an authorized user does something unwittingly that allows services to become inaccessible. These kinds of attacks primarily depend on flaws in the TCP/IP protocols of a network.
Detailed LAND Attack Description
This section details an example of carrying out a LAND attack. For this purpose, configure the monitoring port of the switch and then generate the attack traffic using the IP packet builder tool. Consider a network that connects three hosts: one represents the Attack host, one is the victim host, and one is wired to the SPAN port, i.e., monitoring port for tracking the network traffic shared between the other two hosts. Suppose the IP addresses of hosts A, B and C are 192.168.2, 192.168.2.4, and 192.168.2.6, respectively.
To configure the switch monitoring port or a SPAN port, first of all, connect a host to the console port on the switch. Now type these commands in the hosts terminal:
Each switch vendor specifies its own series of steps and commands to configure a SPAN port. To elaborate further, we will use the Cisco switch as an example. The above commands inform the switch to track the incoming and outgoing network traffic, shared between the other two hosts, and then sends a copy of them to host 3.
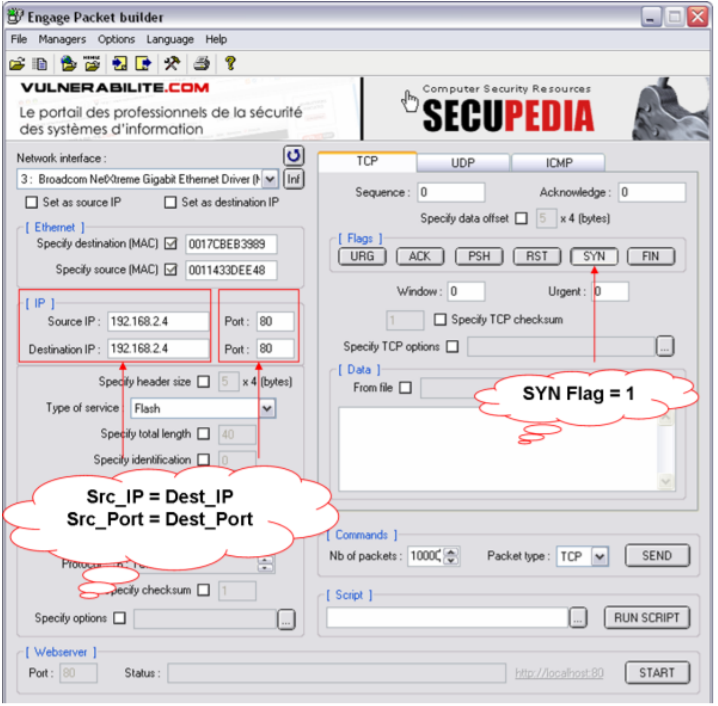
After the switch configuration, generate the land attack traffic. Use the target host’s IP and an open port as both source and the destination to generate a fake TCP SYN packet. It can be done with the help of an open-source command-line utility like FrameIP packet generator or Engage Packet Builder.
The screenshot above shows the creation of a fake TCP SYN packet to utilize in the attack. The generated packet has the same IP address and the port number for both the source and the destination. Moreover, The destination MAC address is the same as the MAC address of the target host B.
After generating the TCP SYN packet, ensure that the required traffic has been produced. The following screenshot shows that host C uses View Sniffer to catch the shared traffic between two hosts. It remarkably shows that the Victim host (B in our case) has been overflowed with Land attack packets successfully.
Detection and Prevention
Multiple servers and Operating systems like MS Windows 2003 and Classic Cisco IOS software are vulnerable to this attack. In order to detect a land attack, configure the land attack defense. By doing so, the system may sound an alarm and drop the packet whenever the attack is detected. To enable detection of land attacks, first of all, configure interfaces and assign IP addresses to them as shown below:
After configuring the interfaces, configure the security policies and the security zones to “trustZone” from “untrustZone.”
Now configure the syslog using the following commands and then commit the configuration:
Summary
Land attacks are interesting as they are extremely deliberate and require humans to execute, sustain, and monitor them. Stopping these kinds of Network Denial attacks would be impossible. It is always possible that an attacker will send so much data to a target computer that it won’t process it.
Increased network speed, vendor fixes, firewalls, Intrusion Detection and Prevention program (IDS/IPS) tools or hardware equipment, and proper network setup can help reduce the effects of these attacks. Most of all, during the process of protecting the operating system, it is recommended that the default TCP/IP stack configurations be modified according to the security standards.