In this blog, we will illustrate the method to install Memcached in Windows.
How to Install Memcached in Windows?
Memcached is a general-purpose memory caching solution that reduces the stress on databases and functions similarly to caching and sessions. In order to install Memcached in Windows, follow the below provided instructions.
Step 1: Download Memcached Setup
First, download the Memcached zip setup using the below-provided link according to your system specification. As we have downloaded the setup for “64-bit system”:
https://static.runoob.com/download/memcached-win64-1.4.4-14.zip
//For 32bit system
https://static.runoob.com/download/memcached-1.2.6-win32-bin.zip
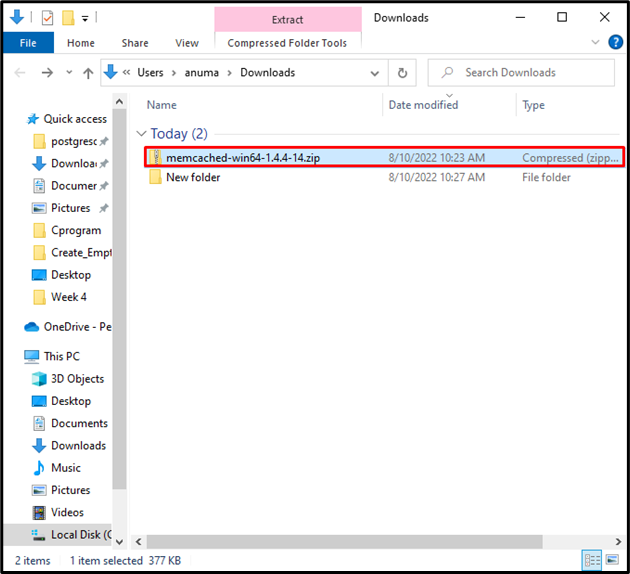
The above-provided link will automatically download the Memcached zip setup and will save it in “Downloads” directory:
Step 2: Unzip the Memcached Setup File
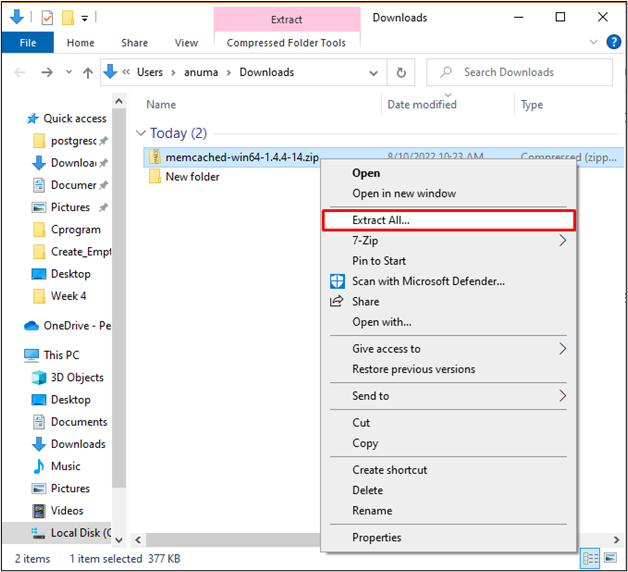
Open the “Downloads” directory and right-click on the Memcached zip setup file. Then choose “Extract All” from the displayed options:
Choose the location where the extracted Memcached setup will be saved:
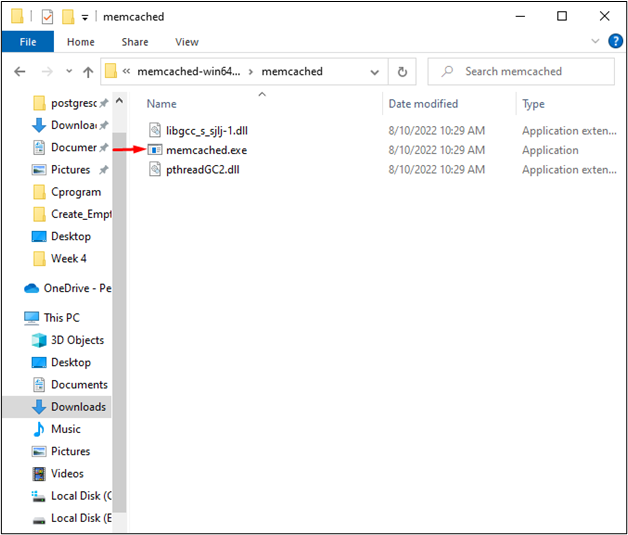
Open the extracted folder, and you will find the Memcached execution file:
Step 3: Copy Path
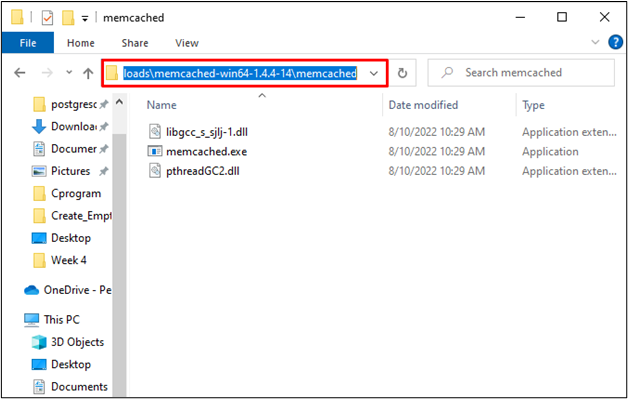
Copy the path from the “Address” bar where you have found the “memcached.exe” file:
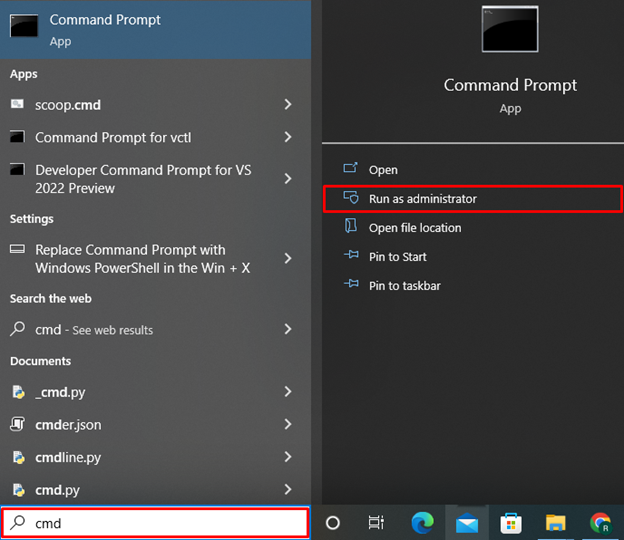
Step 4: Open Windows Command Prompt
Type “cmd” in the “Startup” menu and open the Command Prompt from the search result:
Step 5: Install Memcached
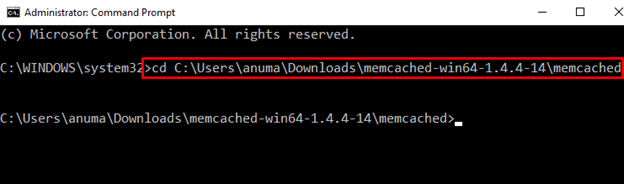
Use the “cd” command to open the directory where you have found the “memcached.exe” file:
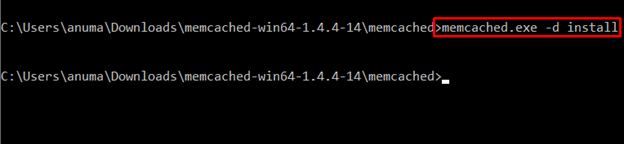
Then, execute the below-provided command to install Memcached on the system:
The successful execution of the command shows that the Memcached has been installed successfully on the system:
Step 6: Start Memcached Service
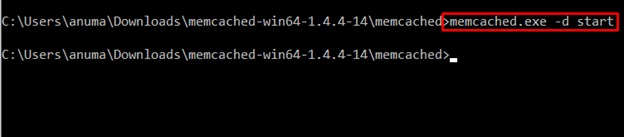
Next, start Memcached services using the below-given command:
Step 7: Verify Memcached Installation
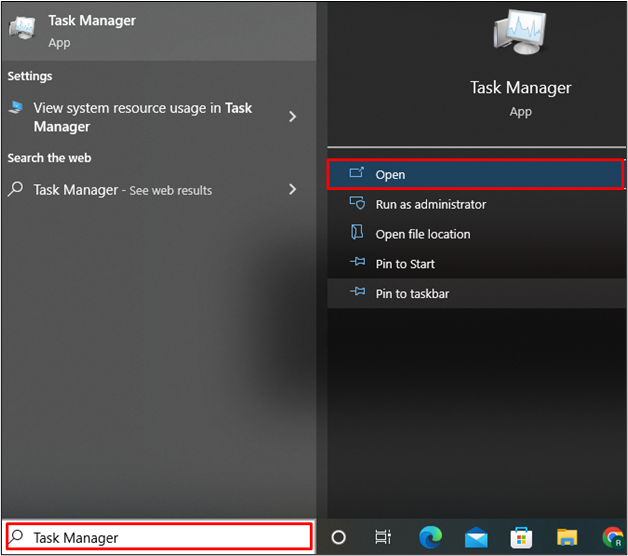
In order to verify Memcached installation and check whether the Memcached service is activated or not, open the Task Manager application by searching “Task Manager” in the “Startup” menu:
From the “Services” menu, you can see that Memcached is successfully installed and running on the system:
How to Uninstall Memcached From Windows?
Let’s check out the method to uninstall Memcached from the windows. The uninstallation of Memcached comprises the following steps:
Step 1: Open Command Prompt
Type “cmd” in the “Startup” menu to open the Command Prompt:
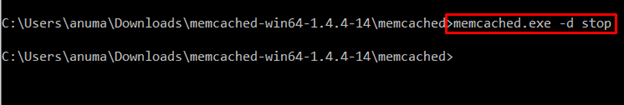
Step 2: Stop Memcached Service
Before uninstallation, stop the Memcached service via the following command:
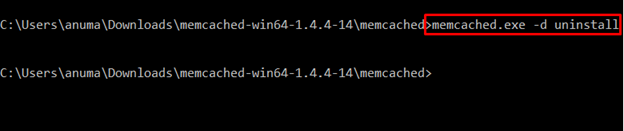
Step 3: Uninstall Memcached
Now uninstall Memcached from the system using the below-provided command:
Step 4: Verify Memcached Uninstallation
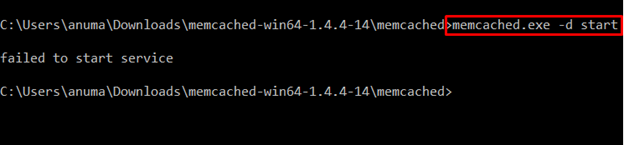
Let’s verify the Memcached service uninstallation. To do so, we try to start the Memcached service via the following command:
The output “failed to start service” indicates that we have successfully uninstalled Memcached from Windows:
We have briefly demonstrated the installation and uninstallation procedure of Memcached in Windows.
Conclusion
Firstly, download either the 32-bit or 64-bit setup file of Memcached. Then, go to the Windows Command Prompt and open the folder where the memcached.exe file exists. Then run the “memcached.exe -d install” command to install Memcached on the system. This post has demonstrated the simplest way to install Memcached on Windows.