In this technologically rich era, you require a high-speed network connection to ensure data’s efficacy over the internet. Multiple factors contribute to the successful transmission of data, and bandwidth is one of the critical success factors to be considered; Bandwidth tells how much data or information is being transmitted in a specified amount of time over the specific internet connection? Speed is another factor that is sometimes mistakenly assumed as bandwidth; both are related to data transmission reported over the network, but differently. Bandwidth determines how much, and speed tells how fast the information is flowing. There are various measuring units for bandwidth, majorly they are “bits” and “bytes” (where 1byte=8bits), however, the specified time is “per second“; for instance, measuring would be like “kilobits per second“, “megabits per second“, “gigabits per second“, “terabits per second“, or one can replace bits with bytes.
Majorly, bandwidth can be divided into two categories:
- Symmetrical
- Asymmetrical
Symmetrical: Two things are considered while measuring bandwidth: upload capacity of data flow. The other one is download; symmetrical upload and download volumes of data transmission will be the same.
Asymmetrical: Asymmetrical is quite different; upload and download volumes are not the same. Uploading is usually lower than downloading; your download speed will be greater than uploading in such situations.
What is the importance of Bandwidth?
Bandwidth is essential for your network as, for instance, a highway has six lanes, on a length of 100 meters, up to a hundred vehicles can pass through it, or the route can allow 100 cars. On the other hand, a 3-lane road may not allow 100 vehicles to pass through it. So, the wider the road (greater the bandwidth), the maximum traffic flow (maximum data transmission flow), and vice versa. For better transmission of data over the network, bandwidth should be more outstanding.
How to find apps that are using bandwidth in windows
There are multiple ways you can check the bandwidth used by the programs.
Task Manager
Task Manager is a built-in windows-based tool to manage different tasks and processes currently running on your machine. Open “Task Manager” by using the keyboard shortcut “ctrl+shift+esc“, on opening, seven tabs are available in “Task Manager”:
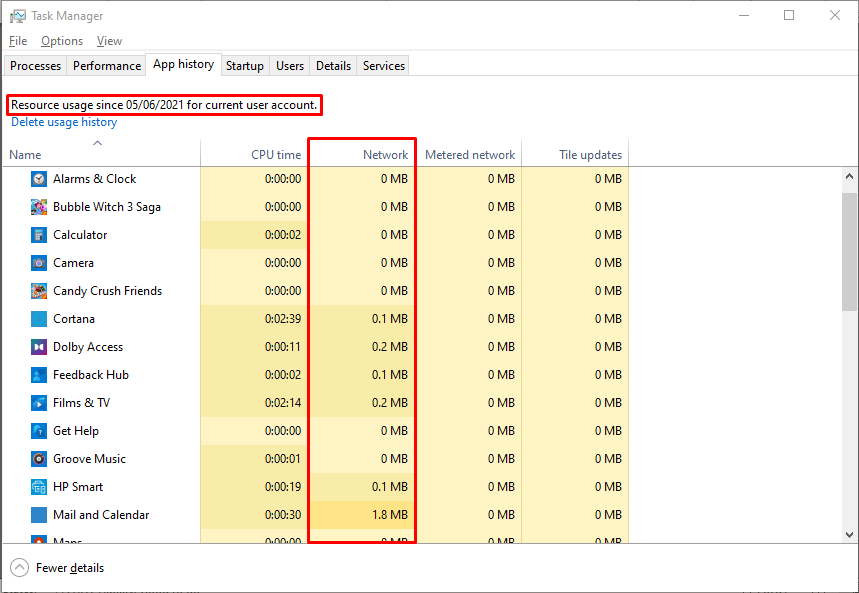
Now you have to switch to a tab named “App history“, there you will find the network usage for each application. This tab shows only a limited number of applications, most of which are built-in apps or downloaded from the Microsoft store.
So, we may consider “Resource Monitor” a better alternative to the more detailed “Task Manager” view for a thorough inspection.
Resource Monitor
One may check the apps using bandwidth and manage it by following how much bandwidth applications use. To monitor the bandwidth using “Resource Monitor”, follow the steps given below:
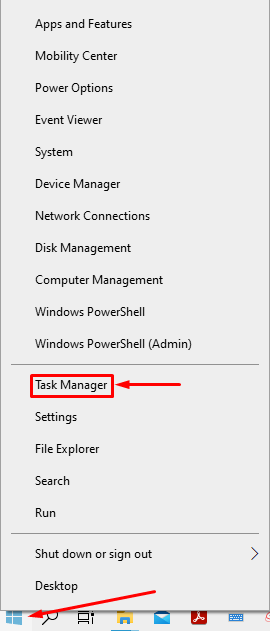
Open task manager by “ctrl+shift+esc,” or you can follow the steps shown below to open task manager; click the right mouse button on the “Start” icon available on “Taskbar”.
Look for the “Task Manager” here and click on it;
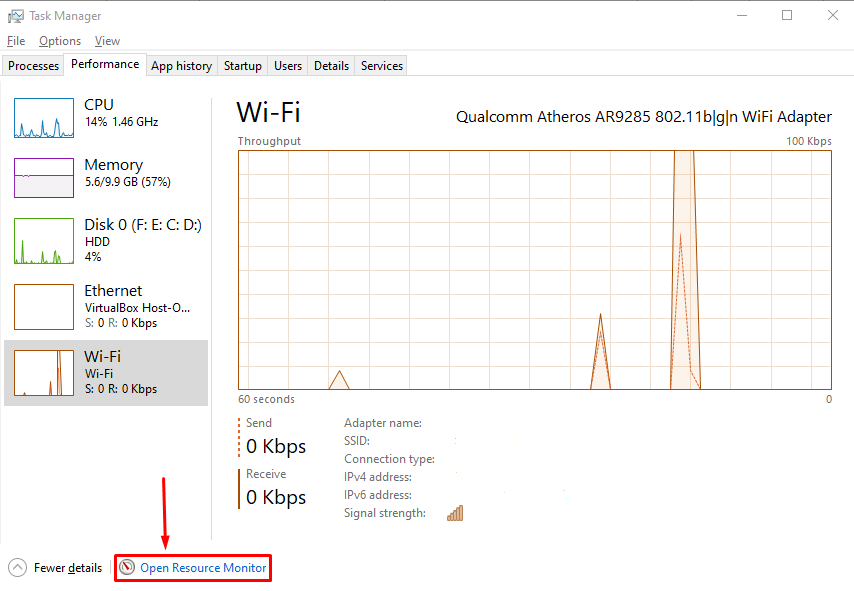
Move to the “Performance” tab, and you will find a window as shown below;
You can see “Open Resource Monitor” at the end of the image;
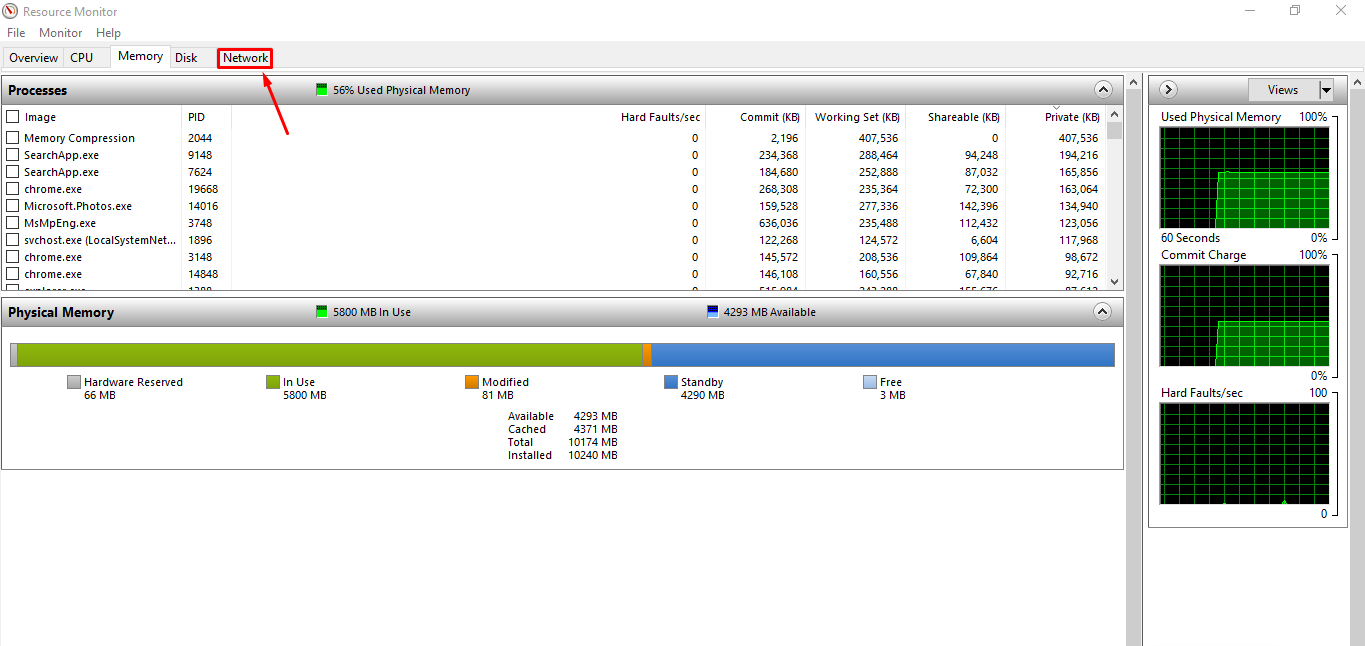
On the opening of “Open Resource Monitor“, you will find multiple tabs there, switch to the “Network” tab,
Once you clicked on the “Network” tab, there are four kinds of monitoring behaviors available:
Processes with Network Activity
- Network Activity
- TCP Connections
- Listening Ports
We will discuss them one by one in detail:
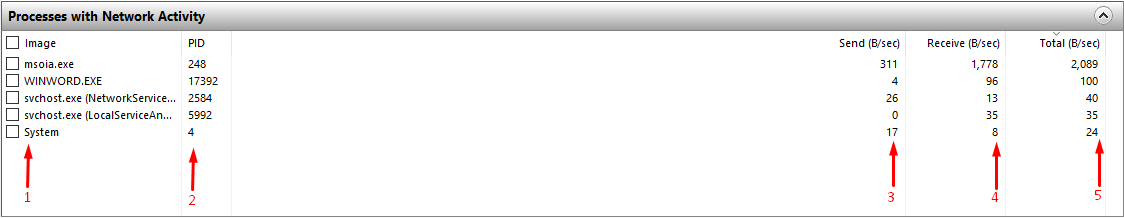
Processes with Network Activity: The initial display of this monitor is shown below; it has five columns, the “1st” column shows the operations,” 2nd” displays processes id’s (“PID“). Moreover, the “3rd” and “4th” columns indicate the number of bytes(B) sent and received per second, respectively; however, the” 5th” column shows the total number of bytes consumed by each process.
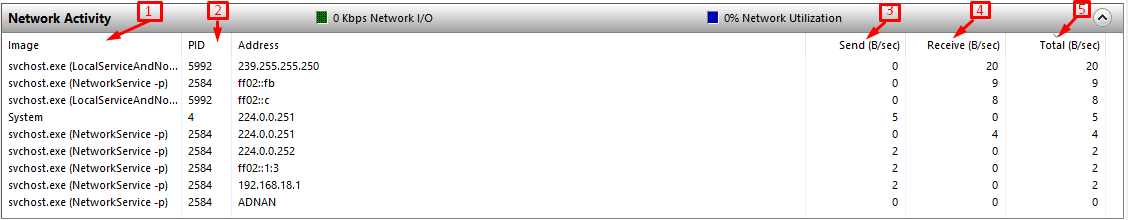
Network Activity: This section contains one extra column than the above section (Processes with Network Activity); it shows the “Address” of each process. Another difference is that it includes two others, “Network I/O” and “Network Utilization“, representing how much network is being utilized and how much-loaded network is, respectively.
TCP Connections: The third section is quite different from the above two, “Local Address” represents the overcrowded network adapters, the next column shows the port number where there is communication activity, quality of internet connection is defined on several packet loss, and lastly, latency is the time taken by data to travel from one point to other.
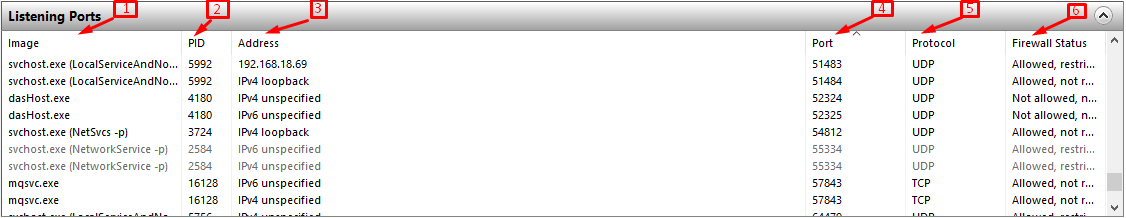
Listening ports: There are three columns in this section; one that differs is “Address“, which shows the local process, listening to the relevant procedure, and the last one is “Firewall status“, which shows the allowed/not allowed status of the operations.
Third-Party Tools
Apart from windows-based Task Manager, few third-party tools provide you with checking and controlling bandwidth. Few popular and efficient tools are given here:
NetTraffic
This tool provides free access to all users; anyone can download and monitor the bandwidth. The image below shows the network traffic analyzer with different interfaces; you can check for statistics.
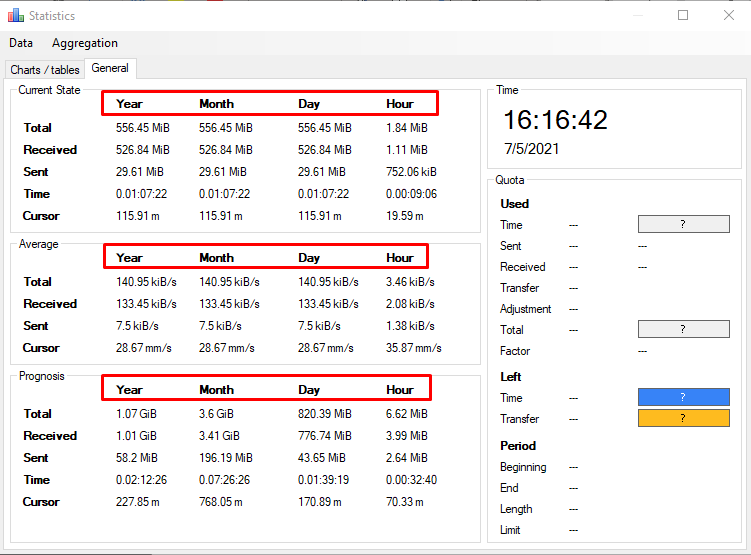
With the help of this tool, you can monitor the number of bytes sent and received, and it reports the hourly, daily, monthly, and yearly transfer rate: as shown below. The exciting thing is that it shows the transmission rate of three different states: “Current state“, “Average state“, and “Prognosis—forecast of likely outcome“.
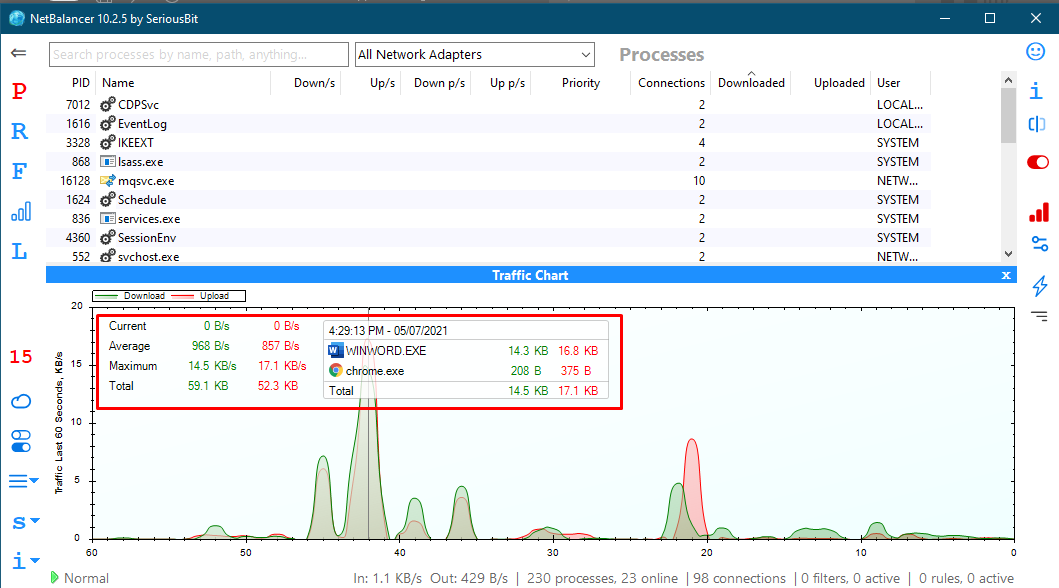
NetBalancer
Another tool shows a detailed overview of running processes, online processes, and each application’s uploading/downloading status. NetBalancer also shows the output in different scenarios:
- Current: This state shows the network flow in the current state.
- Average: This state reports the average flow during a specific time.
- Maximum: It states the complete readings noted in 60sec.
- Total: As the name suggests, it provides the total of all above.
How to increase current bandwidth:
If you are facing bandwidth issues, you can go for bandwidth increment, but you must check how much bandwidth each user is utilizing before this. If anyone uses more bandwidth than others on the network, you can tell them to reduce bandwidth usage. A slang term is used for this phenomenon known as “Bandwidth Hog“.
Another way is to contact your internet service providers to provide you with a better connection, allowing you to perform your tasks efficiently without interruption.
Conclusion
Bandwidth is an essential part of a network; the more significant the bandwidth, the more consistently you can perform data transmission over the connection. Internet service providers provide you the demanded bandwidth: However, sometimes, you may encounter issues transferring information even when you have enough bandwidth. To avoid such a situation, monitor your bandwidth, check where the bandwidth is being consumed.
This write-up provided a brief overview of bandwidth and demonstrated how to monitor your bandwidth to avoid shortage issues. We have enlisted a few tools that can help you to check your bandwidth. Still, using the Windows built-in “Resource Monitor” tool is recommended because it is built in a Windows application, which means it is more secure than third-party tools downloaded from the internet. It provides you a detailed explanation of usage over the network.