This blog will state the approaches to cope with the error while terminating a process in Windows.
How to Fix “Error Unable to Terminate Process Access is Denied” on Windows?
To resolve the error while terminating a process in Windows, consider the following solutions:
- Trigger the “ALT + F4” Combined Keys.
- Restart the System.
- Utilize “WMIC(Windows Management Instrumentation Console)”.
- Apply the “taskkill” command in Command Prompt.
- Utilize the “Process Hacker” Tool.
Quick Fix 1:Trigger the ALT + F4 Combined Keys
The “ALT + F4” or “ALT + FN + F4” is a key combination that effectively ends unresponsive programs. This can be an alternative approach when you cannot terminate the process via the “Task Manager”.
Quick Fix 2: Restart the System
One of the foremost approaches to cope with such a situation can also be simply restarting the PC/Laptop. This approach works for almost all the encountered bottlenecks related to hardware and software. If the issue is still there, try considering the next approaches.
Fix 3: Utilize “WMIC (Windows Management Instrumentation Console)”
This feature allows the users to apply “Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI)” operations using the command prompt. Therefore, apply this procedure to end the desired process by utilizing the below-listed steps.
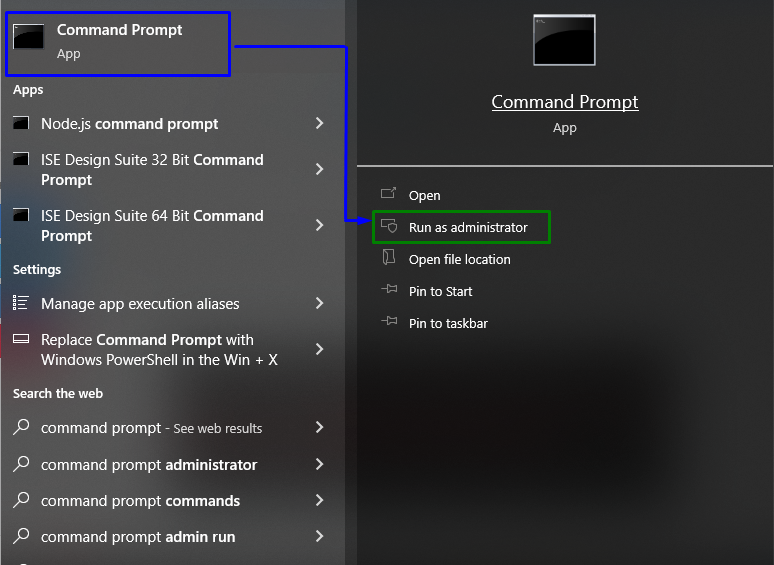
Step 1: Run “Command Prompt”
Open up the Command Prompt being an “Administrator”:
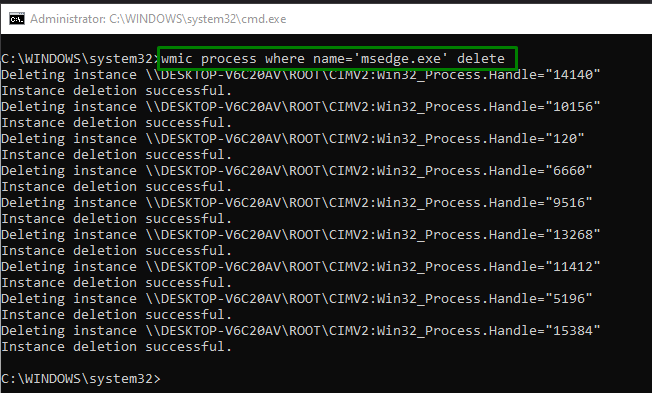
Step 2: Terminate the Process
Now, input the below-provided command to end or terminate the process:
Note that the “processname” in the above command corresponds to the process that needs to be terminated:
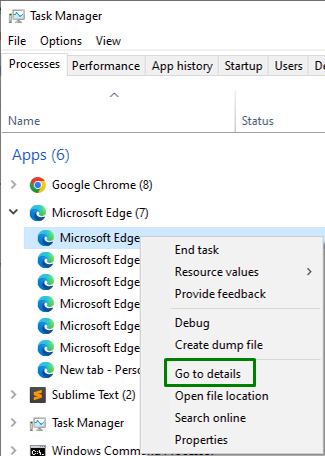
If you are unable to identify the process name for applying the command, right-click on the particular “process” in the “Task Manager” and trigger “Go to details”, as follows:
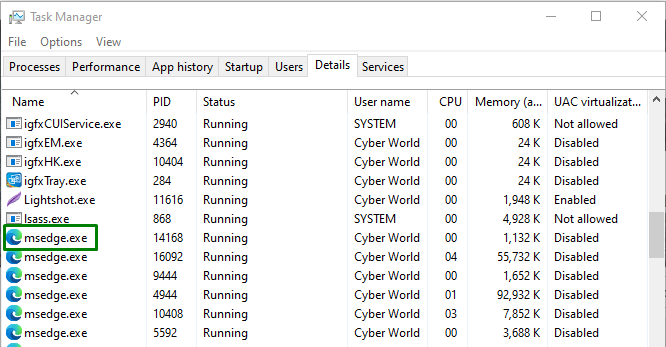
Here, confirm the process name, as highlighted below:
Fix 4: Apply the “taskkill” Command in Command Prompt
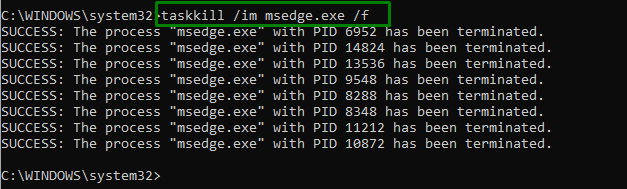
This particular command allows the user to kill a task from the “Windows Command Line” via “process id”. For doing so, simply input the provided command in the “Administrative Command Prompt”:
In the above command, likewise, replace the “process-name” with the desired process that needs to end:
As evident from the above command, the desired process is successfully terminated.
Fix 5: Utilize the “Process Hacker” Tool
This tool effectively monitors system resources. Therefore, utilizing this particular tool effectively resolves the issues while terminating the process by implementing the following steps.
Step 1: Download the “Process Hacker” Tool
Follow the link to download this particular tool and check out the on-screen instructions to install it.
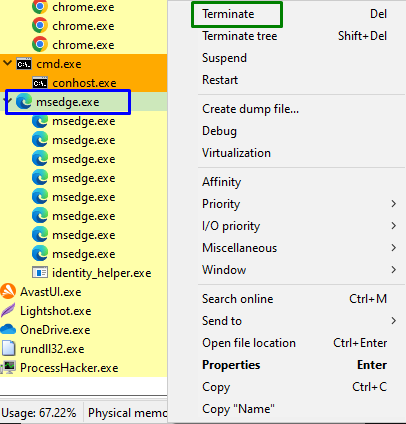
Step 2: Terminate the Desired Process
Open the tool and right-click on the process causing issues. After that, trigger “Terminate” to end the process instantly:
After doing so, the particular process will likely terminate, and the discussed limitation will sort out.
Conclusion
To resolve the “Error Unable to Terminate Process Access is Denied” in Windows, trigger the “ALT + F4” combined keys, restart the system, utilize “WMIC (Windows Management Instrumentation Console)”, apply the “taskkill” command in Command Prompt, or utilize “Process Hacker” tool. This write-up elaborated on the approaches to resolve the error while terminating a process in Windows.