Ingress is used to manage application incoming traffic and also for SSL termination. In contrast, secrets are used to store confidential information and TLS certificates for application.
This post will illustrate:
- What are the Kubernetes Secrets?
- Prerequisite: Generate Private Key and Certificate
- How to Create Secret TLS in Kubernetes?
- How to Create a Secret Through Yaml File?
- How to Embed Secret With Kubernetes Pod?
- Conclusion
What are the Kubernetes Secrets?
The Secrets are one of the Kubernetes resources, used to store confidential information such as user login credentials, keys, certificates, or tokens. The secrets can be created individually and connected to pods. It prevents the developer from providing confidential data in code and also provides an extra layer of security. Different kinds of secrets can be created and used. The most commonly used secrets are:
Generic Secret: The generic secrets are utilized to store basic information such as passwords, tokens, API keys, OAuth keys, and so on.
TLS Secret: TLS secrets are used to store private keys and certificates that are signed by the CA. To ensure the security of applications running inside Kubernetes and for securing communication within the cluster, the user usually needs to create and embed TLS secrets to the pod.
Docker Registry: It is used to store the docker registry credential to easily pull the images from the registry.
Prerequisite: Generate Private Key and Certificate
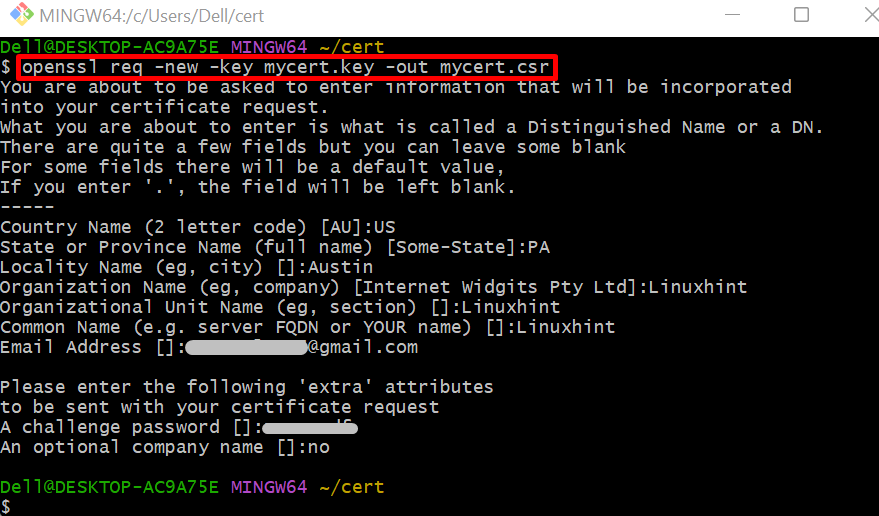
To create the certificate and private key for security improvement, utilize OpenSSL that creates the CSR (certificate signing request) and private key. Then, use CSR to generate the self-signed or CA certificates.
To utilize the OpenSSL commands on Windows, users are required to install Git. For this purpose, follow our linked “Install git on Windows” article.
After installing git, follow the below instructions to generate a private key and signed certificate.
Step 1: Launch Git Bash Terminal
Make a search for “Git Bash” in the Start menu and launch the terminal:
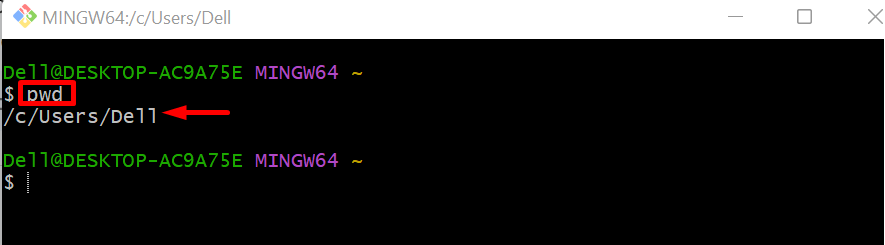
To check the current directory use the “pwd” command:
Currently, we are working in the %USERPROFILE% directory:
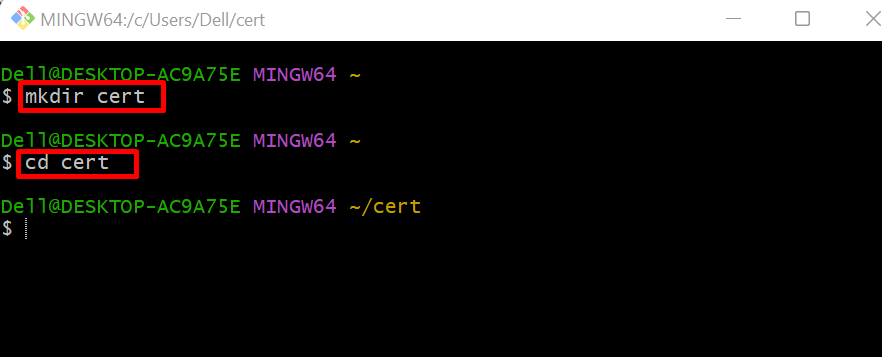
Step 2: Create New Directory
Create a new directory to save the certificates and private key:
Navigate to the newly created directory using the “cd” command:
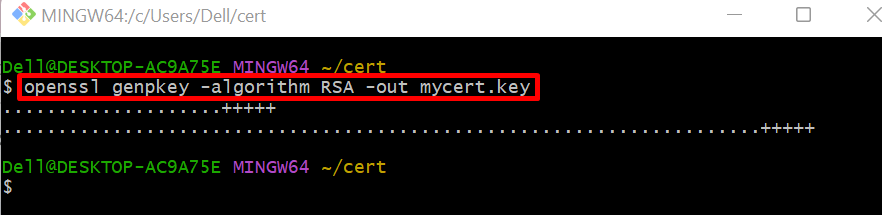
Step 3: Generate Private Key
Now, generate the private key through the given command. Here, the generated private key will be saved in “mycert.key”:
Step 4: Generate CSR
To generate the CSR (certificate service request) to get a signed certificate, use the given command:
Step 5: Generate Certificate
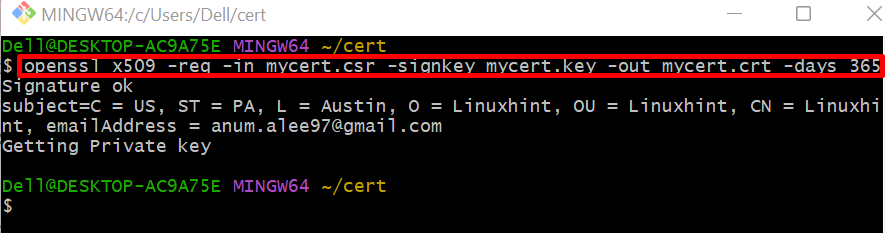
Lastly, using the generated private key and CSR, create a certificate and save it in the “mycert.crt” file. For this purpose, execute the below command:
After generating the TLS certificates, the user can create the secret TLS by following the below section.
How to Create Secret TLS in Kubernetes?
To ensure the application security and secure communication within and outside the Kubernetes cluster, the TLS (Transport Layer Security) certificates are essential that are used in data encrypting. The Kubernetes secret allows us to embed the TLS certificate with running pods through secret TLS. To create a secret TLS in Kubernetes, go through the following instructions.
Step 1: Start Minikube Cluster
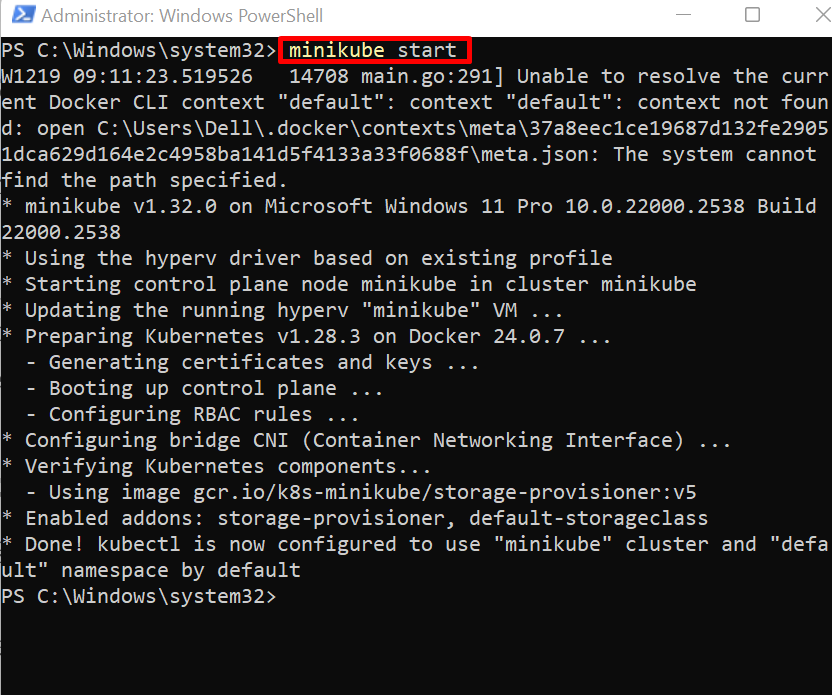
To start the minikube cluster, first, launch the Windows PowerShell as administrator. After that, create and run the cluster using the “minikube start” command:
Step 2: Get Nodes
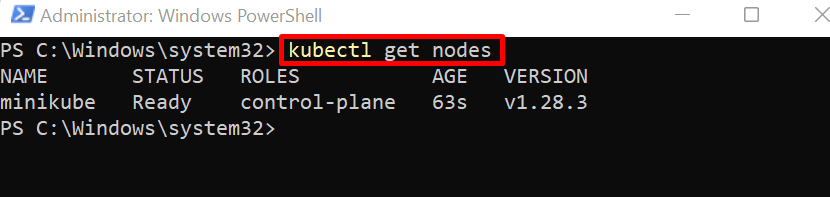
Access the Kubernetes node to check if the cluster is started or not:
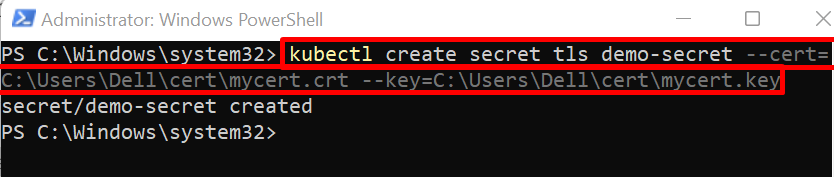
Step 3: Create Secret TLS
Create the TLS secret in Kubernetes using “kubectl create secret <secret-type> <secret-name> –cert=<path-to-tls certificate> –key=<path-to-private-key>” command. Here, the secret type can be “generic”, “tls”, or “docker-registry”. To create a TLS secret, we have set the secret type as “tls”:
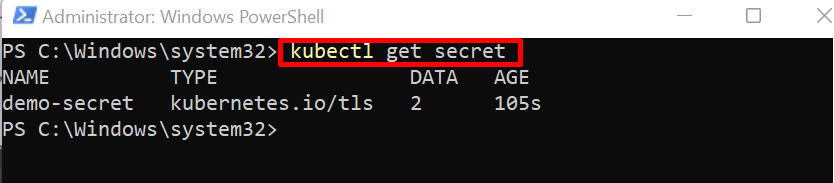
Step 4: Get Secrets
For confirmation, list down the Kubernetes secret using the given command:
Here, you can see we have effectively created a “demo-secret” that contains “2” data values:
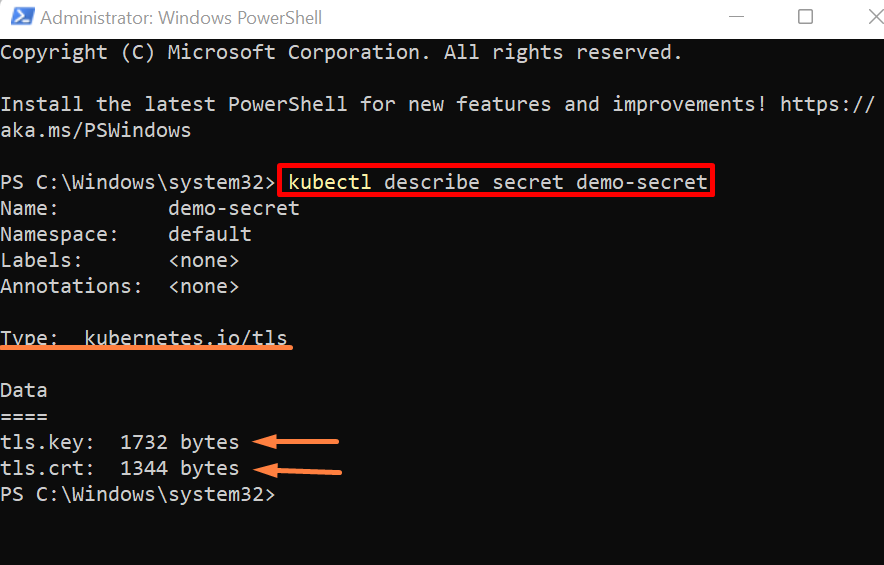
Step 5: Describe Secret
To view how data are viewed or stored in secret, describe the secret using the “kubectl describe secret <secret-name>” command:
You can see values are stored in bytes and cannot be directly viewed unlike Kubernetes ConfigMaps:
How to Create a Secret TLS Through Yaml File?
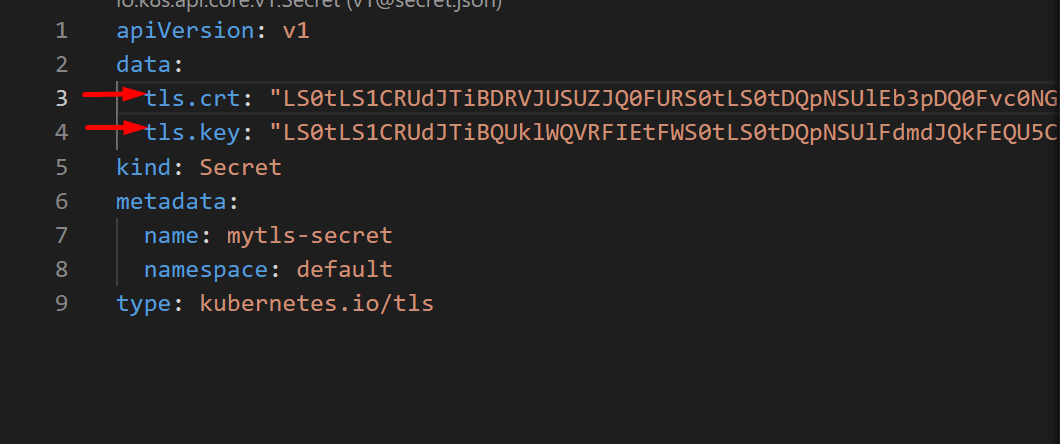
To create a secret TLS through a yaml file, first, create a “secret.yml” file, add the tls base64 encoded certificate in the “tls.crt” key, and add the base64 encoded key in the “tls.key”.
For demonstration, follow the listed steps.
Step 1: Create Yaml File
Create a file named “secret.yml” and paste the given code:
data:
tls.crt: "base64 encoded cert"
tls.key: "base64 encoded key"
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: mytls-secret
namespace: default
type: kubernetes.io/tls
In the above snippet, replace the “tls.crt” and “tls.key” key values with your original certificate and key values:
Step 2: Create a Secret
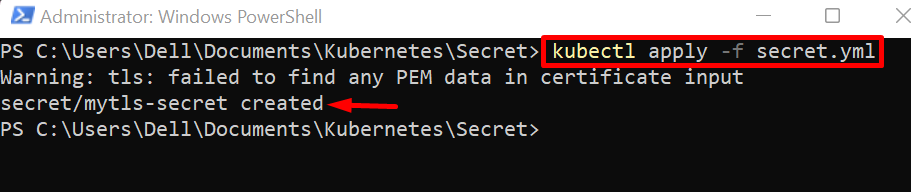
Now, apply the secret yaml file through the “kubectl apply -f <path-to-secret.yml>” command:
The output shows that we have successfully created the “mytls-secret” using yaml file:
Note: View TLS Certificate and Private Key
To view the base64 encoded certificate and use it in the yaml file, run the “cat <path-to-certificate file> | base64” command in the git bash terminal:
In order to view the base64 encoded key, use “cat <path-to-key file> | base64” command:
How to Embed Secret TLS With Kubernetes Pod?
After creating the secret TSL, the user can embed it with the Kubernetes pod. To do so, use the following instructions.
Step 1: Create Yaml File
Make a file named “pod.yml” file and paste the below snippet into the file:
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: demo-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: html-cont
image: rafia098/html-img:1.0
envFrom:
- secretRef:
name: demo-secret
In the above snippet:
- “kind” key specifies the Kubernetes resource that the user is creating.
- “name” key will set the pod name.
- “containers” key will store the container information.
- “name” key under the “containers” key will set the container name.
- “image” key will provide the application or container image to create and start the application inside the container.
- “envFrom” key will set the environment variable from other Kubernetes resources. Here, to embed the secret TLS in a pod, “secretRef” is used to provide a secret reference. To embed the above secret TLS, specify the name of the secret in the “name” key.
Step 2: Create or Upgrade the Pod
Next, open the folder where the “pod.yml” file is created:
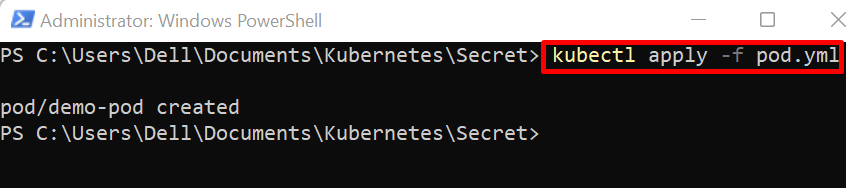
Apply the yaml file to create or reconfigure the pod using the “kubectl apply” command:
Step 3: Access Kubernetes Pods
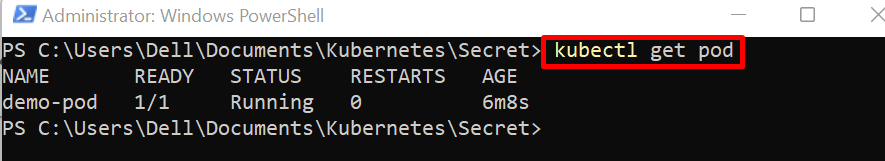
For verification, list down the Kubernetes pods:
Here, you can see we have created the “demo-pod” successfully:
Step 4: Describe the Pod
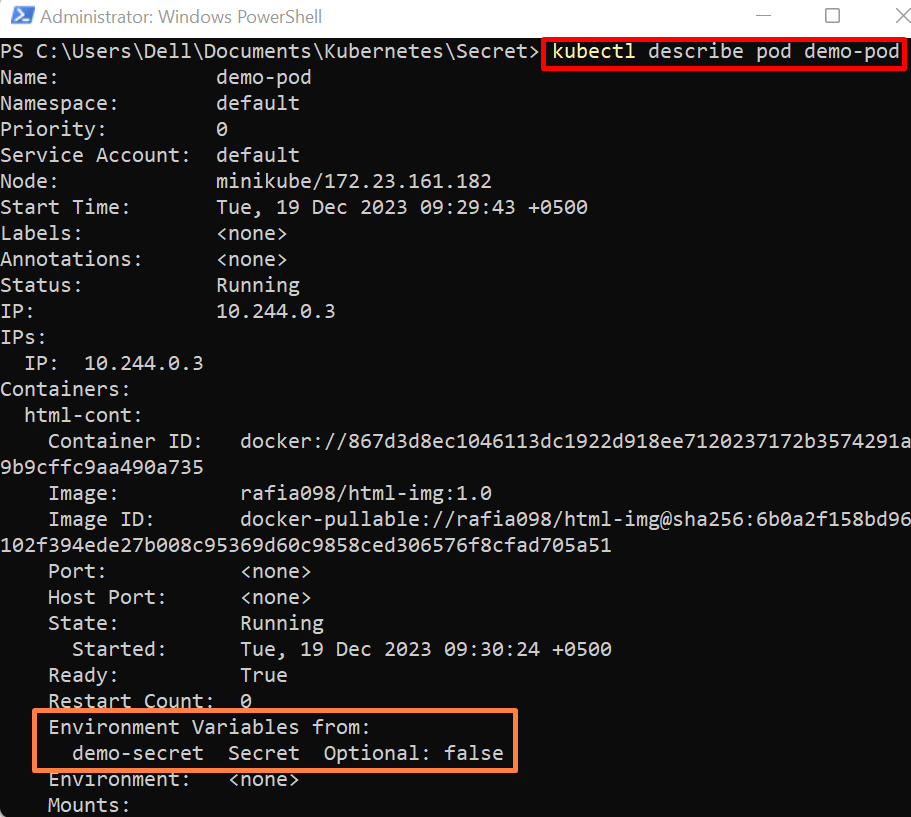
To check if the pod has embedded the secret TLS or not, describe the pod using the below command:
The below output shows that we have successfully embedded the TLS secret with pod:
We have covered how to create secret TLS and embed it with the Kubernetes application running in the pod.
Conclusion
To create the secret TLS in Kubernetes, first, create the TLS signed certificate and private key. After that, start the Kubernetes cluster and run the “kubectl create secret <secret-type> <secret-name> –cert=<path-to-tls certificate> –key=<path-to-private-key>” command. Users can also create the secret TLS using yaml manifest. This post has illustrated how to create the secret TLS and how to embed the secret with a running application or pod.