The blog will cover the following:
- Method 1: Use the dict() Method to Convert a List of Tuples to a Dict
- Method 2: Use the map() Method With the dict() Constructor
- Method 3: Use the zip() Method With the dict() Constructor
Method 1: Use the dict() Method to Convert a List of Tuples to a Dict
The dict() constructor can be used to generate Dictionary objects from a list of tuples in Python. However, you cannot just pass in the list of tuples. Rather, you need to use list comprehension to fetch the two elements of the tuples and pass them into the dict() constructor, as it takes two arguments.
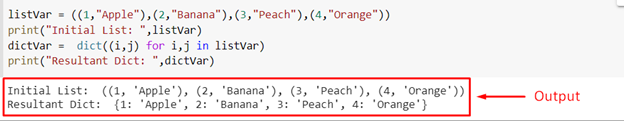
To demonstrate the working of the dict() method to create a dict from a list of tuples, take the following code:
print("Initial List: ",listVar)
dictVar = dict((i,j) for i,j in listVar)
print("Resultant Dict: ",dictVar)
When this code is executed, it produces the following output on the terminal:
From the output, you can easily observe that the list of types was successfully converted into a Python Dictionary.
Method 2: Use the map() Method With the dict() Constructor
Another way of converting a list of tuples into a Python dictionary is by using the map() method within the dict() constructor and passing the tuples list into the map() method. However, to be able to convert the list into a dict, the map() method will require two arguments. Therefore, you simply provide “reversed” as the first argument, which will reverse the placement of the elements in the tuple.
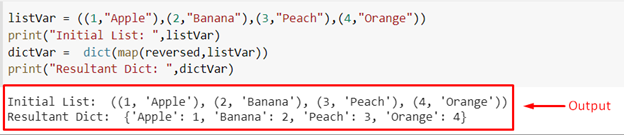
To demonstrate the working of the map() method, use the following code snippet:
print("Initial List: ",listVar)
dictVar = dict(map(reversed,listVar))
print("Resultant Dict: ",dictVar)
When this code is executed, it produces the following result on the terminal:
From the output, you can see that the list of tuples has been converted into a dictionary successfully. However, the elements of the tuple have been reversed.
Method 3: Use the zip() Method With the dict() Constructor
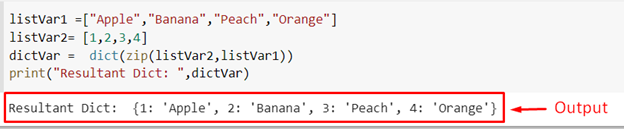
If the values of the tuple are placed inside separate lists, the user can use the zip() method within the dict() constructor to create a Python dictionary. To demonstrate this, take the following code snippet:
listVar2= [1,2,3,4]
dictVar = dict(zip(listVar2,listVar1))
print("Resultant Dict: ",dictVar)
When this code snippet is executed, it will produce the following results on the terminal:
As you can see, the elements from the two different lists have been merged to form a Python Dictionary.
Conclusion
A list of types can be converted into a Python dictionary by using the dict() constructor with either the list comprehension approach or by using the map() method within the dict() constructor. Moreover, if the elements to be formed into a Python dict are placed in separate lists, then the user can utilize the zip() method within the dict() constructor.