Where is time in Wireshark capture?
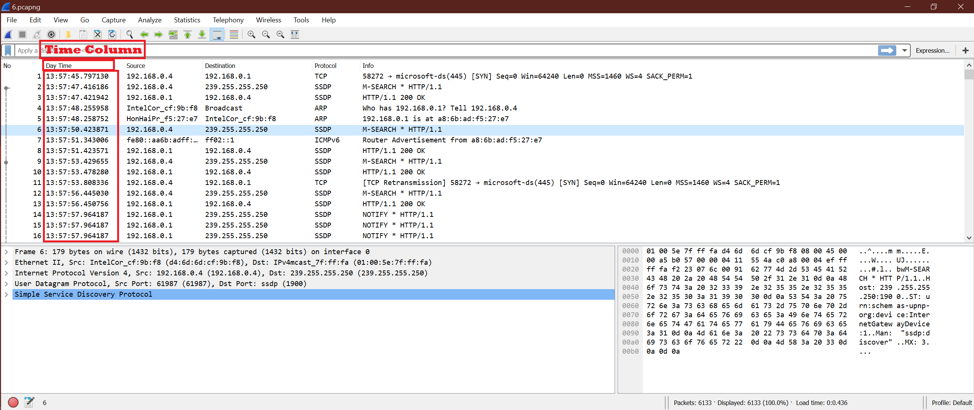
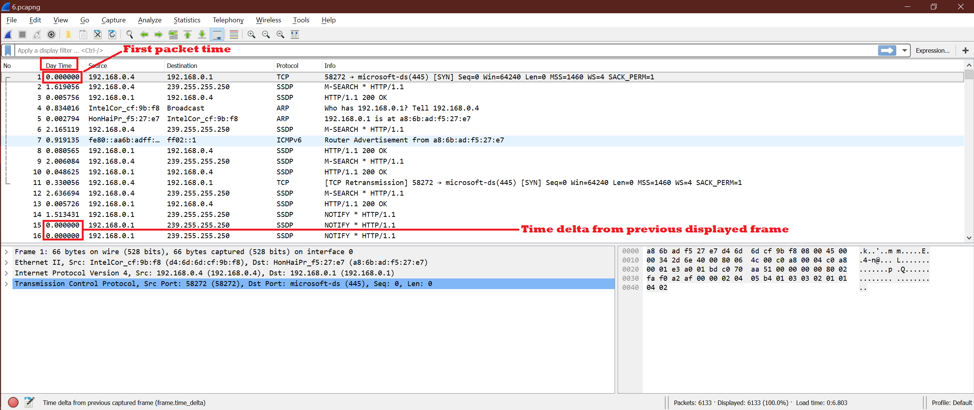
Let’s open one saved capture to understand the time option in Wireshark. Now we can see below screenshot that the second column is a time-related column.
Where is “Time Display Format” in Wireshark capture?
Now we can check what the “Time Display Format” in Wireshark is.
Go to View->Time Display Format. Here is the output
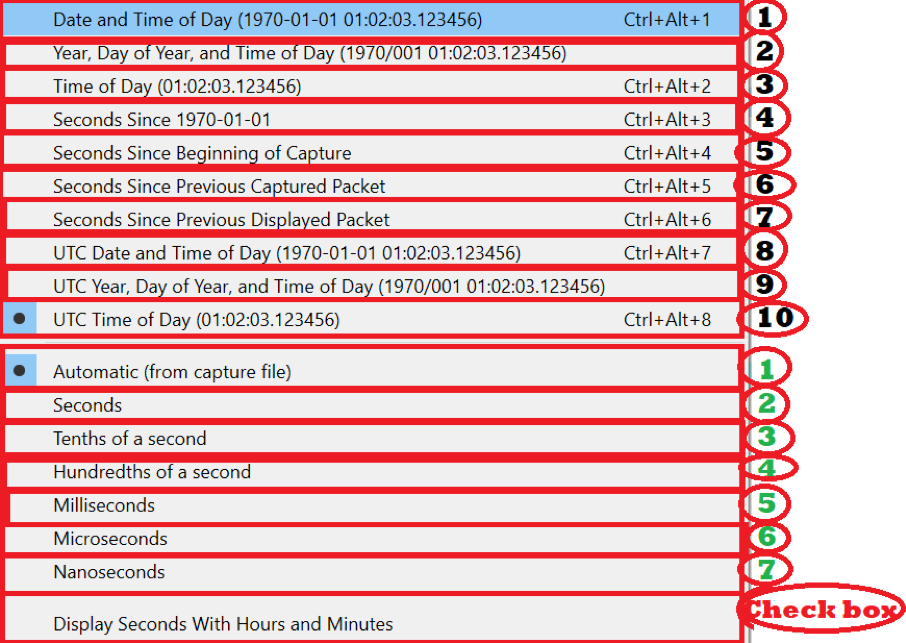
Meaning of each option:
To understand this, we will select one option and see the effect on Wireshark capture. Let’s label each option one number for easy understanding.
As we see, there are two sections
The First 1 to 10 options are for time display format, and the next 1 to 7 options are for the time unit.
Let’s keep next option 1 (See below screenshot)
constant and make changes for the first 1-10 options.
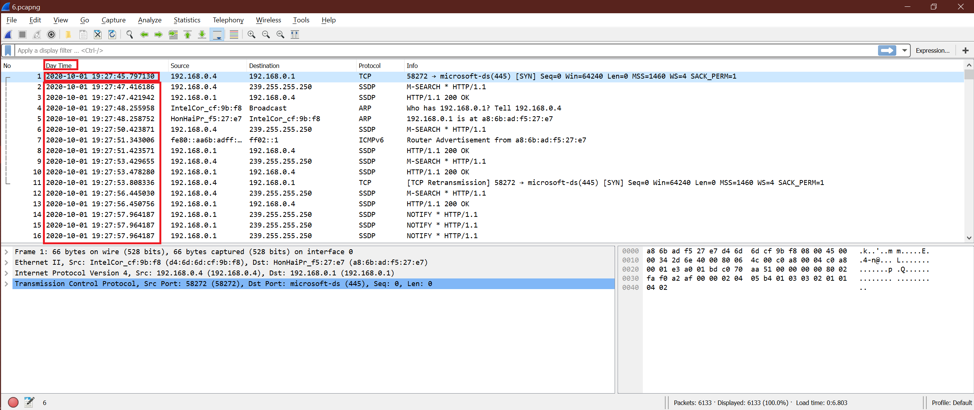
Option 1:
Now we will see the date and time for each packet of Wireshark. Here is the output screen
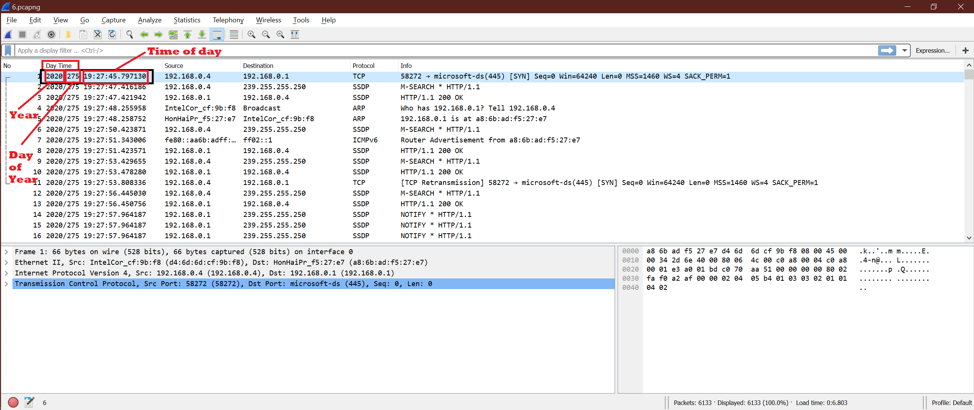
Option 2:
Now we will see the year, day of the year, and time of the day. Here is the output screen
Option 3:
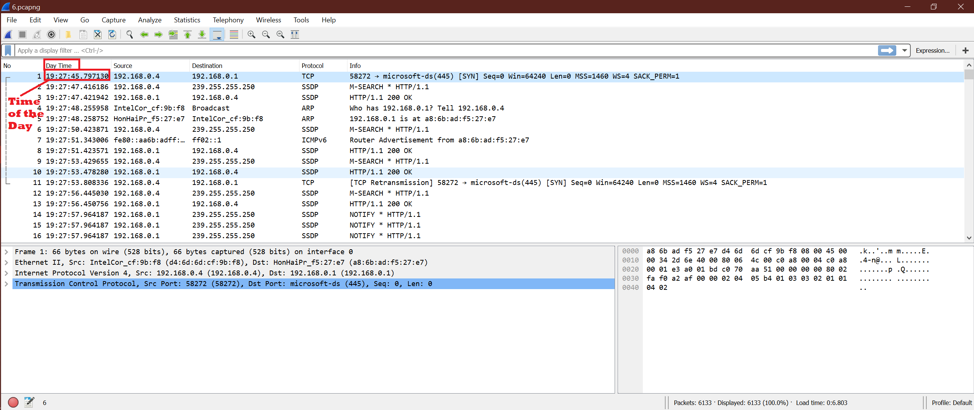
After selecting this option, we can see only the Time of the Day. No year is shown.
See the below screenshot.
Option 4:
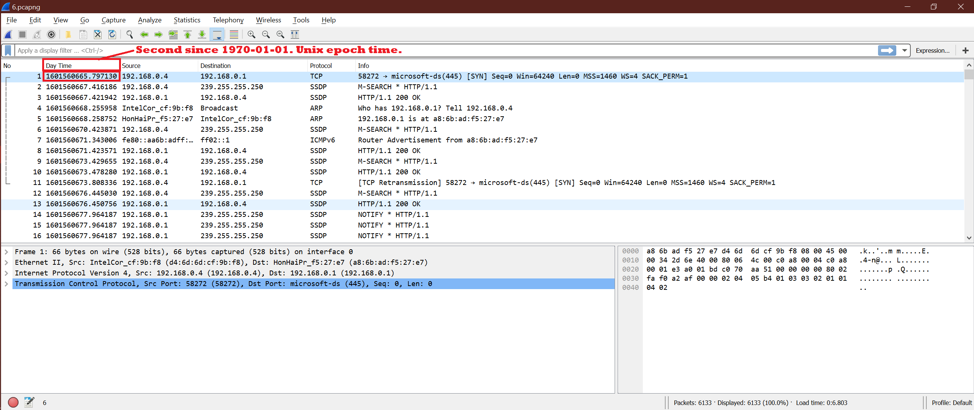
This option enables time in second in Epoch Time style. Here is the screenshot.
Option 5:
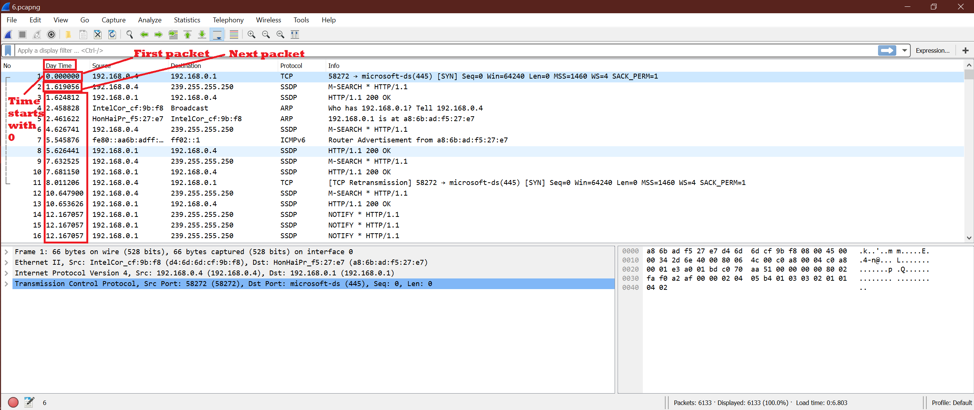
After selecting this option, we will see the first packet of captured time is set to 0.00 second, and after how many seconds the next packet was captured. So we will see the time will be increasing.
See the below screenshot.
Option 6:
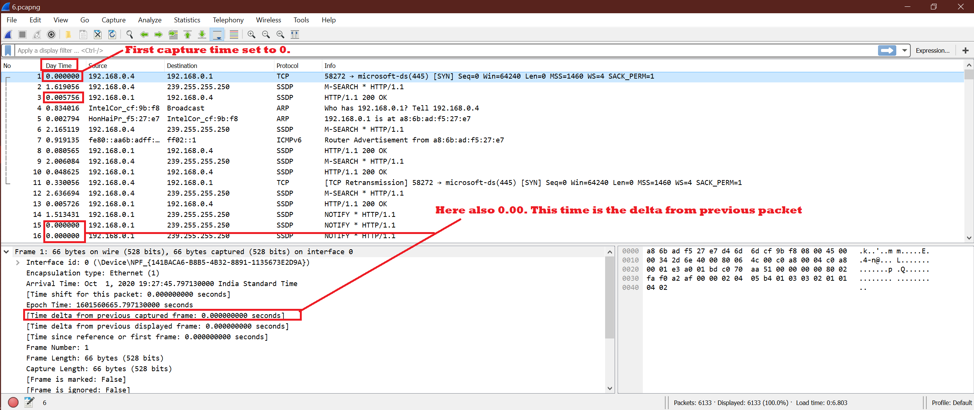
This shows the time for each packet with reference to the previous capture packet. So we will see time as “Time delta from previously captured frame” second for the current packet.
See the below screenshot.
Option 7:
This option shows the time as “Time delta from previously displayed frame” second for the current packet. Actually, “option 6” and “option 7” are the same for maximum times. That’s why we do not see any differences.
See the below screenshot.
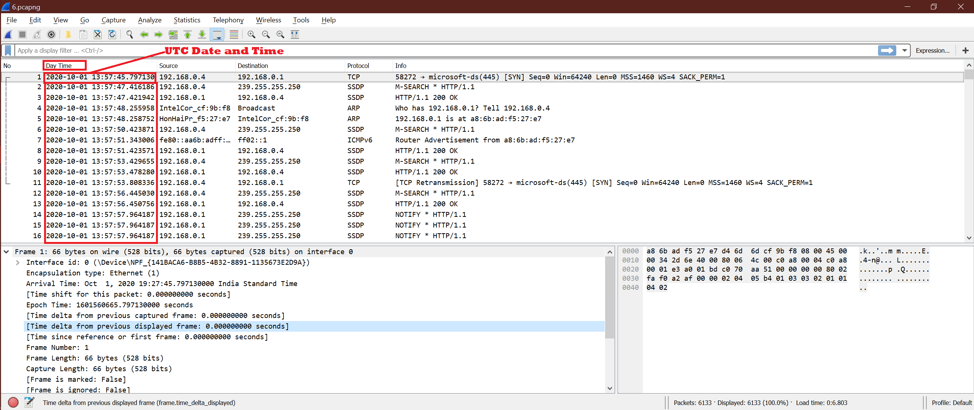
Option 8:
This shows the time as UTC [Coordinated Universal Time] Date and Time of the day. This option is almost the same as “option 1,” but the Time of day is different.
See the below screenshot.
Option 9:
Now we will see UTC year, day of the year, and time of the day.
Here is the output screen
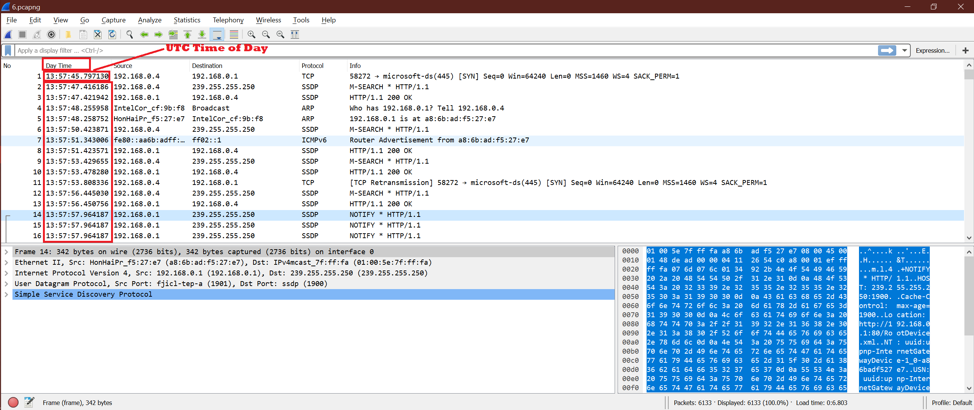
Option 10:
After selecting this option, we can see only UTC Time of Day. No year is shown here.
We are done with the first set of options. Now, let’s see how the time unit affects the Wireshark packet time.
Keep below time format constant
Option 1:
This gives the default Date and Time from capture.
See the below screenshot.
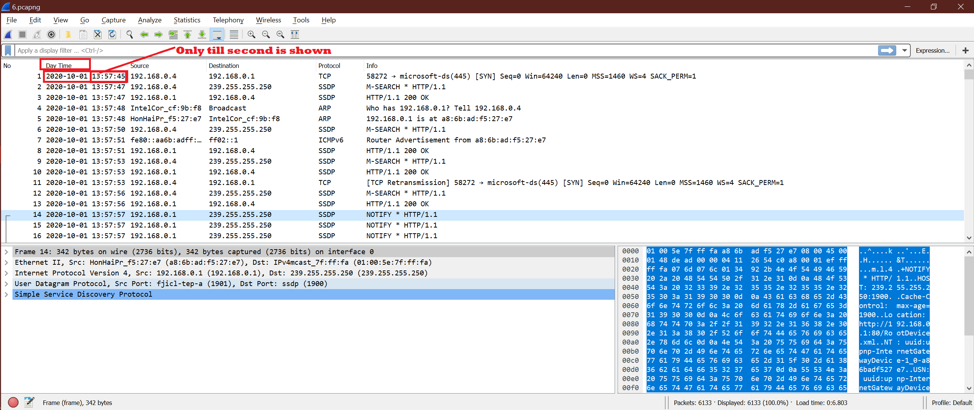
Option 2:
Now see the difference between option1 and this option. We can see time is shown till the second.
Check the below screenshot.
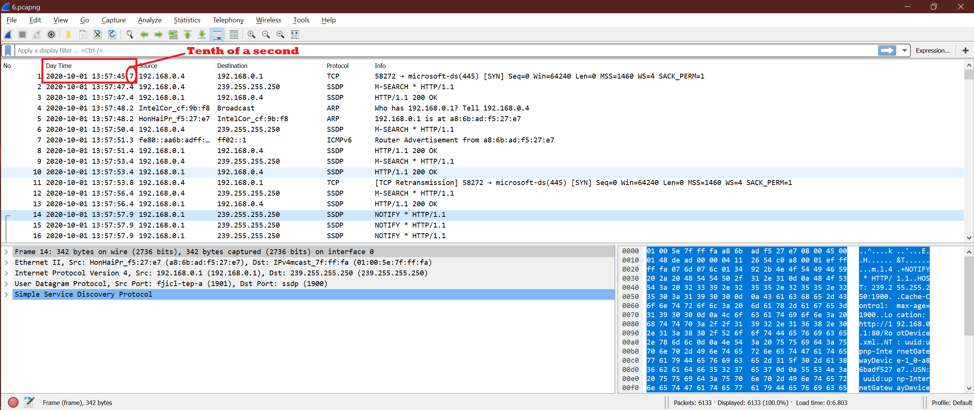
Option 3:
This option shows “Tenth of Second” for time.
Check the below screenshot.
Option 4:
This option shows “Hundredths of Second” for time.
Check the below screenshot.
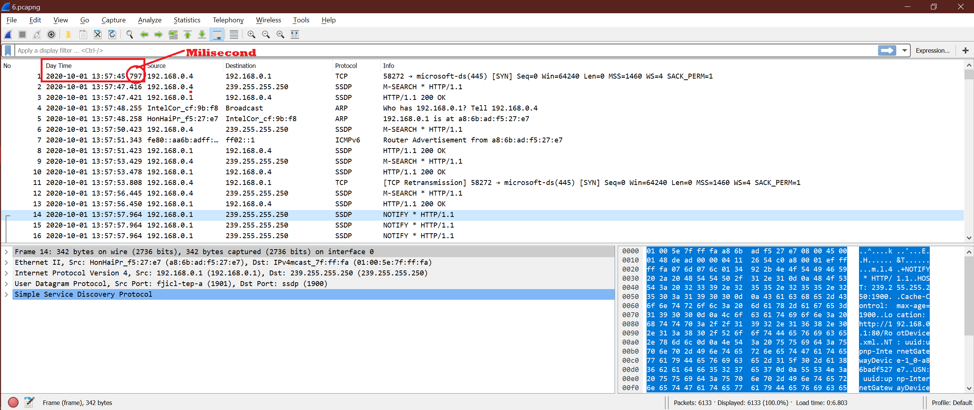
Option 5:
This shows the millisecond part after second. Look at the below screenshot.
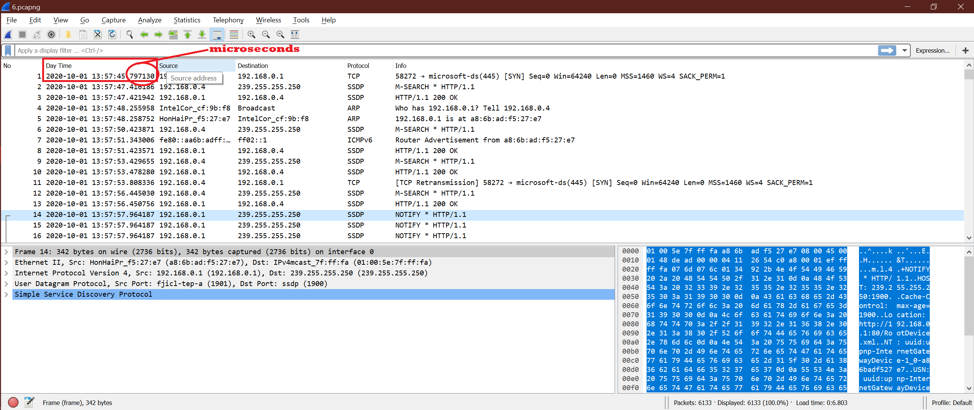
Option 6:
Now we can see a microsecond part of the time. See the below screenshot.
Option 7:
This option enables a microsecond part of the time. See the below screenshot.
Check Box
As our current Time Format is already having Hours and Minutes, so it does not affect.
So, we can play a combination of all these options.
Try one random combination:
Let’s see the effect of the below combination
Output [Look at Day Time column]:
Conclusion:
Now we know the time formats and units, we may think, what is the use of all these different options? This help does Wireshark capture analysis. We may need a different time scale to see many factors from Wireshark captures. So, it’s all about quick and better Wireshark capture analysis.