Reproducing the Error
Create two numpy arrays: day1_budget with two dimensions (2×2) and day2-budget with one dimension. Try to concatenate both of them using the concatenate() function.
# Create numpy array - day1_budget
day1_budget = numpy.array([[2000,1200],[2200,4500]])
print(day1_budget,"\n")
# Create numpy array - day2_budget
day2_budget = numpy.array([8400,1000])
print(day2_budget,"\n")
numpy.concatenate([day1_budget, day2_budget])
Output
You can see that an error is encountered.
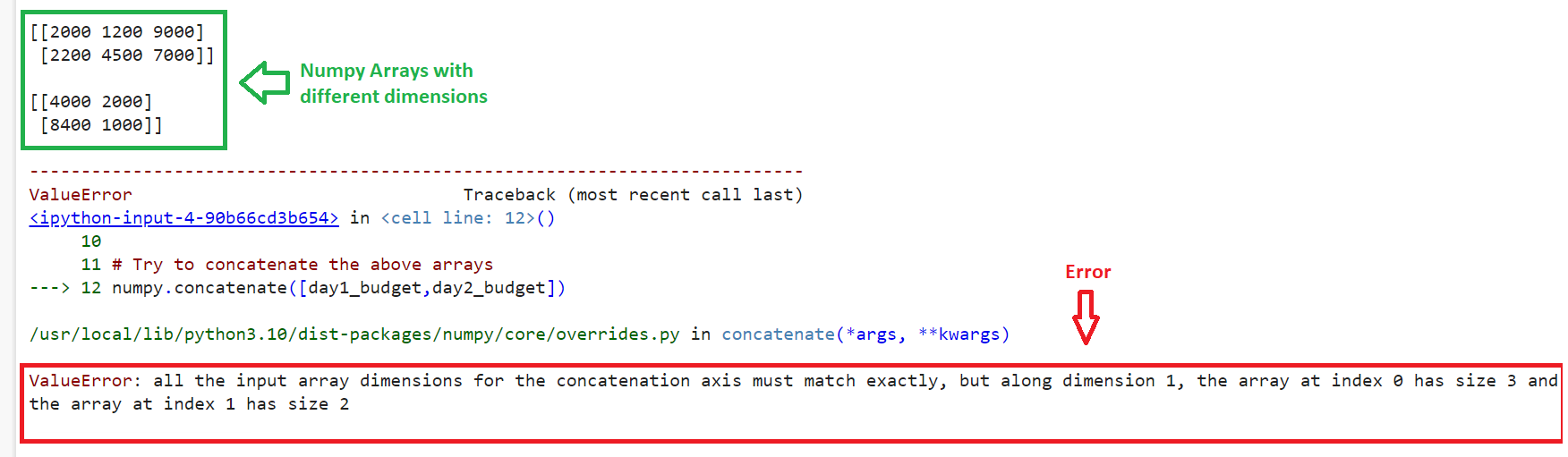
Create two numpy arrays: day1_budget with 2×3 dimensions and day2-budget with 2×2 dimensions. Try to concatenate both of them using the concatenate() function.
# Create numpy array - day1_budget
day1_budget = numpy.array([[2000,1200,9000],[2200,4500,7000]])
print(day1_budget,"\n")
# Create numpy array - day2_budget
day2_budget = numpy.array([[4000,2000],[8400,1000]])
print(day2_budget,"\n")
# Try to concatenate the above arrays
numpy.concatenate([day1_budget,day2_budget])
Output
You can see that an error is encountered, which is similar to the above error that we are discussing in this guide.
Solution 1: Check the Dimensions Manually
This is the manual scenario where the developer has to create numpy arrays and check if their dimensions are equal. If both dimensions are the same, concatenate the arrays.
Let’s create two numpy arrays, day1_budget and day2_budget, both with 2×2 dimensions. Use the concatenate() function to concatenate day1_budget and day2_budget.
# Create numpy array - day1_budget
day1_budget = numpy.array([[2000,1200],[2200,7000]])
print(day1_budget,"\n")
# Create numpy array - day2_budget
day2_budget = numpy.array([[4000,2000],[8400,1000]])
print(day2_budget,"\n")
# Concatenate the above arrays
numpy.concatenate([day1_budget,day2_budget])
Output
You can see that both arrays have been concatenated.
Solution 2: Using numpy.column_stack()
If you want to join arrays with different dimensions, you can use numpy.column_stack() function which will stack the one-dimensional arrays as columns into a two-dimensional array.
Syntax
It takes a tuple of arrays as the parameter.
Example 1
Let’s create two numpy arrays: day1_budget with 2×3 dimensions and day2_budget with 2×2 dimensions. Use the numpy.column_stack() function to concatenate both of them.
# Create numpy array - day1_budget
day1_budget = numpy.array([[2000,1200,6000],[2200,7000,2300]])
print(day1_budget,"\n")
# Create numpy array - day2_budget
day2_budget = numpy.array([[4000,2000],[8400,1000]])
print(day2_budget,"\n")
# Concatenate the above arrays using column_stack()
numpy.column_stack((day1_budget,day2_budget))
Output
You can see that the second array has been concatenated to the first array as two new columns.
Example 2
Let’s create three numpy arrays: day1_budget with 2×3 dimensions, day2_budget with 2×2 dimensions, and day3_budget with 2×1 dimension. Use the numpy.column_stack() function to concatenate all of them.
# Create numpy array - day1_budget
day1_budget = numpy.array([[2000,1200,6000],[2200,7000,2300]])
print(day1_budget,"\n")
# Create numpy array - day2_budget
day2_budget = numpy.array([[4000,2000],[8400,1000]])
print(day2_budget,"\n")
# Create numpy array - day3_budget
day3_budget = numpy.array([[500],[400]])
print(day3_budget,"\n")
# Concatenate the above three arrays using column_stack()
numpy.column_stack((day1_budget,day2_budget,day3_budget))
Output
You can see that all the arrays have been concatenated.
Solution 3: Using numpy.c_()
Use numpy.c_() to concatenate the numpy array along the second axis.
Syntax
It does not take any parameters, as it is not a function. It returns the concatenated array.
Example
Let’s create two numpy arrays: day1_budget with 2×3 dimensions and day2_budget with 2×2 dimensions. Use numpy.c_() to concatenate both of them.
# Create numpy array - day1_budget
day1_budget = numpy.array([[2000,1200,6000],[2200,7000,2300]])
print(day1_budget,"\n")
# Create numpy array - day2_budget
day2_budget = numpy.array([[4000,2000],[8400,1000]])
print(day2_budget,"\n")
# Concatenate the above arrays using c_()
numpy.c_[day1_budget,day2_budget]
Output
You can see that the second array has been concatenated to the first array, adding two new columns.
Conclusion
Now you are able to fix the issue while concatenating the numpy arrays with different dimensions. If the arrays have different dimensions, use either the numpy.column_stack() function or numpy.c_() to concatenate them along the columns. Otherwise, make the dimensions equal for both the arrays and concatenate them.