Hackers want to be anonymous and hard to be detected while doing their work. Tools can be used in order to hide the hacker’s identity from being exposed. VPN (Virtual Private Network), Proxyservers and RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) are some of the tools to guard their identity.
In order to do penetration testing anonymously and decrease the possibility of identity detection, hackers need to use an intermediary machine whose IP address will be left on the target system. This can be done by using a proxy. A proxy or proxy server is a dedicated computer or software system running on a computer which acts as an intermediary between an end device, such as a computer and another server which a client is requesting any services from. By connecting to the Internet through proxies, the client IP address will not be shown but rather the IP of the proxy server. it can provide a client with more privacy then if simply connecting directly to the Internet.
In this article, i will discuss about a built-in anonymity service in Kali Linux and or others penetration testing based systems, it is Proxychains.
Hi, I am Bimando, the author of this article. If you like this article please have a look at buying my book Practical Ethical Hacking: For Penetration Testers with Kali Linux. I worked hard on it with the Linux Hint Team to produce a high quality product I know you will love it and learn a lot.
PROXYCHAINS FEATURES
- Support SOCKS5, SOCKS4, and HTTP CONNECT proxy servers.
- Proxychains can be mixed up with a different proxy types in a list
- Proxychains also supports any kinds of chaining option methods, like: random, which takes a random proxy in the list stored in a configuration file, or chaining proxies in the exact order list, different proxies are separated by a new line in a file. There is also a dynamic option, that lets Proxychains go through the live only proxies, it will exclude the dead or unreachable proxies, the dynamic option often called smart option.
- Proxychains can be used with servers, like squid, sendmail, etc.
- Proxychains is capable to do DNS resolving through proxy.
- Proxychains can handle any TCP client application, ie., nmap, telnet.
PROXYCHAINS SYNTAX
Instead of running a penetration test tool, or creating multiple requests to any target directly using our IP, we can let Proxychains cover and handle the job. Add command “proxychains” for every job, that means we enable Proxychains service. For example, we want to scan available hosts and its ports in our network using Nmap using Proxychains the command should look like this:
proxychains nmap 192.168.1.1/24
Lets take a minute to break up the syntax above:
– proxychains : tell our machine to run proxychains service
– nmap : what job proxychains to be covered
– 192.168.1.1/24 or any arguments needed by certain job or tool, in this case is our scan range needed by Nmap to run the scan.
Wrap up, the syntax is simple, as it is only adds proxychains on start of every command. The rest after the proxychain command is the job and its arguments.
HOW TO USE PROXYCHAINS
Before we are using proxychains, we need to setup proxychains configuration file. We also need a list of proxy server. Proxychains configuration file located on /etc/proxychains.conf
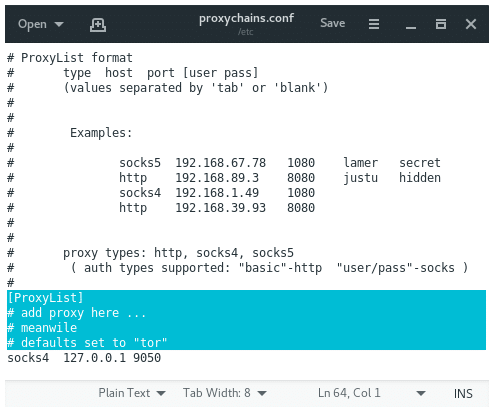
Open proxychains.conf file in your desirable text editor and set up some configuration. Scroll down until you reach the bottom, at the end of file you will find:
[ProxyList] # add proxy here ... # meanwile # defaults set to "tor" socks4 127.0.0.1 9050
By default proxychains directly sends the traffic first through our host at 127.0.0.1 on port 9050 (the default Tor configuration). If you are using Tor, leave this as it is. If you are not using Tor, you will need to comment out this line.
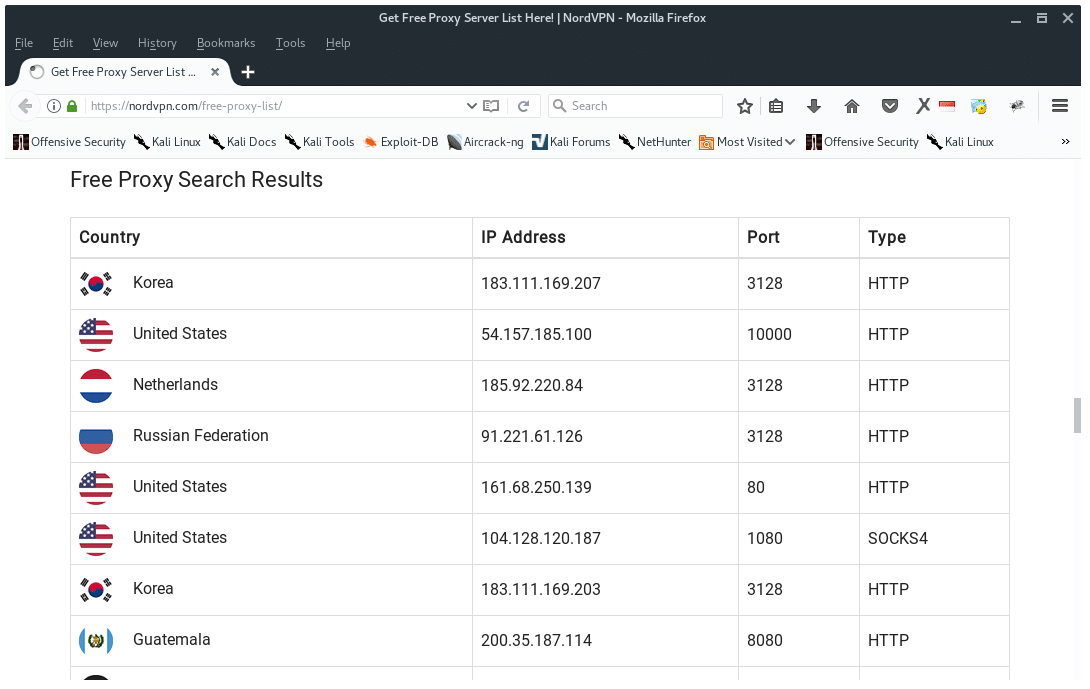
Now, we need to add more proxies. There are free proxy servers on the Internet, you may look at Google for it or click this link Here I am using NordVPN free proxy service, as it has very detailed information on their web site as you see below.
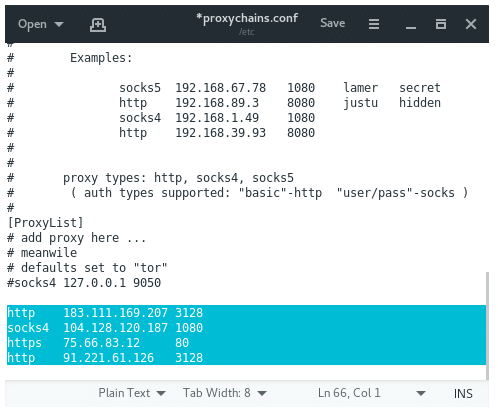
Comment the default proxy for Tor if you are not using Tor then add the proxy on Proxychains config file, then save it. it should look like this:
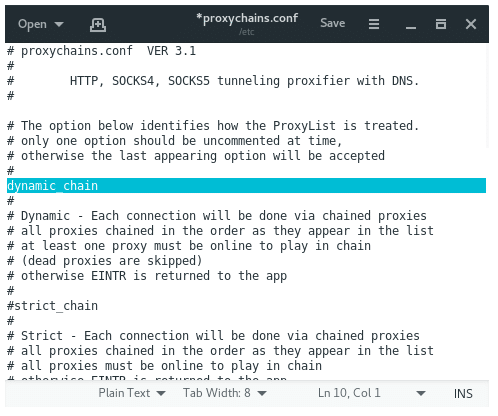
DYNAMIC_CHAIN VS RANDOM_CHAIN
Dynamic chaining will enable us to run our traffic through every proxy on our list, and if one of the proxies is down or not responding, the dead proxies are skipped, it will automatically go to the next proxy in the list without throwing an error. Each connection will be done via chained proxies. All proxies will be chained in the order as they appear in the list. Activating dynamic chaining allows for greater anonymity and trouble-free hacking experience. To enable dynamic chaining, in the configuration file, uncomment “dynamic_chains” line.
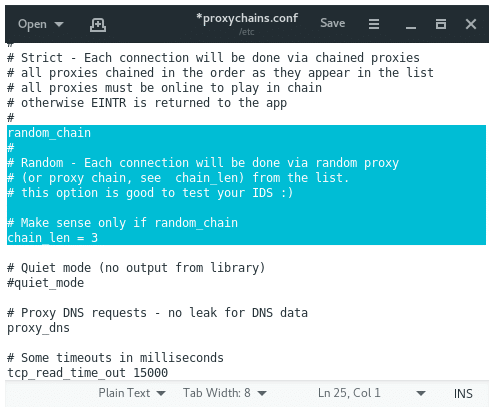
Random chaining will allow proxychains to randomly choose IP addresses from our list and each time we use proxychains, the chain of proxy will look different to the target, making it harder to track our traffic from its source.
To activate random chaining comment out “dynamic chains” and uncomment “random chain”. Since we can only use one of these options at a time, make certain that you comment out the other options in this section before using proxychains.
You may also want to uncomment the line with “chain_len”. This option will determine how many of the IP addresses in your chain will be used in creating your random proxy chain.
Ok, now you know how hackers use proxychains to cover their identity and stay anonymous without worrying about being detected by target IDS or forensic investigators.