How does the Truncate table command work in SQLite
The TRUNCATE TABLE command is not supported by SQLite to delete the rows or to delete the data of the entire table without changing the structure of the table, but we can have this task done in another way which is using the DELETE clause. The DELETE clause will delete all the data from the table but it is slightly different from the TRUNCATE clause, some of the important differences are:
| TRUNCATE | DELETE |
|---|---|
| This is used to delete rows from the entire table | This is used either to delete a specific row (using WHERE) or all the rows (without using WHERE) |
| Faster execution | Slow execution as compared to TRUNCATE |
| We can truncate using ALTER permission | We can delete using DELETE permission |
| Cannot be used with indexed views | Can be used with indexed views |
| It is a DDL (Data Definition Language) command | It is a DML (Data Manipulation Language) command |
Syntax of the DELETE command
The general syntax of the DELETE command is given below which will perform the functionality of TRUNCATE in SQLite:
The explanation of this syntax is simple as:
- Use the DELETE clause so that it can perform the delete action
- Use the FROM clause to tell from where the delete action is to be performed
- Replace the table_name, with the table name you want to modify
How to use DELETE command instead of TRUNCATE in SQLite
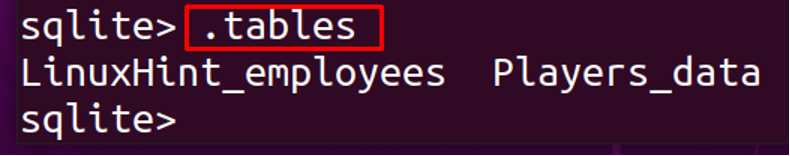
First, we will display all the tables, available in the database:
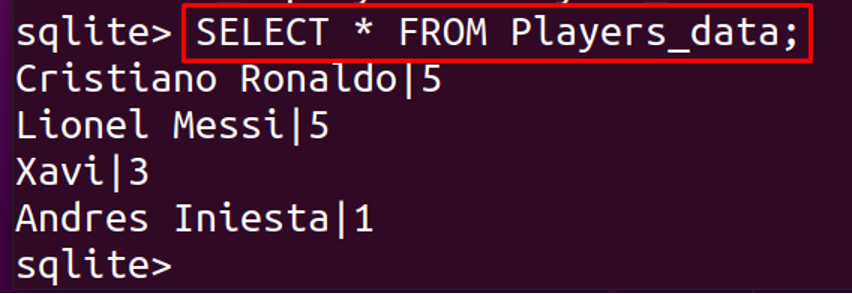
Now we will display the contents of the table, named, Players_data, using the command:
Now to delete all the rows, we will use the DELETE clause without using the WHERE clause as:
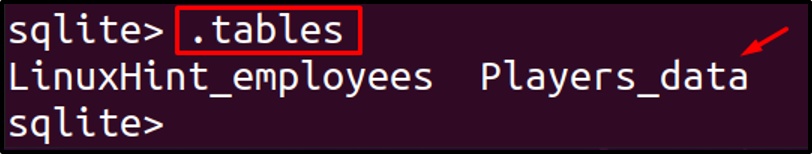
We will display the table to confirm whether the table is present or deleted from the database:
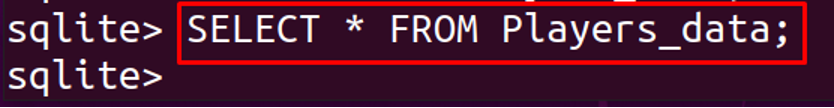
Now, again we will confirm the successful execution of the above command by displaying the entire data of the table using:
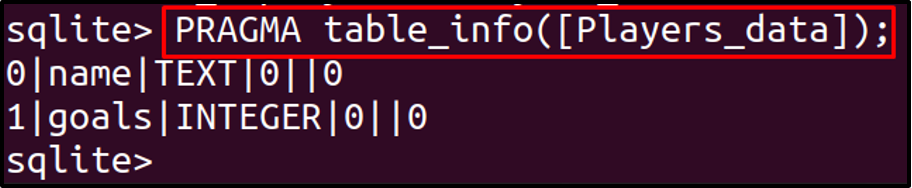
To confirm whether the columns are present or not, we will display the details of the table:
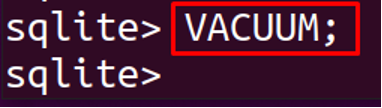
We can see from the above output, the rows of the table have been deleted without deleting the structure of a table, but the size of the table is the same as before with the data of rows because it only erases the data. So to make the space occupied by that data, we will vacuum it by running the following command:
What is the difference between DELETE and DROP clauses in SQLite
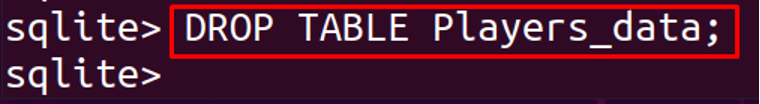
The DELETE clause is used to remove the data of one or multiple rows, but the DROP clause is used to delete the entire table from the database. For example, in the above example, we deleted the Players_data using the DELETE clause, which only removes the rows of the table. Now we will drop the same table, Players_data, using the DROP clause as:
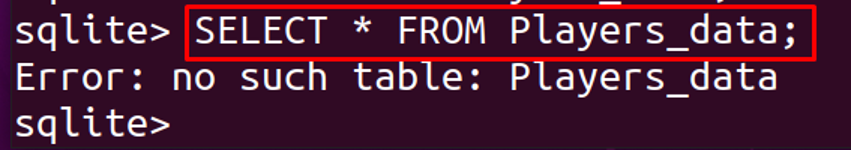
Now, we will again display the table using:
The entire table, Players_data, has been deleted from the database using the DROP TABLE clause.
Conclusion
There are slight differences in SQLite with the other relational databases such as the TRUNCATE TABLE clause is not supported by SQLite, but we can use the DELETE clause for the same purpose. In this article, we learned how to use the DELETE clause to remove the data from a table without removing the table from the database. We also learned the difference between DELETE and DROP clauses.