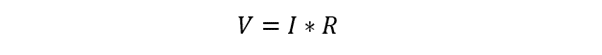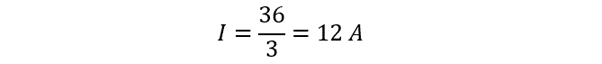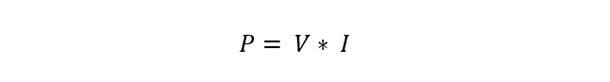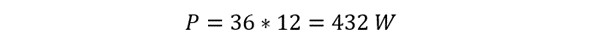What is Watt’s Law?
As per Watt’s law, the power (P) within an electrical circuit is the combined result of the voltage (V) and current (I) present in that particular circuit. It is named after the Scottish engineer James Watt, who made significant contributions to the development of the steam engine.
The Formula for Watt’s Law
The mathematical representation of Watt’s Law can be expressed through the following formula:
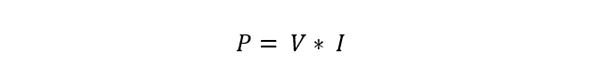
In the aforementioned formula, P represents the power measured in watts, V represents the voltage measured in volts, and I represent the current measured in amperes.
The formula illustrates that the power (P) utilized or generated by a device or circuit is equivalent to the multiplication of the voltage (V) across the device and the current (I) flowing through it.
Example of Watt’s Law
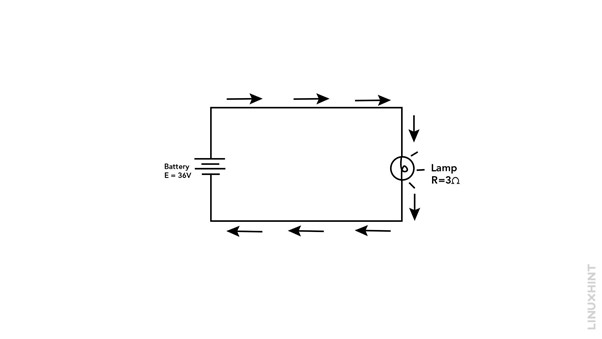
Consider a practical example to illustrate the application of Watt’s aw. Consider a circuit where a voltage of 36 volts (V) is present and a bulb of resistance 3 ohms is connected to it. To find the power (P) consumed by the circuit, we can use Watt’s l6aw:
First, we need to find the value of current and for that use the Ohms law:
Now using the Watts law to calculate the power of the circuit:
Therefore, in this example, the power consumed by the circuit is 432 watts.
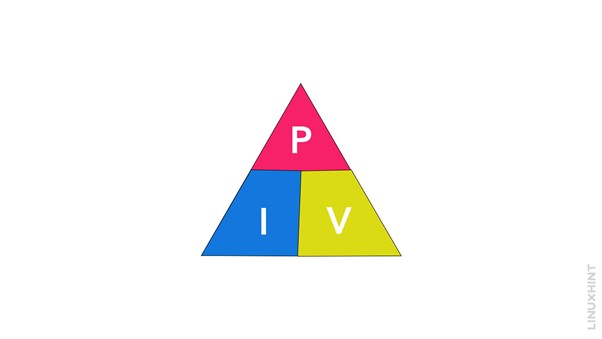
Watt’s Law Triangle
The Watt’s Law triangle is a graphical representation that helps us solve for any of the three variables (P, V, I) in Watt’s Law. The triangle is formed by placing the letter “P” (for power) at the top, “V” (for voltage) at the bottom left, and “I” (for current) on the bottom right.
To solve for a specific variable, cover that variable with your finger, and the remaining two variables will form the equation needed to solve for the covered variable. For example:
- To find the power (P), cover “P” on the triangle: V x I
- To find the voltage (V), cover “V” on the triangle: P / I
- To find the current (I), cover “I” on the triangle: P / V
By rearranging the variables and using the appropriate units, you can easily calculate the unknown values in an electrical circuit.
Conclusion
Watt’s Law, an essential principle in electrical engineering, defines the correlation between power, voltage, and current. It serves as a fundamental concept in the field. Using the formula P = V x I, engineers and technicians can determine the power consumed or supplied by a device or circuit. The Watt’s Law triangle serves as a useful tool for quick calculations and conversions.