Adobe Reader is a software application developed by Adobe Systems that is used to view, print, and annotate the Portable Document Format (PDF) files. PDF is a popular file format which is used for documents, forms, and other types of digital content that are intended to be shared and printed across multiple platforms. With it, the users can open and view the PDF documents, as well as fill out the PDF forms and add annotations such as comments, highlights, and notes. It also includes basic tools to edit the PDF files such as the ability to add text and images, as well as the ability to combine multiple PDF files into one document.
Adobe Reader also includes advanced features such as the ability to search for text within a PDF document, the ability to add digital signatures to PDF files, and the ability to access and share the PDF files online using Adobe’s Document Cloud service. It is used by a wide range of individuals and organizations including students, businesses, government agencies, and non-profit organizations. It is used for a variety of purposes including reading and printing documents, filling out and submitting forms, and collaborating on documents with others.
Adobe Reader is a widely used software and it’s usually pre-installed in most systems. In summary, Adobe Reader can be installed in Linux Mint by downloading the “.deb” package from the Adobe website and using the “sudo dpkg -i adobereader-*.deb” terminal command to install it. Alternatively, you can install it by adding a PPA to your system using the “sudo add-apt-repository ppa:mike-diehl/acroread” command and then the “sudo apt-get update” and “sudo apt-get install acroread”.
Steps to Install the Adobe Reader in Linux Mint
Installing the Adobe Reader in Linux Mint can be done in a few different ways, depending on your preferences and needs. First, we update our packages using the following command:
This command is used to update the package list and refresh the package cache on a Linux system. It is a good practice to run this command before installing a new software or upgrading the existing packages to ensure that the system is aware of the latest versions of the available packages. When we execute it, it first takes the permission from the user to update the enlisted packages or not. By entering “y”, you enable the compiler to update all packages.
Now, we download the Adobe Reader “.deb” package from the Adobe website. Make sure to download the package that corresponds to your Linux Mint version.
The command that we executed is used to download the Adobe Reader package for Linux using the wget command. A wget command enables you to get the files from the internet. The specific URL in the command is the download location for the Adobe Reader 9.5.5 package for Linux. The package name is ” AdbeRdr9.5.5-1_i386linux_enu.deb“.
The “sudo dpkg –add-architecture i386” command is used to add the i386 architecture to the dpkg package manager. The “.deb” package files, unique to Debian-based distributions like Ubuntu and Linux Mint, are managed on Linux systems by the dpkg package manager. The architecture of a package refers to the type of CPU on which it is built for such as x86_64 (64-bit) or i386 (32-bit). The “–add-architecture” option tells the dpkg to add the specified architecture (i386 in this case) to the list of architectures that dpkg can handle. This is necessary when you try to install the 32-bit packages on a 64-bit system since, by default, dpkg is only able to handle the native architecture of the system.
You can install the package by executing the “sudo dpkg” command in the terminal after it is downloaded.
This command is used to install the Adobe Reader package that you downloaded using the wget command. The “sudo” command is used to run the command with superuser privileges. The “dpkg” is the package manager for Debian-based systems like Linux Mint. The “-i” option tells dpkg to install the package.
When you run this command, dpkg installs the Adobe Reader package and any required dependencies. Once the installation is complete, you can launch the Adobe Reader by searching for it in the application launcher or by running the “acroread” command in the terminal.
There is another command that can be used to install the package which is as follows:
The command that is previously mentioned is used to install the Adobe Reader package that you downloaded. The “apt” is the package manager for Ubuntu-based systems. The “install” option tells apt to install the package.
When you run this command, apt installs the Adobe Reader package and any required dependencies. Once the installation is complete, you can launch the Adobe Reader by searching for it in the application launcher or by running the “acroread” command in the terminal. If any dependencies are missing, run the following command to get them:
This command is used to fix the broken packages and dependencies on a Linux system. The “-f” option or “–fix-broken” tells the apt-get to fix any broken packages on the system. This option is useful when a package installation or removal is interrupted or failed, leaving the system in an inconsistent state. It is important to note that if a package is broken, it may not function properly. Running this command tries to fix the package, but it may not always be successful. If the command is not successful in fixing the package, you may need to uninstall and reinstall the package or manually resolve the dependencies issue.
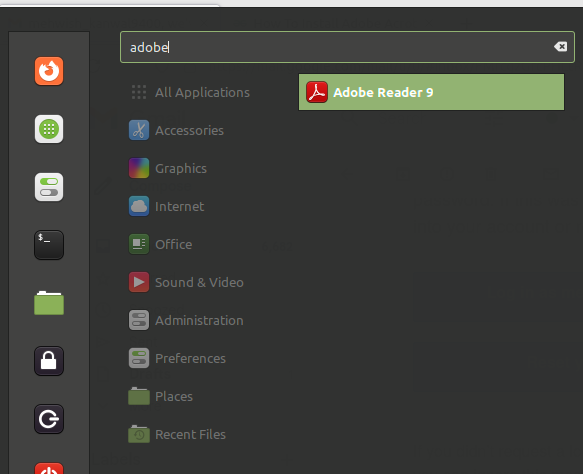
Once the installation is complete, you can launch the Adobe Reader by searching for it in the application launcher or by running the “acroread” command in the terminal.
Conclusion
We studied about the Adobe Reader and how it can be installed in Linux Mint. We tried to explain each step briefly to make it easy for you to understand the purpose of every step. We hope that this article will assist you in learning how to install the Adobe Reader by utilizing multiple commands.